Embed presentation




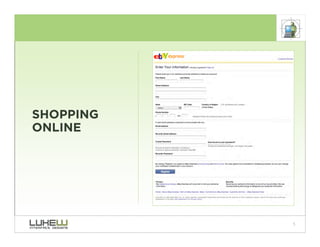

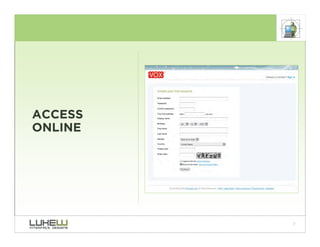




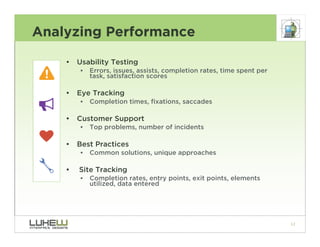
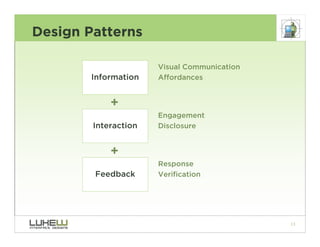


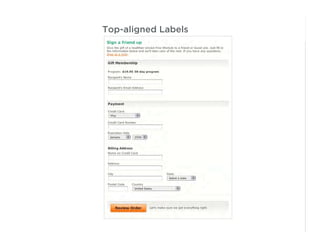
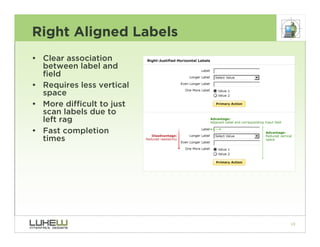

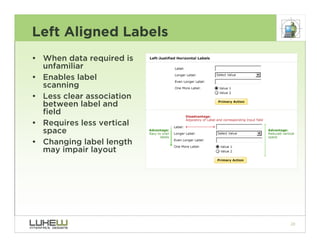
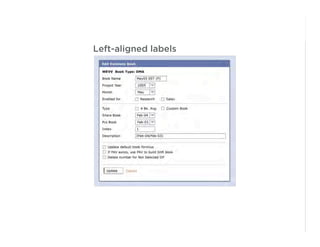
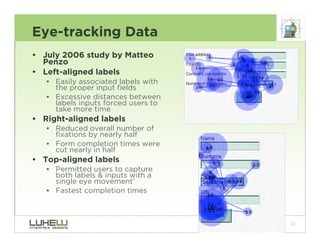


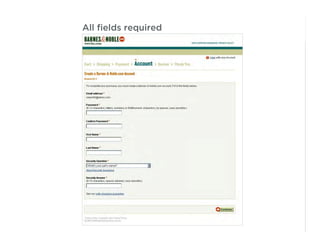

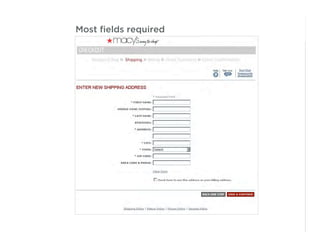
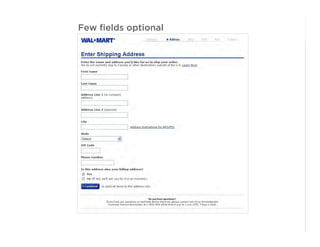



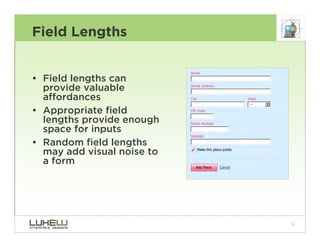







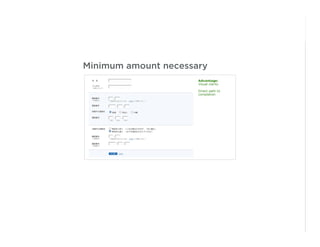

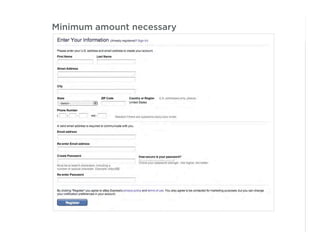



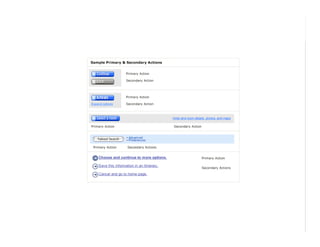
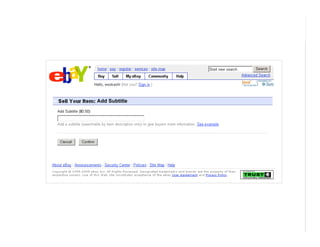


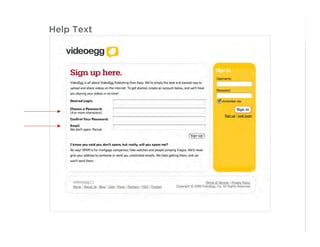
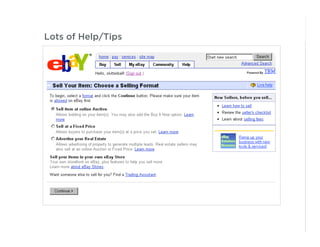
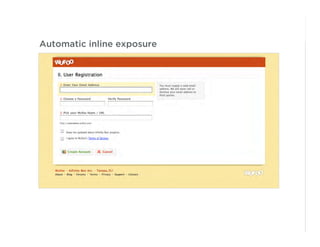
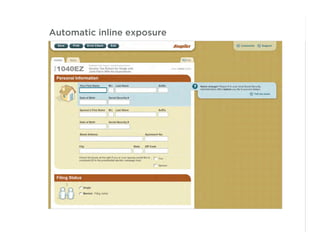
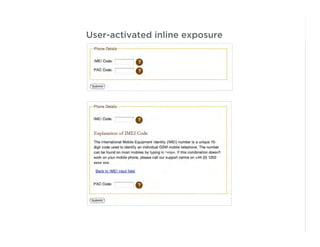
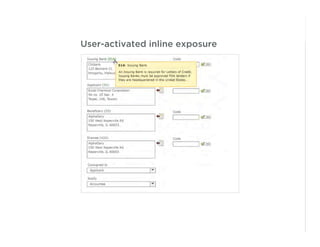
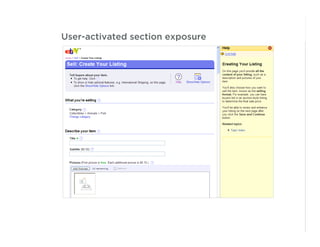






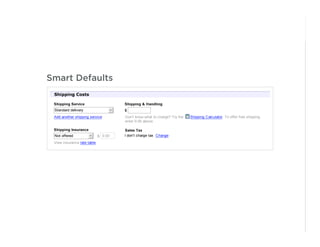
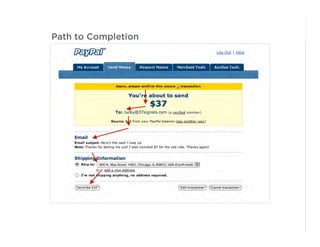
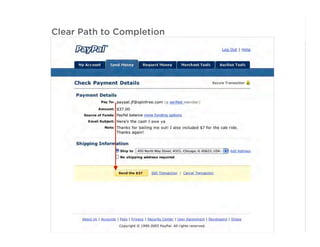






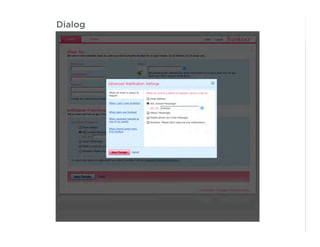
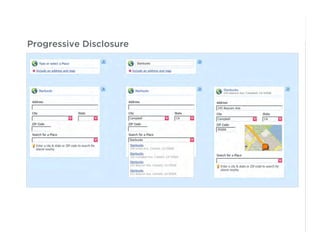
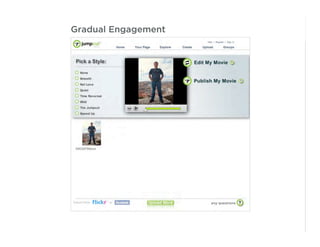
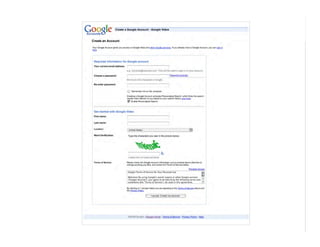












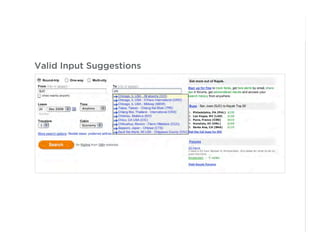



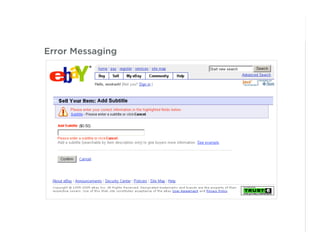
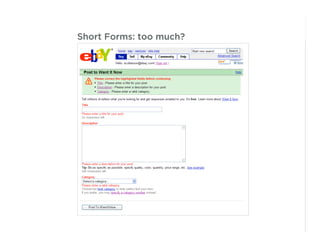
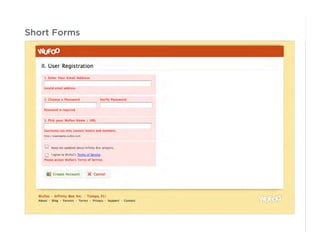
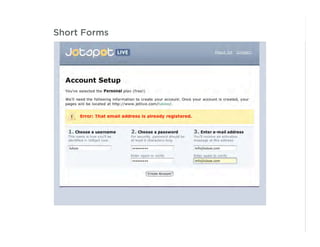










This document outlines best practices for form design. It discusses why form design matters for enabling commerce, access, and engagement online. It then covers design principles like minimizing pain points for users and ensuring a clear path to completion. Specific design patterns are examined, including layout, required fields, and help text. The document recommends top-aligned labels for familiar data, right-aligned labels when space is limited, and left-aligned labels for unfamiliar data. It also suggests using the minimum necessary visual elements and dynamic help systems for unfamiliar forms.















































































































