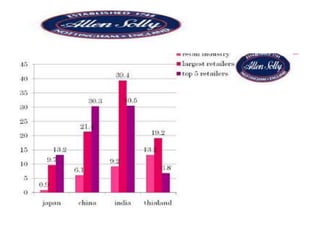
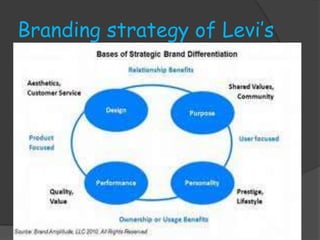
The document discusses branding and brand strategy. It provides definitions of branding, explaining that branding goes beyond just a company's name or logo and encompasses a company's entire identity and customer experience. It also discusses elements of strong brands, benefits of global versus local brands, and strategies for brand positioning, name selection, sponsorship, and development through line extensions, brand extensions, etc. Examples provided include branding strategies of well-known brands like Allen Solly and Levi's.






![Elements of Brand
Brand elements
Brands are communicated through various elements[8]:
Name: The word or words used to identify the company, product,
service, concept
Logo: The visual trademark that identifies the brand
Tagline or Catchphrase: "The Quicker Picker Upper" is
associated with Bounty; "Can you hear me now" is an important
part of the Verizon brand.
Shapes: The distinctive shape of the Coca-Cola bottle or the
Volkswagen Beetle are trademarked elements of those brands.
Graphics: The dynamic ribbon is also a trademarked part of Coca-
Cola's brand.
Colour: Owens-Corning is the only brand of fibreglass insulation
that can be pink.
Sounds: A unique tune or set of notes can "denote" a brand:
NBC's chimes are one of the most famous examples.
Movement: Lamborghini has trademarked the upward motion of its
car doors.
Smells: Scents, such as the rose-jasmine-musk of Chanel No. 5 is
trademarked.
Taste: KFC has trademarked its special recipe of 11 herbs and
spices for fried chicken](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marketingppt-120930224233-phpapp01/85/Marketing-ppt-7-320.jpg)