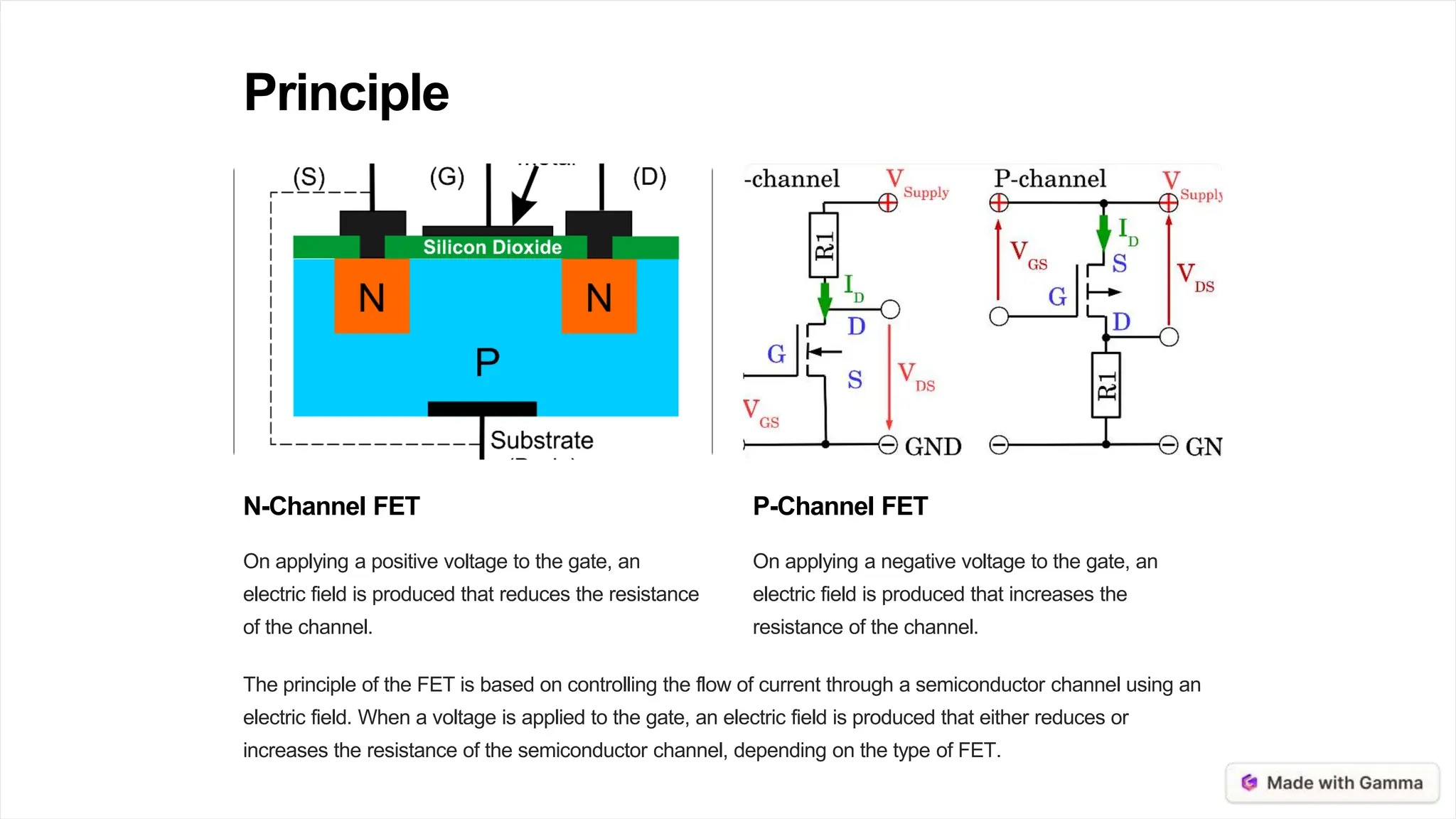
A field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current. There are several types of FETs that are used for different applications, such as MOSFETs which can be found in power electronics and digital circuits, JFETs which are used for signal amplification, and MESFETs which are used for microwave amplification. FETs have advantages over bipolar junction transistors like high input impedance and low noise, but are more sensitive to temperature changes. Research is ongoing to improve FET performance and explore new applications in areas like quantum computing and terahertz electronics.