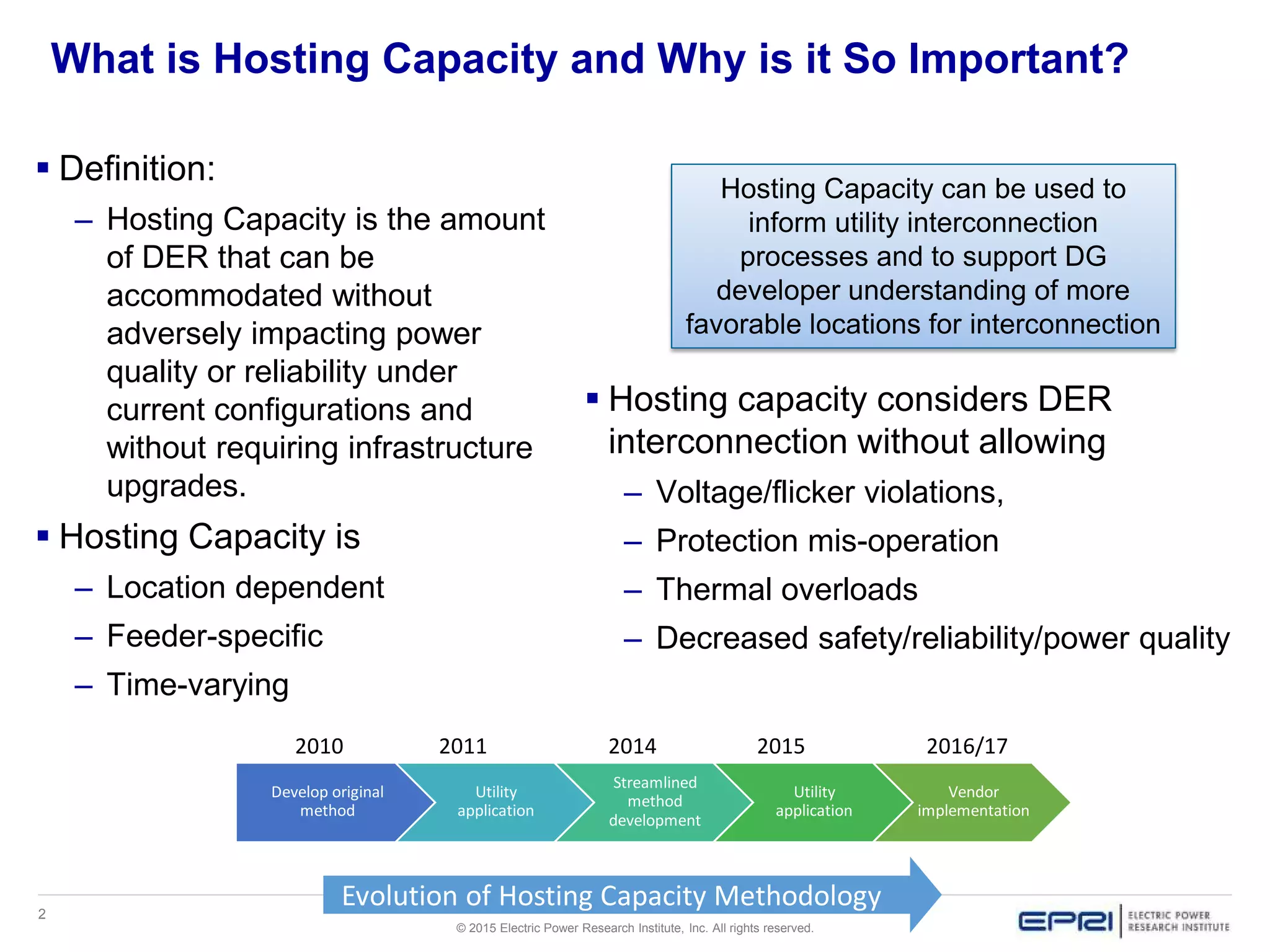
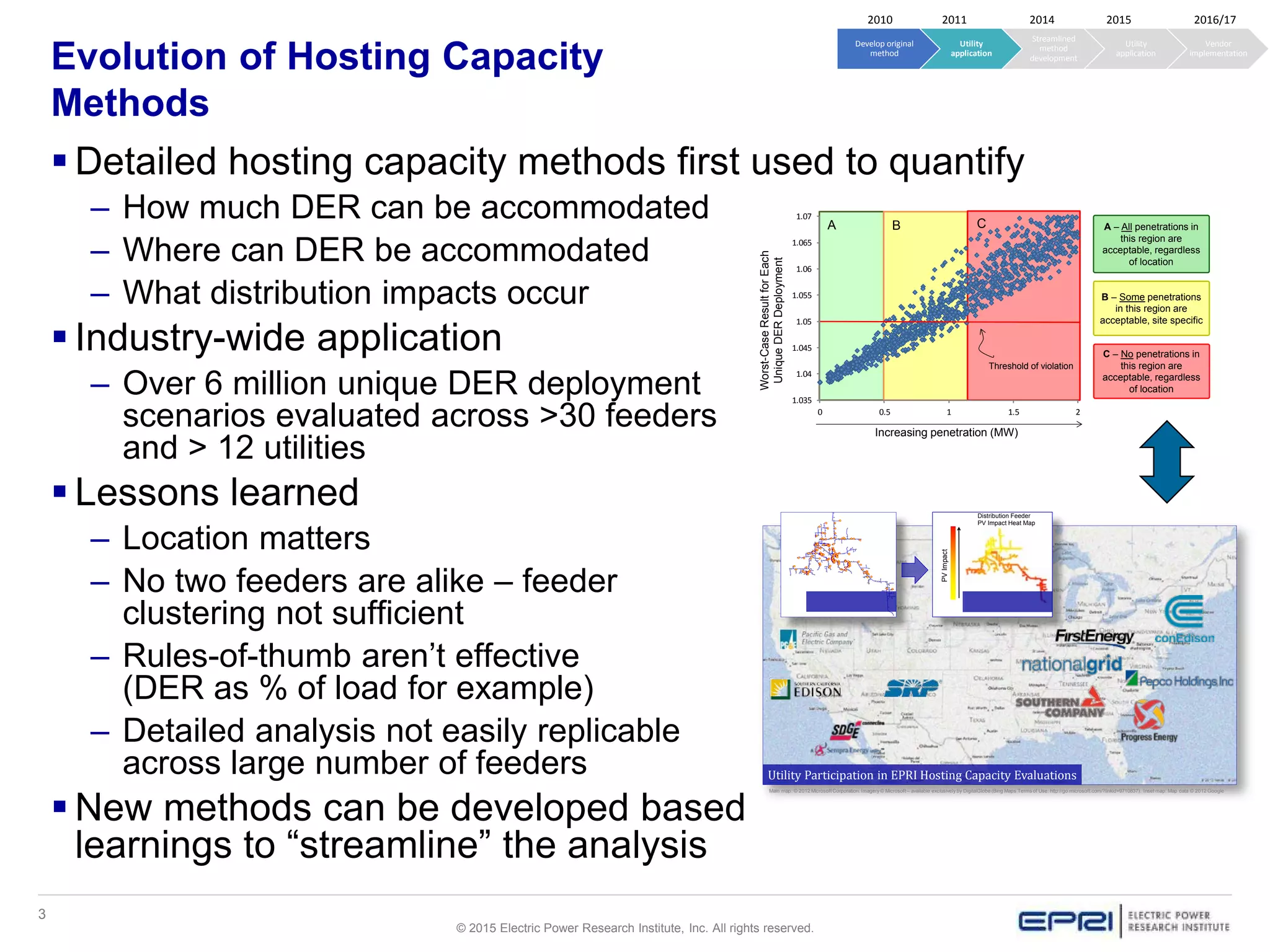
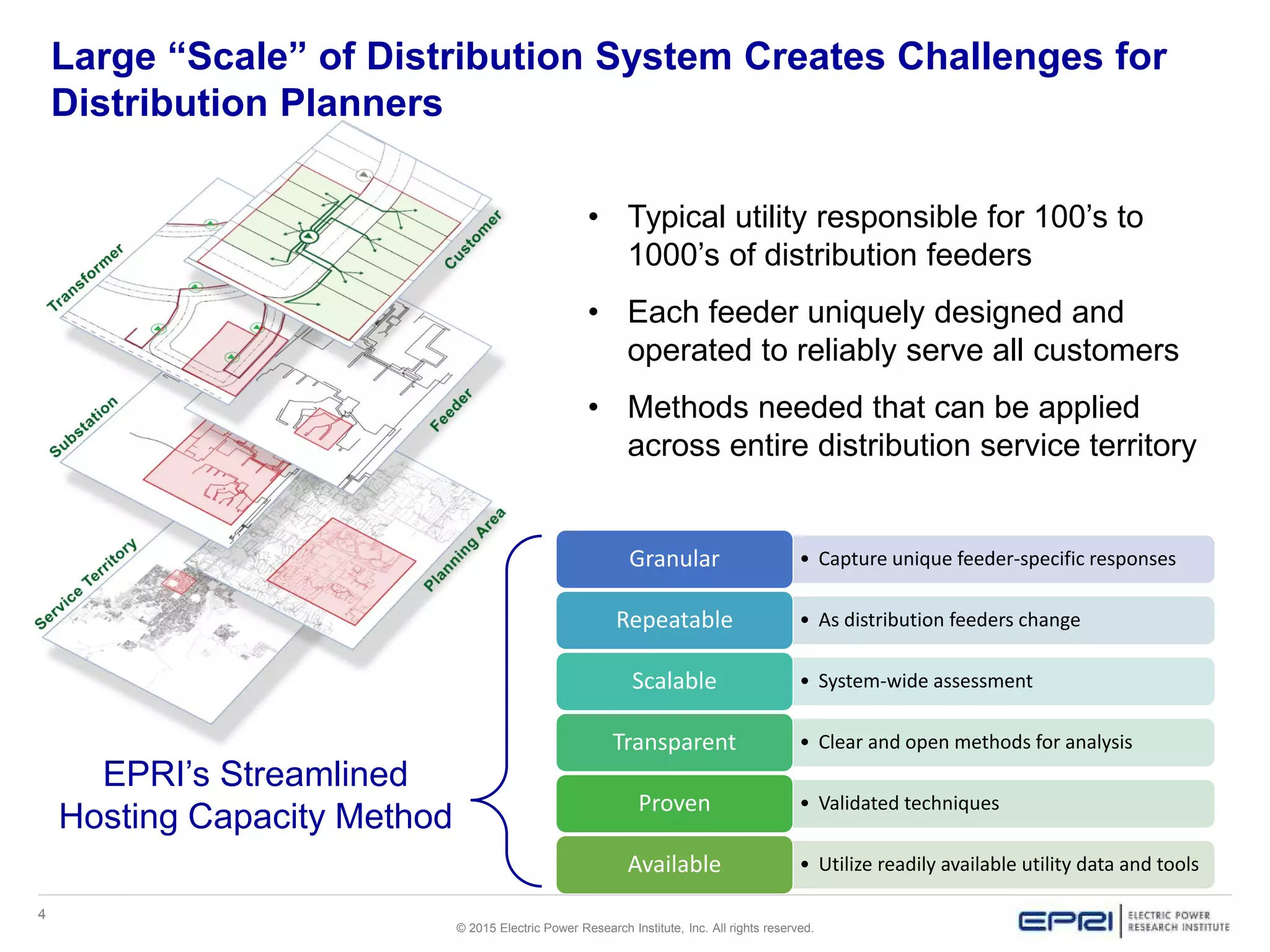
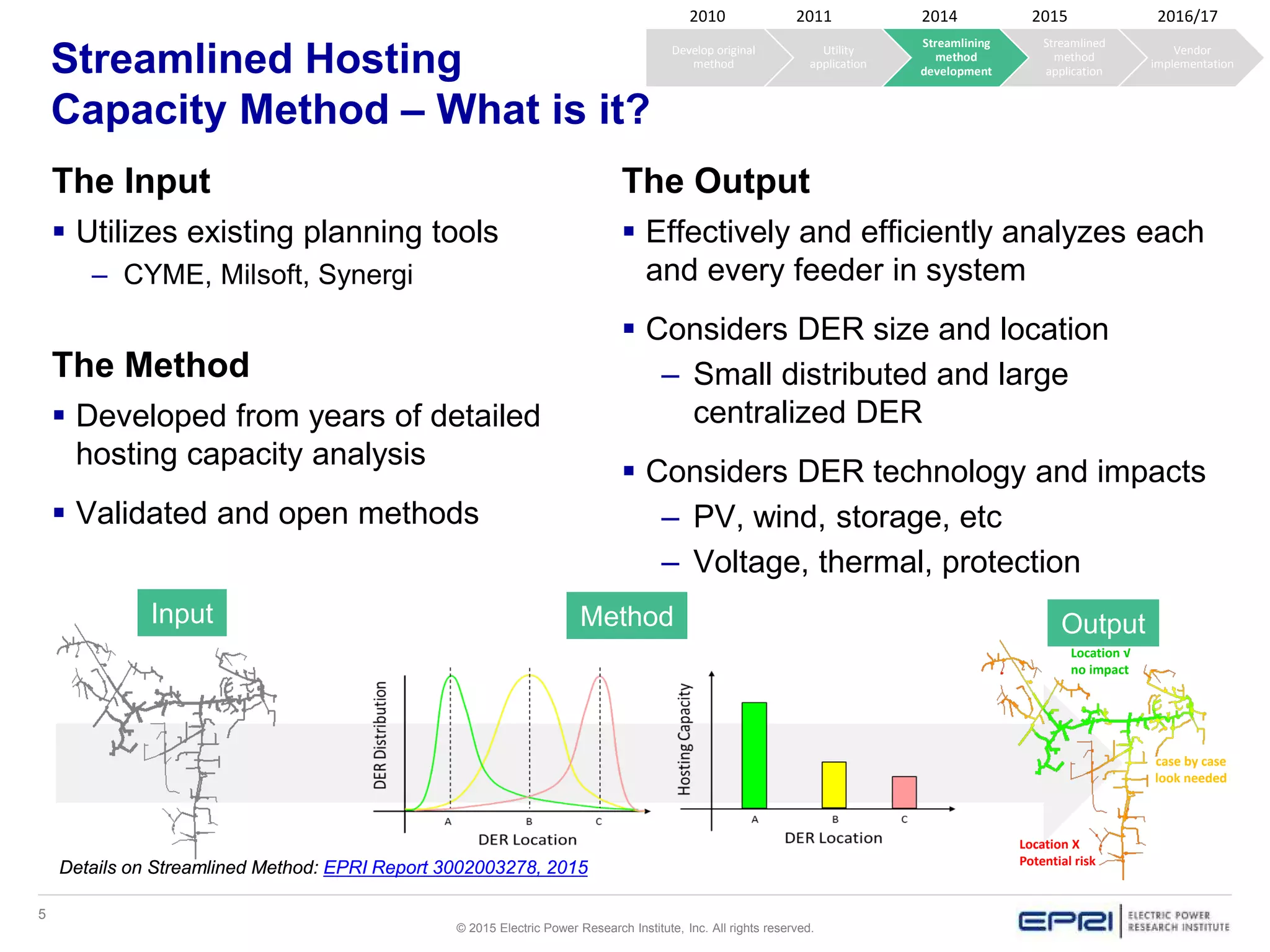
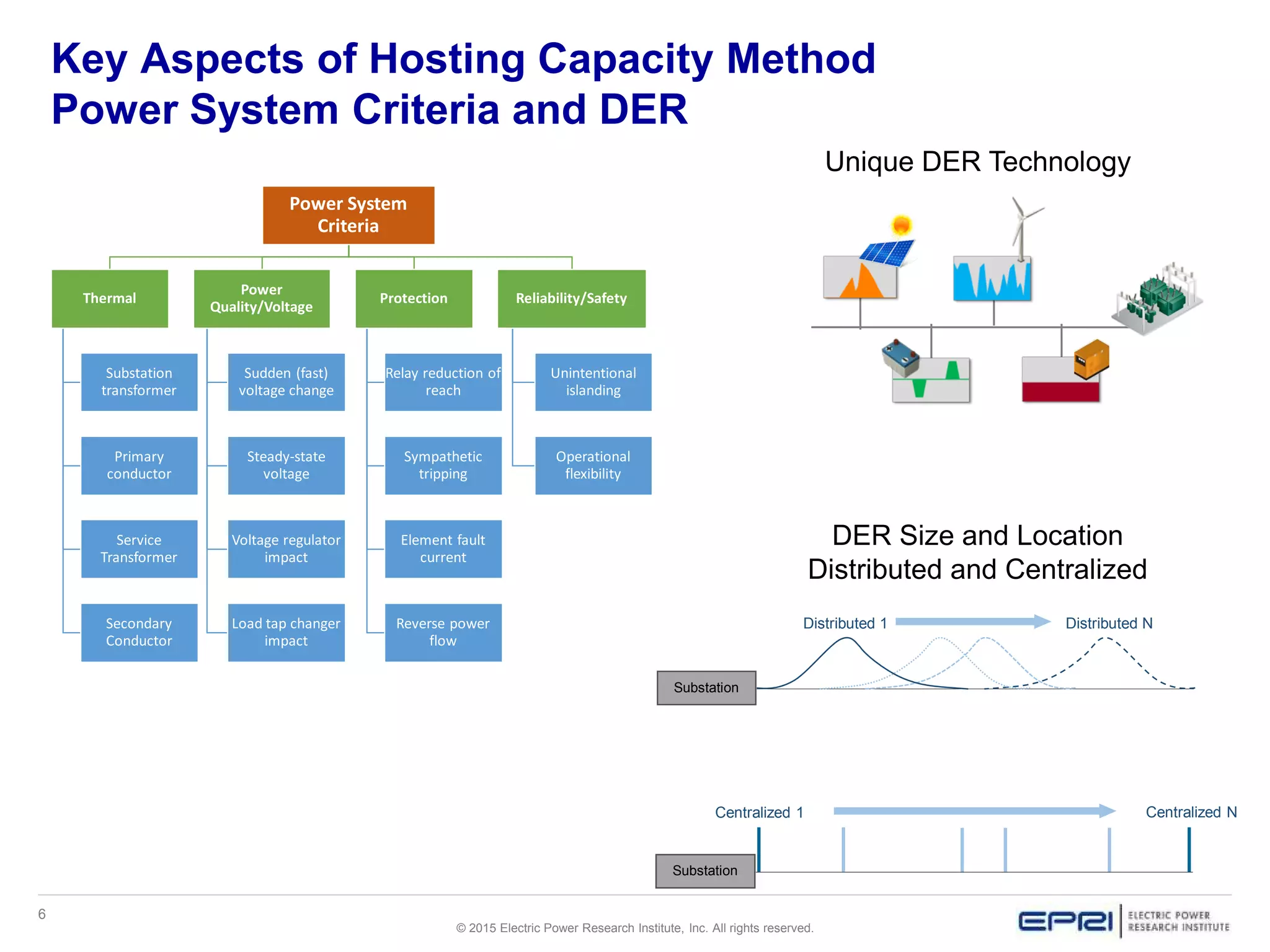
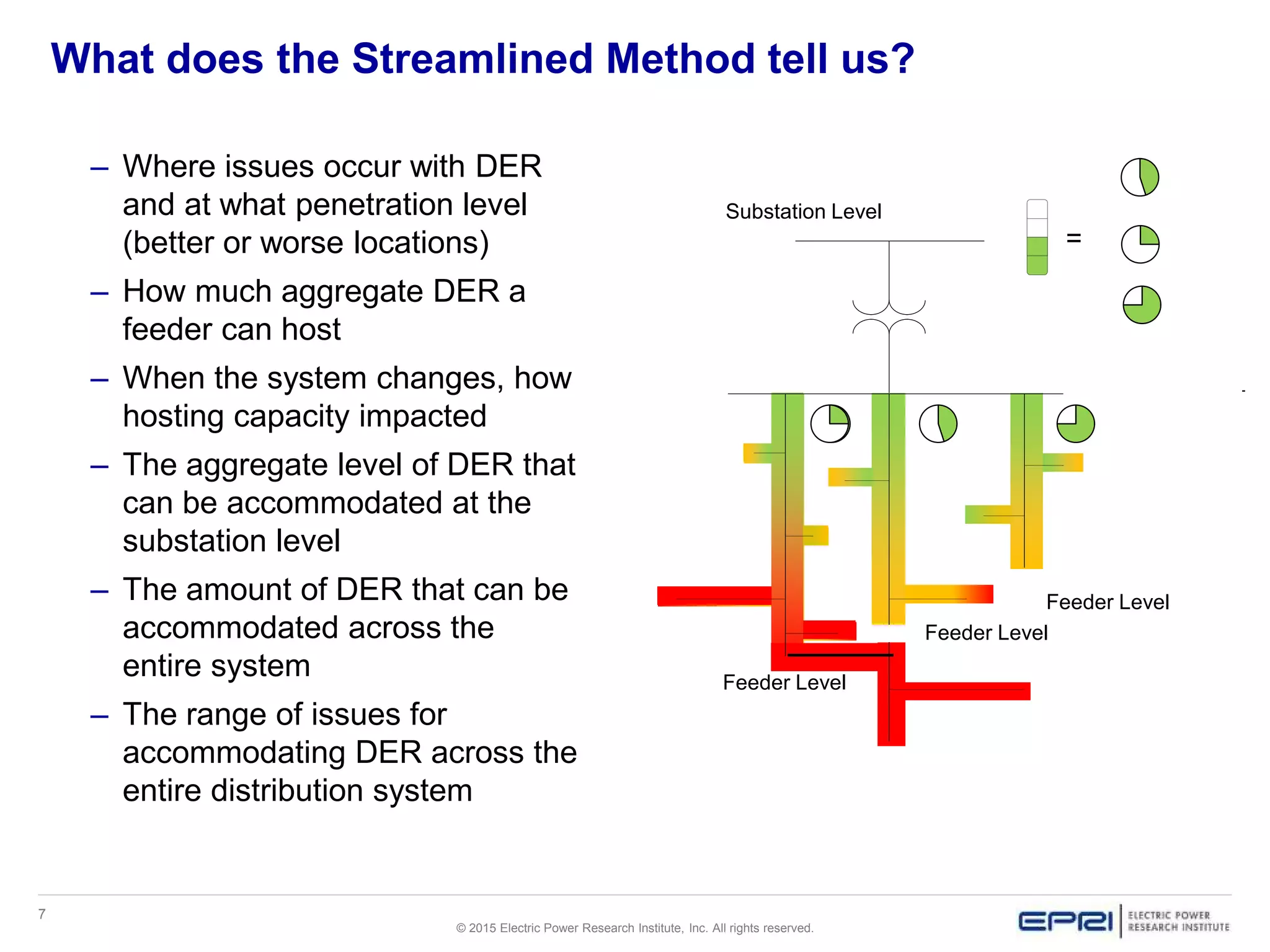
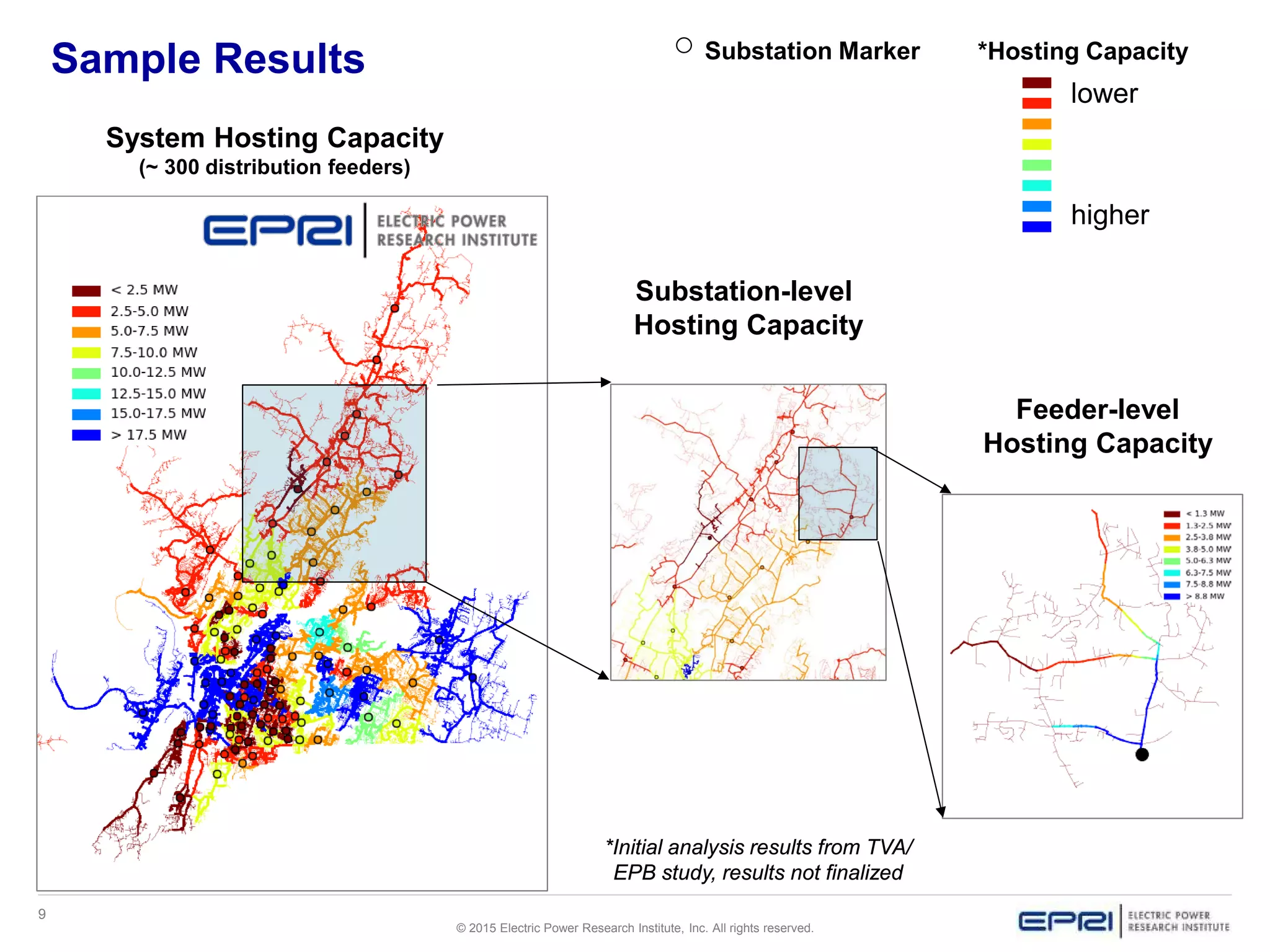
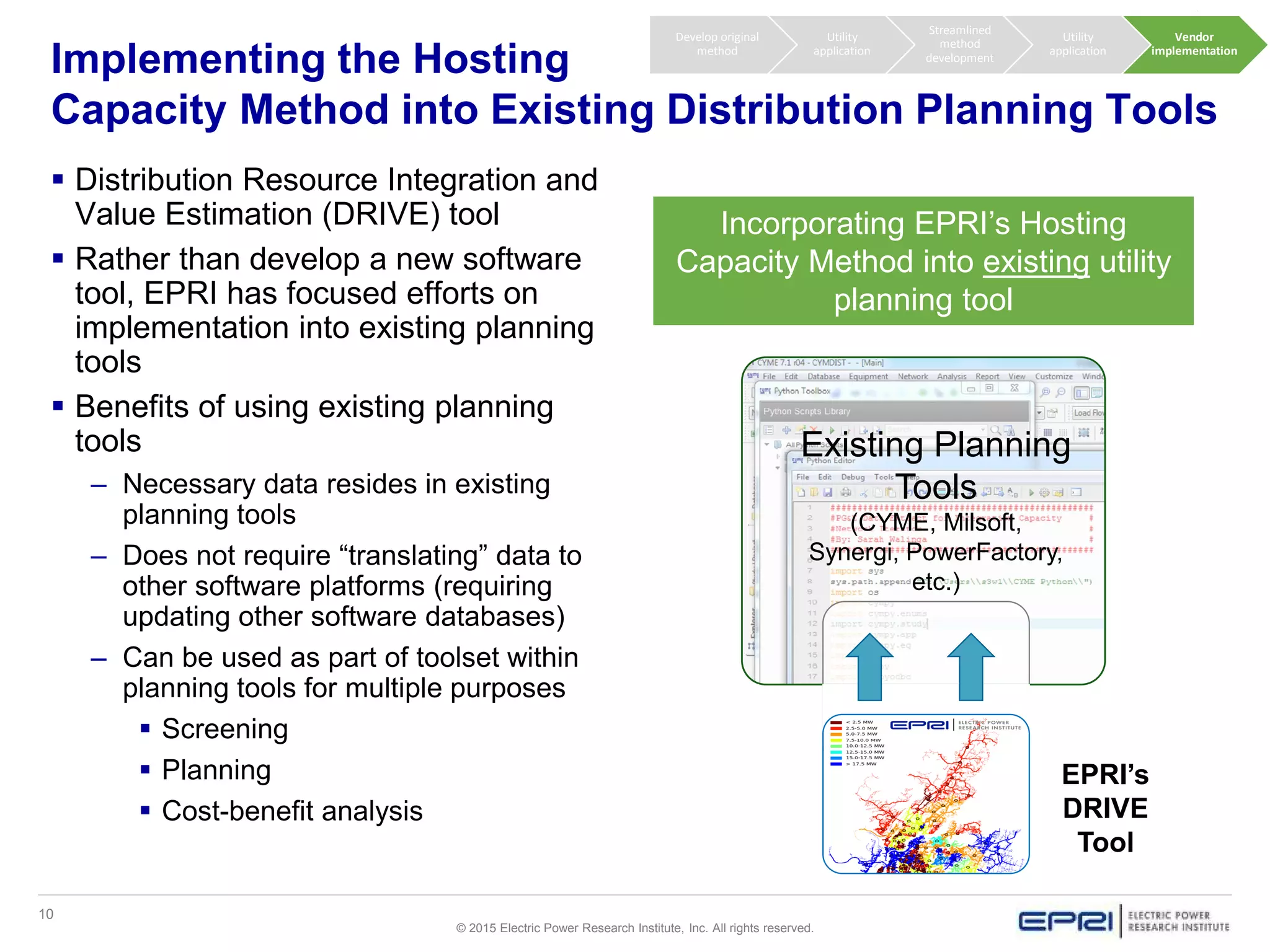
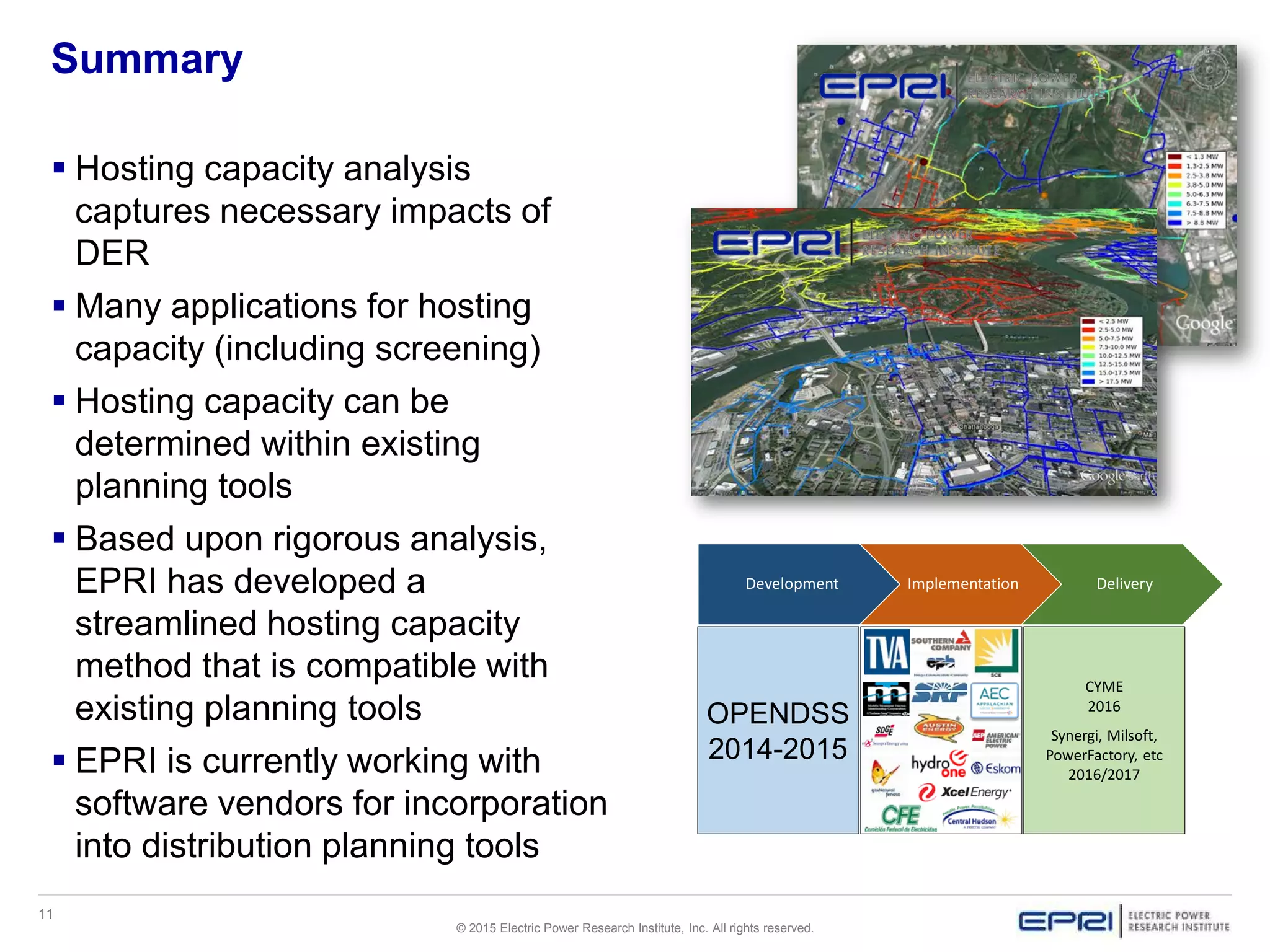
This document discusses EPRI's work developing and implementing hosting capacity methods to evaluate the amount of distributed energy resources (DER) that can be accommodated on electric distribution systems without upgrades. It summarizes the evolution of hosting capacity methods from detailed analyses of individual feeders to a streamlined method that can be applied across entire utility systems using existing planning tools. The streamlined method provides location-specific hosting capacity values while considering multiple power system impacts. EPRI is working with software vendors to incorporate this method into common distribution planning tools to help utilities evaluate DER on their systems.