003 adult burns
•
1 like•44 views
This document provides guidelines for the assessment and management of adult burn patients. It includes taking a thorough history, examining the burn wound to determine depth and total body surface area affected, considering potential airway involvement, and initiating fluid resuscitation according to the Parkland formula for large burns over 20% TBSA. Patients should be admitted if they have over 10% TBSA burns, full thickness burns, inhalation injury, electrical or chemical burns, or other high risk criteria. Stable patients with smaller burns can be discharged with arrangements for follow-up.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Aspirin administration for ems

The document discusses guidelines for EMT-Bs administering aspirin for cardiac events. It provides information on cardiac anatomy and physiology, including the four chambers of the heart and blood flow. It describes pathologies that can cause cardiac events like atherosclerosis and risks like hypertension. It discusses angina, including stable versus unstable types, signs and symptoms, and treatment. It also covers acute coronary syndrome/myocardial infarction, including pathophysiology, effects, goals of treatment, and field assessment focusing on vital signs, history, and physical exam including OPQRST. The guidelines specify giving 324mg of aspirin as soon as possible for patients with new chest pain suggestive of a heart attack to reduce mortality and further cardiac events. Precautions for
Burns

This document discusses burns, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, assessment, and management. It notes that burns can be devastating and affect all body systems. Assessment involves determining burn size, depth, and other injuries. Major burns over 25% of total body surface area require fluid resuscitation, wound care, possible escharotomy, and potential grafting. Management aims to resuscitate fluid losses, control pain, prevent infection, and promote wound healing. Outcomes depend on early treatment and the depth and extent of the thermal injury.
Hemodynamics Lecture ARMC

This document provides an overview of hemodynamic principles and invasive hemodynamic monitoring. It defines key terms like preload, afterload, contractility and discusses how they impact cardiac output. Specific monitoring tools like arterial lines, central venous pressure monitors and pulmonary artery catheters are explained. Treatment strategies to optimize cardiac output by manipulating heart rate, contractility, preload and afterload are outlined.
ACCLIMATISATION, HA DISEASES, COLD INJURIES-Maj Dr ID Khan

This document provides information about acclimatization to high altitudes and cold environments. It discusses physiological changes that occur at altitude, guidelines for gradual ascent to avoid illness, and schedules for acclimatizing in stages. It also describes cold injuries like frostbite and hypothermia, as well as heat illnesses like heat exhaustion and heat stroke. The document emphasizes the importance of gradual acclimatization, adequate hydration, and rest in managing extreme environmental conditions.
Preventing Heat Injury

Bournville Harriers Club member and coach, Dr Mike Berry MD, MRCP
(UK), who is a Consultant Respiratory Physician and Honorary Senior Lecturer
in Medicine at the University Hospital Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust Selly
Oak Hospital Birmingham has very kindly provided some excellent and valuable
advice on heat injury prevention following worrying comments at the club
about running in the heat.
This is a really useful guide which is applicable to training and racing in
warm weather.
Burn management

The document provides information on burn management, including the functions of skin, types of burn injuries, burn classification and assessment, initial patient treatment, airway management, fluid resuscitation, prevention of hypothermia, pain management, and management of inhalation injuries and carbon monoxide poisoning. Key aspects include classifying burns by depth and extent of injury to guide treatment, maintaining adequate fluid resuscitation based on the Parkland or Galveston formula to prevent hypovolemia, preventing hypothermia, and providing adequate pain management which is crucial for patient care and recovery.
BURNS

WARNING: VERY VISUAL PRESENTATION. My first presentation on burns and their various medical, surgical and nursing interventions. It's a total crash course. Pardon me for forgetting the references. PS: All images are from Google.
91971688-Care-of-the-Burn-Patient-Jaf.ppt

Care of the Burn Patient provides guidelines for treating burn injuries. It outlines conducting a primary and secondary survey to assess airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure. This includes estimating burn size using the Rule of Nines or Lund & Browder chart for children. It also describes fluid resuscitation using the Parkland formula to replace fluid losses from capillary leakage in burned tissue. Proper burn management focuses on stopping the burning process, providing oxygen, intravenous fluids, pain control, and preventing infection.
Recommended
Aspirin administration for ems

The document discusses guidelines for EMT-Bs administering aspirin for cardiac events. It provides information on cardiac anatomy and physiology, including the four chambers of the heart and blood flow. It describes pathologies that can cause cardiac events like atherosclerosis and risks like hypertension. It discusses angina, including stable versus unstable types, signs and symptoms, and treatment. It also covers acute coronary syndrome/myocardial infarction, including pathophysiology, effects, goals of treatment, and field assessment focusing on vital signs, history, and physical exam including OPQRST. The guidelines specify giving 324mg of aspirin as soon as possible for patients with new chest pain suggestive of a heart attack to reduce mortality and further cardiac events. Precautions for
Burns

This document discusses burns, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, assessment, and management. It notes that burns can be devastating and affect all body systems. Assessment involves determining burn size, depth, and other injuries. Major burns over 25% of total body surface area require fluid resuscitation, wound care, possible escharotomy, and potential grafting. Management aims to resuscitate fluid losses, control pain, prevent infection, and promote wound healing. Outcomes depend on early treatment and the depth and extent of the thermal injury.
Hemodynamics Lecture ARMC

This document provides an overview of hemodynamic principles and invasive hemodynamic monitoring. It defines key terms like preload, afterload, contractility and discusses how they impact cardiac output. Specific monitoring tools like arterial lines, central venous pressure monitors and pulmonary artery catheters are explained. Treatment strategies to optimize cardiac output by manipulating heart rate, contractility, preload and afterload are outlined.
ACCLIMATISATION, HA DISEASES, COLD INJURIES-Maj Dr ID Khan

This document provides information about acclimatization to high altitudes and cold environments. It discusses physiological changes that occur at altitude, guidelines for gradual ascent to avoid illness, and schedules for acclimatizing in stages. It also describes cold injuries like frostbite and hypothermia, as well as heat illnesses like heat exhaustion and heat stroke. The document emphasizes the importance of gradual acclimatization, adequate hydration, and rest in managing extreme environmental conditions.
Preventing Heat Injury

Bournville Harriers Club member and coach, Dr Mike Berry MD, MRCP
(UK), who is a Consultant Respiratory Physician and Honorary Senior Lecturer
in Medicine at the University Hospital Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust Selly
Oak Hospital Birmingham has very kindly provided some excellent and valuable
advice on heat injury prevention following worrying comments at the club
about running in the heat.
This is a really useful guide which is applicable to training and racing in
warm weather.
Burn management

The document provides information on burn management, including the functions of skin, types of burn injuries, burn classification and assessment, initial patient treatment, airway management, fluid resuscitation, prevention of hypothermia, pain management, and management of inhalation injuries and carbon monoxide poisoning. Key aspects include classifying burns by depth and extent of injury to guide treatment, maintaining adequate fluid resuscitation based on the Parkland or Galveston formula to prevent hypovolemia, preventing hypothermia, and providing adequate pain management which is crucial for patient care and recovery.
BURNS

WARNING: VERY VISUAL PRESENTATION. My first presentation on burns and their various medical, surgical and nursing interventions. It's a total crash course. Pardon me for forgetting the references. PS: All images are from Google.
91971688-Care-of-the-Burn-Patient-Jaf.ppt

Care of the Burn Patient provides guidelines for treating burn injuries. It outlines conducting a primary and secondary survey to assess airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure. This includes estimating burn size using the Rule of Nines or Lund & Browder chart for children. It also describes fluid resuscitation using the Parkland formula to replace fluid losses from capillary leakage in burned tissue. Proper burn management focuses on stopping the burning process, providing oxygen, intravenous fluids, pain control, and preventing infection.
Burn CME .pptx

- A 11-year-old girl presented with a 1% second degree burn on her right hand after accidentally dipping it in hot porridge.
- She was initially treated with topical creams but referred to the hospital due to worsening symptoms.
- In the hospital she received IV fluids, antibiotics, and wound dressing changes. Her burn wound was cleaned and exposed dermis covered.
- Her condition improved with treatment and she was discharged with oral antibiotics and follow-up appointments. At her follow-up her wound had fully healed.
BURNS- Derm Presentation

Burns can be caused by thermal, electrical or chemical sources and result in partial or complete skin destruction. Initial assessment and treatment follows the ABCDE method - Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure. Circumferential and large burns over 20% total body surface area require aggressive fluid resuscitation according to the Parkland formula to prevent shock. Ongoing monitoring of vital signs, urine output, and compartment pressures is critical in the first 24 hours and beyond to watch for complications like inhalation injury and compartment syndrome. Long term wound care including cleaning, dressings, and skin grafting aims to prevent infection and contractures.
Untitled presentation.pptx

This document discusses the management of burn injuries. It begins by describing the different types of burns and classifying burns based on their severity. It then outlines the three phases of burn care - resuscitative, acute, and rehabilitation. Specific focus is given to the resuscitative phase, covering initial first aid, assessment, cooling, wound care, fluid resuscitation, analgesia, and monitoring. Nutritional support, wound cleansing, and complications are also discussed. Finally, common nursing diagnoses and interventions for burn patients are provided.
Basic Trauma And Burn Management

The document outlines the assessment and treatment of trauma and burn patients, including the primary and secondary surveys to address life-threatening injuries, guidelines for fluid resuscitation in burn shock, and key considerations for special populations like pediatrics. Standardized approaches are recommended to simultaneously assess airway, breathing, circulation, hemorrhage, and potential internal injuries while monitoring for changes in status. Early involvement of surgical specialists and use of radiography to identify fractures and hemorrhages are also discussed.
Management of acute burns

The document provides an overview of the management of acute burns. It discusses the classification of burns, ABCDE assessment and management, fluid resuscitation, wound care, complications, and prognosis. The main points are: burns are classified based on depth rather than degree; ABCDE assessment and treatment includes airway protection, breathing support, IV fluids, dressings, drugs, and exposure prevention; fluid resuscitation is based on Parkland formula; common complications include pulmonary injury, hypothermia, and infection; further treatment may include debridement, skin grafting, and rehabilitation.
Burns

The document discusses the epidemiology, assessment, treatment and management of burns. It notes that the majority of burns in children are scalds, while flame burns are more common in adults. Assessment involves determining the percentage of total body surface area burned and burn depth. Treatment includes fluid resuscitation, wound care using dressings like silver sulfadiazine, and management of complications like inhalation injury and infection. Good outcomes depend on factors like percentage and depth of burns, and presence of an inhalation injury.
Burn management

The document provides an overview of burn injuries including:
- Types of burns such as thermal, chemical, and electrical burns
- Factors that determine burn severity such as depth, extent, location, and patient risk factors
- Immediate management priorities of airway, breathing, circulation and fluid resuscitation
- Wound care including cleaning, dressing, escharotomy/fasciotomy, skin grafting
- Potential complications and long-term management including scar treatment
Management of burns 

This topic is oriented mainly on the Bailey & Love - 26th edition.
This will be of immense help for the MBBS - Students for the Theory as well as Clinical application.
Burns

The document provides an overview of skin anatomy and burn injuries, including:
- The skin has two layers, the epidermis and dermis, and performs several important functions.
- Burn injuries are classified by depth and extent, and can range from superficial first degree burns to full thickness third degree burns. Critical burns involve over 10% total body surface area or certain high risk areas.
- Burn management involves stopping the burning process, assessing airway and circulation, rapidly estimating burn extent, treating the wound, and providing IV fluid resuscitation based on the Parkland formula. Special considerations include pediatrics, geriatrics, inhalation injuries, and various burn depths.
ITTABV1

The document discusses the initial assessment and management of trauma and burn patients. It covers the primary and secondary surveys, with a focus on airway, breathing, circulation, and exposure. Key steps in trauma resuscitation include rapid sequence intubation, needle decompression for tension pneumothorax, and fluid resuscitation. The document also discusses hemorrhagic shock evaluation and algorithms, as well as burn depth, extent, and resuscitation guidelines such as the Parkland formula.
Burns 150415010824-conversion-gate01

This document discusses burns, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, assessment, and management. It notes that burns can be devastating and affect all body systems. Management involves rescue, resuscitation, retrieval to a specialist burns unit, resurfacing wounds, rehabilitation, and reconstruction. For major burns covering over 25% of total body surface area, management requires fluid resuscitation based on the burn size and goal of maintaining tissue perfusion to prevent worsening injury. Ongoing monitoring of fluid balance and urine output is important.
Burn Injury Typess Classification Causes Assesment and Managment 

burn injury types causes classification, its assessment total body surface area burn and management,
BURNS.pptx

This document provides an overview of burns, including:
- Definitions of burns and burn classifications according to cause, depth, and size. Burns can be thermal, chemical, or electrical. They are classified as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, or 4th degree burns depending on depth of tissue damage.
- Criteria for burn patient admission based on factors like burn size, location, age, and presence of inhalation injury.
- Principles of burn management including initial resuscitation following ATLS protocols, fluid resuscitation calculated using the Parkland formula, pain control, and wound care involving cleaning and dressing changes.
burns-1.pptx

Thermal injuries include burns from heat, electricity, chemicals and radiation. Immediate priorities in management are airway control, stopping the burning process, and intravenous access and fluid resuscitation. Assessment of burns considers type, extent, depth, and potential for inhalation injury. Minor burns are treated with cooling, cleaning, covering and pain control while more severe burns require fluid resuscitation and potential referral to a burn unit. Inhalation injuries require airway protection and management of secretions. Electrical burns can deceptively involve deeper internal injuries than skin appearance suggests.
Burns Rohit.pptx

The presentation is about the definition and type of burns classification and total body surface area involved. Fluid therapy in adults and children. Various formulae of calculating fluid requirement.
Protocols for burn centre management and critical care. Most elaborated description of burn management. Latest guidelines and Protocols, relevant investigation and management.
Burns its types, causes and management.

it consist definition, types of burn, its cause, scales to measure degree of burn, first aid management and supportive management along with rehabilitation therapy.
Burn management

This document provides information on burns, including:
- The definition and causes of burns including thermal, electrical, chemical and radiation burns.
- The degrees of burns from first to fourth degree based on depth of tissue damage.
- Methods for estimating the percentage of total body surface area burned including the Rule of Nines.
- Criteria for burn admission to hospital care based on factors like surface area, depth and location of burns.
- Complications that can result from severe burns like infection, shock and organ damage.
- The importance of first aid like cooling the burned area in water to minimize further tissue injury.
Pediatric burns

Burns and scalds account for 6% of pediatric injuries, with preschool children most commonly affected. House fires are a leading cause of fatal burns due to smoke inhalation. Scalds often involve hot drinks, baths, or cooking oils in toddlers. Children have a higher body surface area to weight ratio and thinner skin than adults, making them more susceptible to burns. Severity depends on temperature and duration of contact - even brief contact at high temperatures can cause full thickness burns. Wound management involves cooling, analgesia, fluid resuscitation, and consideration of escharotomy for circumferential burns. Inhalation injuries require 100% oxygen and monitoring of carboxyhemoglobin levels.
Burn Cold Injury

This document provides guidance on the management of burn and cold injuries. It outlines the initial steps of establishing an airway and providing fluid resuscitation for burn injuries. It emphasizes the need to estimate burn size and depth, initiate a burn treatment flow sheet, and identify situations requiring transfer to a burn center. For cold injuries, the summary describes diagnosing the type of injury based on history and findings, measuring core temperature, and using rewarming techniques while monitoring vital signs. Burns and cold injuries require timely treatment to stabilize the patient and prevent complications.
Burning pain 3

This document summarizes a case study presentation on a patient named E.T. who sustained burns from a kerosene stove explosion. The presentation discusses E.T.'s family profile, medical history, examination findings, diagnosis of second degree burns over 14.5% of her total body surface area, and her treatment plan. It also provides information on burn severity classifications, fluid resuscitation protocols, wound care medications, scar management, and complications of burns.
Journal Article Review on Rasamanikya

Rasamanikya is a excellent preparation in the field of Rasashastra, it is used in various Kushtha Roga, Shwasa, Vicharchika, Bhagandara, Vatarakta, and Phiranga Roga. In this article Preparation& Comparative analytical profile for both Formulationon i.e Rasamanikya prepared by Kushmanda swarasa & Churnodhaka Shodita Haratala. The study aims to provide insights into the comparative efficacy and analytical aspects of these formulations for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
More Related Content
Similar to 003 adult burns
Burn CME .pptx

- A 11-year-old girl presented with a 1% second degree burn on her right hand after accidentally dipping it in hot porridge.
- She was initially treated with topical creams but referred to the hospital due to worsening symptoms.
- In the hospital she received IV fluids, antibiotics, and wound dressing changes. Her burn wound was cleaned and exposed dermis covered.
- Her condition improved with treatment and she was discharged with oral antibiotics and follow-up appointments. At her follow-up her wound had fully healed.
BURNS- Derm Presentation

Burns can be caused by thermal, electrical or chemical sources and result in partial or complete skin destruction. Initial assessment and treatment follows the ABCDE method - Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure. Circumferential and large burns over 20% total body surface area require aggressive fluid resuscitation according to the Parkland formula to prevent shock. Ongoing monitoring of vital signs, urine output, and compartment pressures is critical in the first 24 hours and beyond to watch for complications like inhalation injury and compartment syndrome. Long term wound care including cleaning, dressings, and skin grafting aims to prevent infection and contractures.
Untitled presentation.pptx

This document discusses the management of burn injuries. It begins by describing the different types of burns and classifying burns based on their severity. It then outlines the three phases of burn care - resuscitative, acute, and rehabilitation. Specific focus is given to the resuscitative phase, covering initial first aid, assessment, cooling, wound care, fluid resuscitation, analgesia, and monitoring. Nutritional support, wound cleansing, and complications are also discussed. Finally, common nursing diagnoses and interventions for burn patients are provided.
Basic Trauma And Burn Management

The document outlines the assessment and treatment of trauma and burn patients, including the primary and secondary surveys to address life-threatening injuries, guidelines for fluid resuscitation in burn shock, and key considerations for special populations like pediatrics. Standardized approaches are recommended to simultaneously assess airway, breathing, circulation, hemorrhage, and potential internal injuries while monitoring for changes in status. Early involvement of surgical specialists and use of radiography to identify fractures and hemorrhages are also discussed.
Management of acute burns

The document provides an overview of the management of acute burns. It discusses the classification of burns, ABCDE assessment and management, fluid resuscitation, wound care, complications, and prognosis. The main points are: burns are classified based on depth rather than degree; ABCDE assessment and treatment includes airway protection, breathing support, IV fluids, dressings, drugs, and exposure prevention; fluid resuscitation is based on Parkland formula; common complications include pulmonary injury, hypothermia, and infection; further treatment may include debridement, skin grafting, and rehabilitation.
Burns

The document discusses the epidemiology, assessment, treatment and management of burns. It notes that the majority of burns in children are scalds, while flame burns are more common in adults. Assessment involves determining the percentage of total body surface area burned and burn depth. Treatment includes fluid resuscitation, wound care using dressings like silver sulfadiazine, and management of complications like inhalation injury and infection. Good outcomes depend on factors like percentage and depth of burns, and presence of an inhalation injury.
Burn management

The document provides an overview of burn injuries including:
- Types of burns such as thermal, chemical, and electrical burns
- Factors that determine burn severity such as depth, extent, location, and patient risk factors
- Immediate management priorities of airway, breathing, circulation and fluid resuscitation
- Wound care including cleaning, dressing, escharotomy/fasciotomy, skin grafting
- Potential complications and long-term management including scar treatment
Management of burns 

This topic is oriented mainly on the Bailey & Love - 26th edition.
This will be of immense help for the MBBS - Students for the Theory as well as Clinical application.
Burns

The document provides an overview of skin anatomy and burn injuries, including:
- The skin has two layers, the epidermis and dermis, and performs several important functions.
- Burn injuries are classified by depth and extent, and can range from superficial first degree burns to full thickness third degree burns. Critical burns involve over 10% total body surface area or certain high risk areas.
- Burn management involves stopping the burning process, assessing airway and circulation, rapidly estimating burn extent, treating the wound, and providing IV fluid resuscitation based on the Parkland formula. Special considerations include pediatrics, geriatrics, inhalation injuries, and various burn depths.
ITTABV1

The document discusses the initial assessment and management of trauma and burn patients. It covers the primary and secondary surveys, with a focus on airway, breathing, circulation, and exposure. Key steps in trauma resuscitation include rapid sequence intubation, needle decompression for tension pneumothorax, and fluid resuscitation. The document also discusses hemorrhagic shock evaluation and algorithms, as well as burn depth, extent, and resuscitation guidelines such as the Parkland formula.
Burns 150415010824-conversion-gate01

This document discusses burns, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, assessment, and management. It notes that burns can be devastating and affect all body systems. Management involves rescue, resuscitation, retrieval to a specialist burns unit, resurfacing wounds, rehabilitation, and reconstruction. For major burns covering over 25% of total body surface area, management requires fluid resuscitation based on the burn size and goal of maintaining tissue perfusion to prevent worsening injury. Ongoing monitoring of fluid balance and urine output is important.
Burn Injury Typess Classification Causes Assesment and Managment 

burn injury types causes classification, its assessment total body surface area burn and management,
BURNS.pptx

This document provides an overview of burns, including:
- Definitions of burns and burn classifications according to cause, depth, and size. Burns can be thermal, chemical, or electrical. They are classified as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, or 4th degree burns depending on depth of tissue damage.
- Criteria for burn patient admission based on factors like burn size, location, age, and presence of inhalation injury.
- Principles of burn management including initial resuscitation following ATLS protocols, fluid resuscitation calculated using the Parkland formula, pain control, and wound care involving cleaning and dressing changes.
burns-1.pptx

Thermal injuries include burns from heat, electricity, chemicals and radiation. Immediate priorities in management are airway control, stopping the burning process, and intravenous access and fluid resuscitation. Assessment of burns considers type, extent, depth, and potential for inhalation injury. Minor burns are treated with cooling, cleaning, covering and pain control while more severe burns require fluid resuscitation and potential referral to a burn unit. Inhalation injuries require airway protection and management of secretions. Electrical burns can deceptively involve deeper internal injuries than skin appearance suggests.
Burns Rohit.pptx

The presentation is about the definition and type of burns classification and total body surface area involved. Fluid therapy in adults and children. Various formulae of calculating fluid requirement.
Protocols for burn centre management and critical care. Most elaborated description of burn management. Latest guidelines and Protocols, relevant investigation and management.
Burns its types, causes and management.

it consist definition, types of burn, its cause, scales to measure degree of burn, first aid management and supportive management along with rehabilitation therapy.
Burn management

This document provides information on burns, including:
- The definition and causes of burns including thermal, electrical, chemical and radiation burns.
- The degrees of burns from first to fourth degree based on depth of tissue damage.
- Methods for estimating the percentage of total body surface area burned including the Rule of Nines.
- Criteria for burn admission to hospital care based on factors like surface area, depth and location of burns.
- Complications that can result from severe burns like infection, shock and organ damage.
- The importance of first aid like cooling the burned area in water to minimize further tissue injury.
Pediatric burns

Burns and scalds account for 6% of pediatric injuries, with preschool children most commonly affected. House fires are a leading cause of fatal burns due to smoke inhalation. Scalds often involve hot drinks, baths, or cooking oils in toddlers. Children have a higher body surface area to weight ratio and thinner skin than adults, making them more susceptible to burns. Severity depends on temperature and duration of contact - even brief contact at high temperatures can cause full thickness burns. Wound management involves cooling, analgesia, fluid resuscitation, and consideration of escharotomy for circumferential burns. Inhalation injuries require 100% oxygen and monitoring of carboxyhemoglobin levels.
Burn Cold Injury

This document provides guidance on the management of burn and cold injuries. It outlines the initial steps of establishing an airway and providing fluid resuscitation for burn injuries. It emphasizes the need to estimate burn size and depth, initiate a burn treatment flow sheet, and identify situations requiring transfer to a burn center. For cold injuries, the summary describes diagnosing the type of injury based on history and findings, measuring core temperature, and using rewarming techniques while monitoring vital signs. Burns and cold injuries require timely treatment to stabilize the patient and prevent complications.
Burning pain 3

This document summarizes a case study presentation on a patient named E.T. who sustained burns from a kerosene stove explosion. The presentation discusses E.T.'s family profile, medical history, examination findings, diagnosis of second degree burns over 14.5% of her total body surface area, and her treatment plan. It also provides information on burn severity classifications, fluid resuscitation protocols, wound care medications, scar management, and complications of burns.
Similar to 003 adult burns (20)
Burn Injury Typess Classification Causes Assesment and Managment 

Burn Injury Typess Classification Causes Assesment and Managment
Recently uploaded
Journal Article Review on Rasamanikya

Rasamanikya is a excellent preparation in the field of Rasashastra, it is used in various Kushtha Roga, Shwasa, Vicharchika, Bhagandara, Vatarakta, and Phiranga Roga. In this article Preparation& Comparative analytical profile for both Formulationon i.e Rasamanikya prepared by Kushmanda swarasa & Churnodhaka Shodita Haratala. The study aims to provide insights into the comparative efficacy and analytical aspects of these formulations for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Identifying Major Symptoms of Slip Disc.

Our backs are like superheroes, holding us up and helping us move around. But sometimes, even superheroes can get hurt. That’s where slip discs come in.
NARCOTICS- POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR ITS USE

This document outlines policies and procedures for handling narcotic and controlled drugs in NABH accredited hospitals.
All info about Diabetes and how to control it.

One health condition that is becoming more common day by day is diabetes.
According to research conducted by the National Family Health Survey of India, diabetic cases show a projection which might increase to 10.4% by 2030.
The Electrocardiogram - Physiologic Principles

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a quick overview of the physiological basis of a normal electrocardiogram.
Learning objectives:
1. Define an electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrocardiography
2. Describe how dipoles generated by the heart produce the waveforms of the ECG
3. Describe the components of a normal electrocardiogram of a typical bipolar lead (limb II)
4. Differentiate between intervals and segments
5. Enlist some common indications for obtaining an ECG
6. Describe the flow of current around the heart during the cardiac cycle
7. Discuss the placement and polarity of the leads of electrocardiograph
8. Describe the normal electrocardiograms recorded from the limb leads and explain the physiological basis of the different records that are obtained
9. Define mean electrical vector (axis) of the heart and give the normal range
10. Define the mean QRS vector
11. Describe the axes of leads (hexagonal reference system)
12. Comprehend the vectorial analysis of the normal ECG
13. Determine the mean electrical axis of the ventricular QRS and appreciate the mean axis deviation
14. Explain the concepts of current of injury, J point, and their significance
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 11, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 9, Human Physiology - From Cells to Systems, Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
3. Chapter 29, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
4. Electrocardiogram, StatPearls - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549803/
5. ECG in Medical Practice by ABM Abdullah, 4th edition
6. Chapter 3, Cardiology Explained, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2214/
7. ECG Basics, http://www.nataliescasebook.com/tag/e-c-g-basics
Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat

Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/Pt1nA32sdHQ
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/uFdc9F0rlP0
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Hiranandani Hospital Powai News [Read Now].pdf![Hiranandani Hospital Powai News [Read Now].pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Hiranandani Hospital Powai News [Read Now].pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Hiranandani Hospital in Powai, Mumbai, is a premier healthcare institution that has been serving the community with exceptional medical care since its establishment. As a part of the renowned Hiranandani Group, the hospital is committed to delivering world-class healthcare services across a wide range of specialties, including kidney transplantation. With its state-of-the-art facilities, advanced medical technology, and a team of highly skilled healthcare professionals, Hiranandani Hospital has earned a reputation as a trusted name in the healthcare industry. The hospital's patient-centric approach, coupled with its focus on innovation and excellence, ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care in a compassionate and supportive environment.
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/kqbnxVAZs-0
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/SINlygW1Mpc
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
pathology MCQS introduction to pathology general pathology

pathology MCQS introduction to pathology general pathology
Recently uploaded (20)
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes
Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat

Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad
Outbreak management including quarantine, isolation, contact.pptx

Outbreak management including quarantine, isolation, contact.pptx
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad
pathology MCQS introduction to pathology general pathology

pathology MCQS introduction to pathology general pathology
003 adult burns
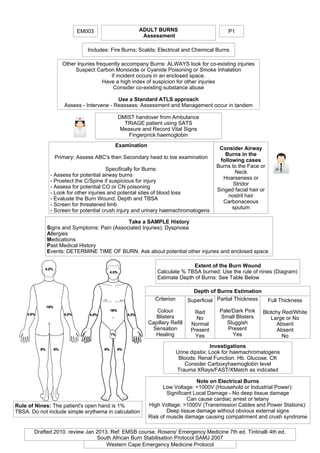
- 1. EM003 ADULT BURNS Assessment Includes: Fire Burns; Scalds; Electrical and Chemical Burns Take a SAMPLE History Signs and Symptoms: Pain (Associated Injuries); Dyspnoea Allergies Medications Past Medical History Events: DETERMINE TIME OF BURN. Ask about potential other injuries and enclosed space Extent of the Burn Wound Calculate % TBSA burned: Use the rule of nines (Diagram) Estimate Depth of Burns: See Table Below Consider Airway Burns in the following cases Burns to the Face or Neck Hoarseness or Stridor Singed facial hair or nostril hair Carbonaceous sputum Depth of Burns Estimation Criterion Colour Blisters Capillary Refill Sensation Healing Superficial Red No Normal Present Yes Partial Thickness Pale/Dark Pink Small Blisters Sluggish Present Yes Full Thickness Blotchy Red/White Large or No Absent Absent No Investigations Urine dipstix: Look for haemachromatogens Bloods: Renal Function. Hb. Glucose. CK Consider Carboxyhaemoglobin level Trauma XRays/FAST/XMatch as indicated Note on Electrical Burns Low Voltage: <1000V (Household or Industrial Power): Significant Local Damage - No deep tissue damage Can cause cardiac arrest or tetany High Voltage: >1000V (Transmission Cables and Power Stations): Deep tissue damage without obvious external signs Risk of muscle damage causing compatrment and crush syndrome Drafted 2010. review Jan 2013. Ref: EMSB course. Rosens' Emergency Medicine 7th ed. Tintinalli 4th ed. South African Burn Stabilisation Protocol SAMJ 2007 P1 Western Cape Emergency Medicine Protocol Other Injuries frequently accompany Burns: ALWAYS look for co-existing injuries Suspect Carbon Monoxide or Cyanide Poisoning or Smoke Inhalation if incident occurs in an enclosed space. Have a high index of suspicion for other injuries Consider co-existing substance abuse Use a Standard ATLS approach Assess - Intervene - Reassess: Assessment and Management occur in tandem DMIST handover from Ambulance TRIAGE patient using SATS Measure and Record Vital Signs Fingerprick haemoglobin Examination Primary: Assess ABC's then Secondary head to toe examination Specifically for Burns: - Assess for potential airway burns - Proetect the C/Spine if suspicious for injury - Assess for potential CO or CN poisoning - Look for other injuries and potental sites of blood loss - Evaluste the Burn Wound: Depth and TBSA - Screen for threatened limb - Screen for potential crush injury and urinary haemachromatogens Rule of Nines: The patient's open hand is 1% TBSA. Do not include simple erythema in calculation
- 2. ADULT BURNS Management EM003 Stabilise ABC's Manage the Burn Wound: Remove the source of heat Cool burns <3 hrs old - rinse with tepid tap water for minimum half hour Remove clothing/jewellery/rings Escharotomies for circumferential burns of the limbs or chest Apply burnshield (or clingfilm) once cooled for first 6 hrs - After 24 hrs use flamazine dressings Give TETANUS and Analgesia Indications for Intubation Airway Burns with predicted deterioration GCS < 8 or inability to maintain airway Not oxygenating Not ventilating Fluid Management If > 20 % TBSA: Insert 2 x large bore IV cannulas (Can be inserted through burned skin) Difficult IV acces: Femoral/Extrenal Jugular/ large bore CVP or IO lines. Cut-down. Insert Urinary Catheter A shocked patient needs to be resuscitated: Give crystalloid boluses (20ml/kg) until shock is reversed. If the patient is bleeding, blood transfusion is indicated Further fluid is given to replace losses occurring through burned skin This is given in addition to any resuscitation fluid needed PARKLANDS FORMULA Calculates the amount of fluid needed over the first 24 hours Calculated from the TIME OF THE BURN 4 ml/kg x Weight x % Body Surface Area Burned Give half over the first 8 hours Give the next half over the next 16 hours Add 10% TBSA if there are associated airway burns MONITOR RESPONSE: Reassess hourly Keep Urine Output > 0,5 ml/kg/hr Monitor HR; BP; ABG; Lactate IV Analgesia - Morphine Reconstitute 10mg in 10 ml water Loading dose: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg (Use less for elderly or frail) Then Bolus 0.05 mg/kg every 15 min Titrate to analgesic effect Beware of decreased BP and respiratory depression Chemical Burns Remove all Clothing Wash with copious amounts of tap water If eyes involved - Irrigate until ph is normal Electrical Burns Attach cardiac monitor May need extra IV fluid Monitor for crush and compartments syndromes 1. >10% BSA any burn thickness 2. Any full thickness burn 3. Electrical or Chemical burns 4. Inhalation burns 5. Hands,Feet,Perineum,Face,Joints 6. Circumferential burns 7. Associated major trauma 8. Extremes of age > 65 9. Severe co-existing medical condition Contact Tygerberg Burns Unit 021-938 84911 If they do not have a bed, refer to secondary level surgical service in your area No admission criteria Stable These patients can be seen and discharged from every level of care with the following Ensure tetanus given Provide analgesia Arrange follow-up for dressings To return earlier if any signs of infection P2 Drafted 2010. review Jan 2013. Ref: EMSB course. Rosens' Emergency Medicine 7th ed. Tintinalli 4th ed. South African Burn Stabilisation Protocol SAMJ 2007 Western Cape Emergency Medicine Protocol Attach Monitors - ECG, SpO2, BP cuff Insert Urinary Catheter and NGT. (Not if Base of Skull Facture) Disposition Discharge Admit - Level 3 Burns Centre