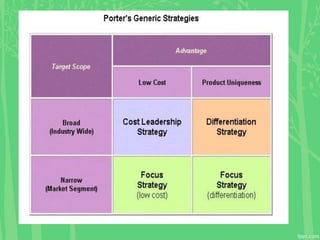
This document discusses Porter's generic strategies, including cost leadership, differentiation, and market segmentation. It defines each strategy and provides examples. Cost leadership involves having the lowest costs or acceptable prices to target a broad market. Differentiation focuses on standing out from competitors through branding, packaging, or other attributes. Market segmentation, also called focus strategy, targets specific niche markets to build expertise and charge premium prices. The document warns that failing to choose cost leadership or differentiation can result in being "stuck in the middle" without a competitive advantage.