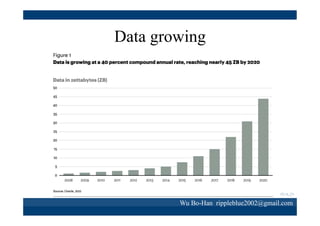
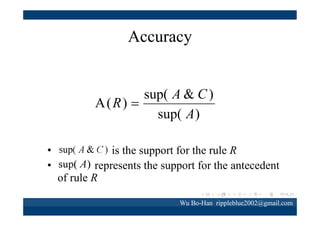
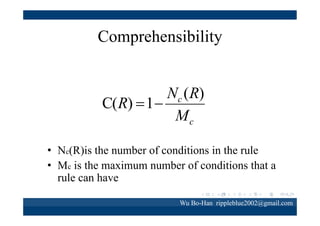
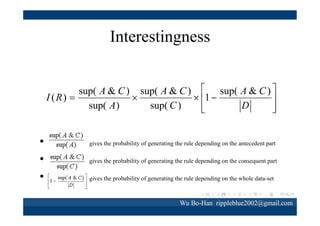
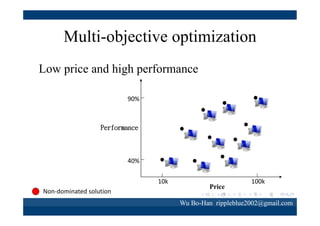
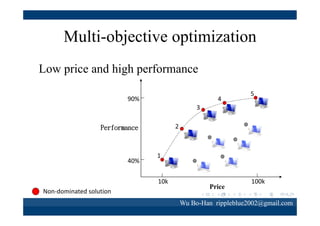
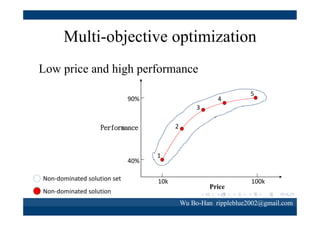
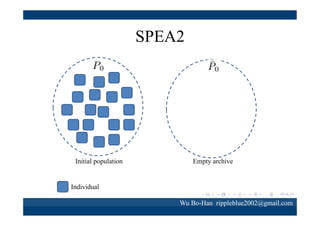
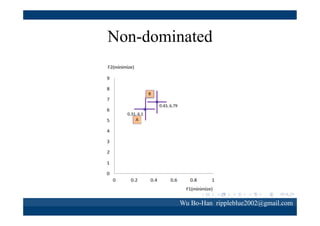
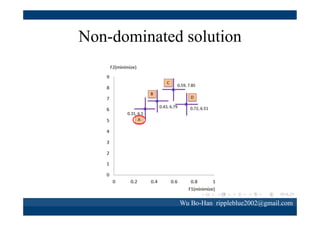
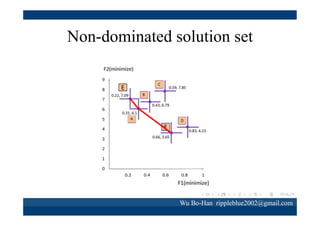
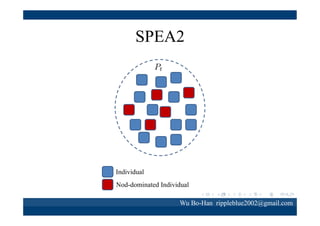
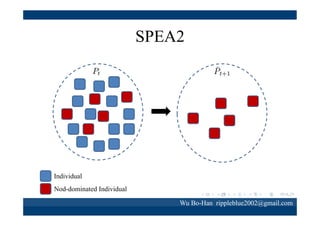
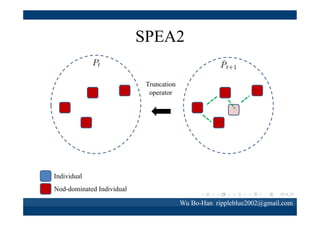
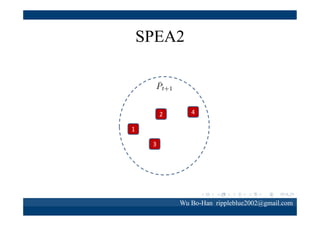
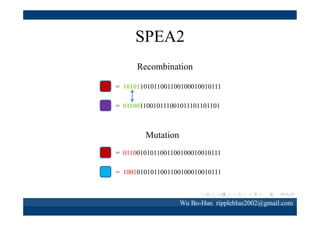
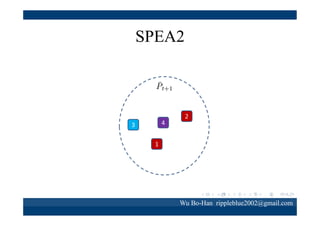
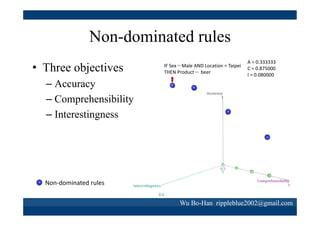
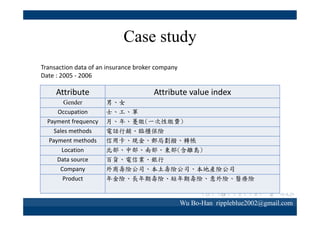
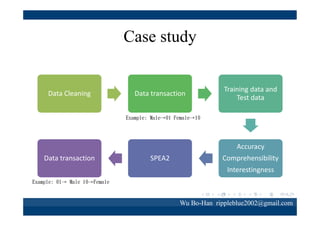
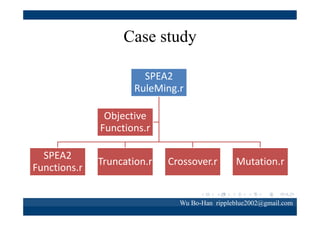
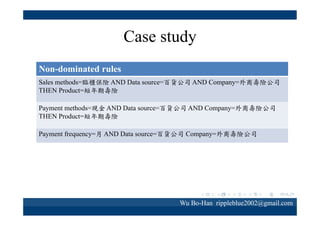
The document discusses using the SPEA2 algorithm for multi-objective optimization to find non-dominated classification rules from transaction data. It describes classification rule mining, objectives of accuracy, comprehensibility and interestingness, and the SPEA2 approach which uses selection, crossover and mutation operators over generations to find a non-dominated solution set. A case study applies SPEA2 on insurance broker transaction data to extract non-dominated rules relating customer attributes to insurance products.