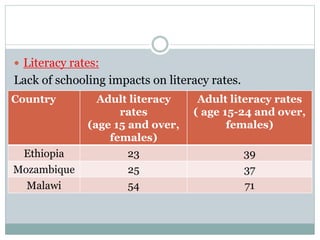
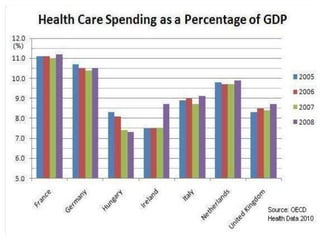
The document classifies countries into three groups: developed (first world), transitional (second world), and developing (third world), highlighting the economic disparities and challenges faced by third world countries such as low per capita income, poor health, and inadequate education. It discusses the impact of population growth, infrastructure, human capital, and governance on development, noting that many developing countries experience high unemployment, underemployment, and corruption. Additionally, it addresses the influence of history, religion, and ethnicity on development outcomes, emphasizing the effects of conflict and trade relationships on economic progress.