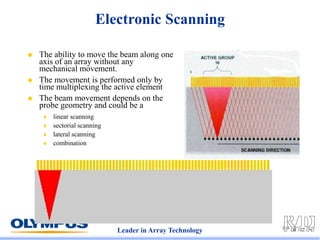
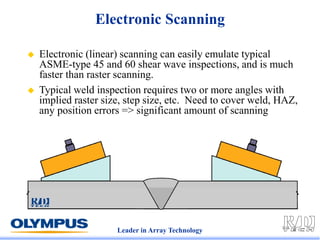
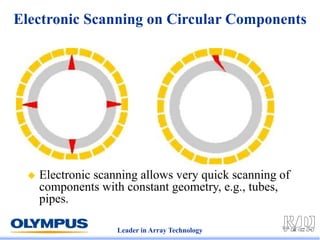
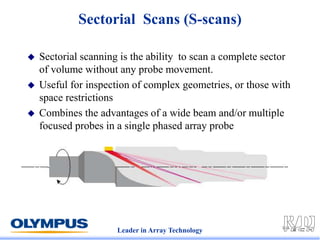
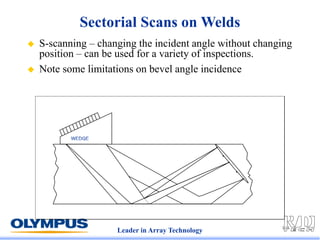
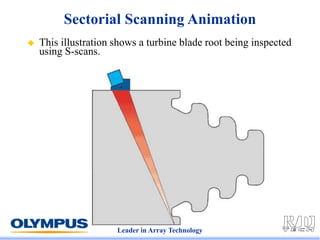
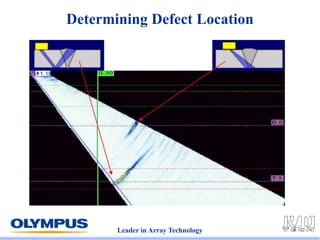
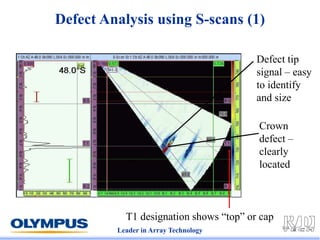
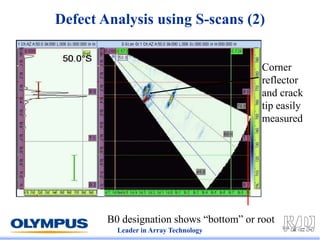
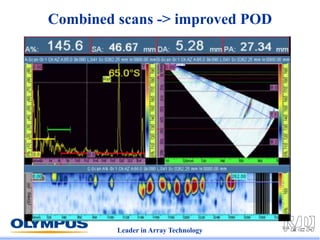
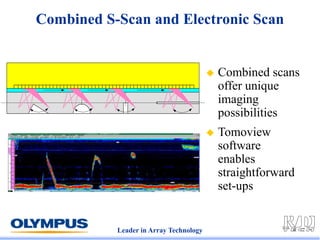
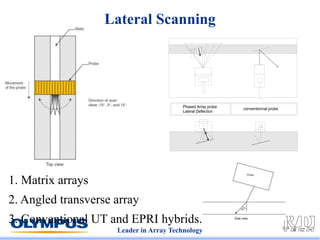
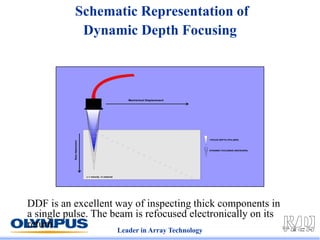
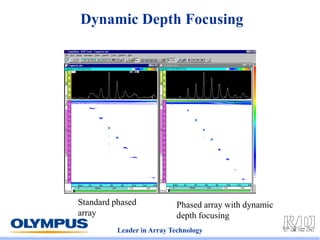
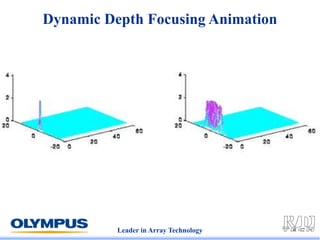
This document discusses various scanning techniques that can be performed using phased array ultrasound, including electronic scanning, sectorial scanning, lateral scanning, and dynamic depth focusing. It provides examples of how these techniques can be used for applications like weld inspection, pipe inspection, and turbine blade inspection. Custom scan patterns and analyses can be designed using software from the company.