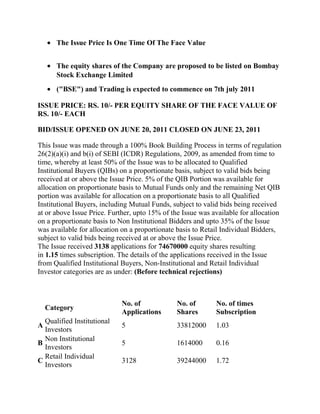
This document provides a summary of Birla Pacific Medspa Limited's initial public offering process and results. The company raised Rs. 65.18 crores through a book built IPO of 65,175,000 shares priced between Rs. 10-11 per share. The issue was oversubscribed 1.18 times with qualified institutional buyers and retail investors subscribing 1.04 and 1.82 times respectively. The shares were allotted at Rs. 10 per share and are expected to begin trading on the Bombay Stock Exchange on July 7, 2011. The IPO proceeds will be used to expand the company's network of healthcare centers across India and for working capital requirements.