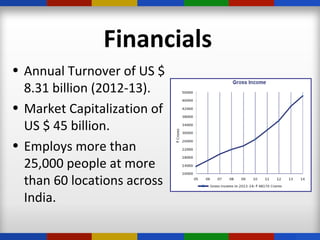
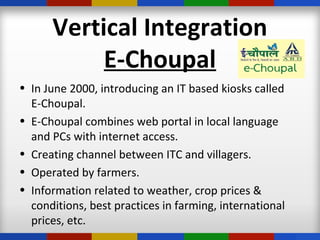
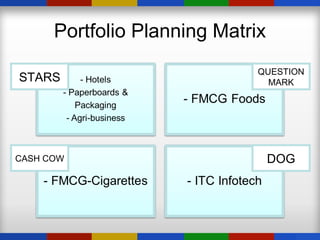
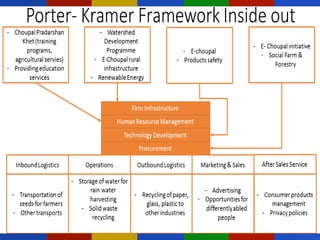
ITC is an Indian conglomerate headquartered in Kolkata, West Bengal. It has diversified into various businesses including FMCG, hotels, paperboards & packaging, agriculture, and IT. ITC has an annual turnover of $8.31 billion and a market capitalization of $45 billion, employing over 25,000 people across India. ITC has pursued diversification and growth through both acquisitions and organic means, leveraging synergies across its divisions.