The document discusses developing a domain model for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It identifies common IoT behaviors like data collection, sense-compute-actuate, and intermittent sensing. An IoT domain model is presented that captures key concepts like entities, sensors, actuators, devices, and software components, as well as their relationships. The domain model provides benefits like a common understanding of IoT terminology, modeling invariant properties, and enabling modular application design.

![``Things’’: Salient Features
• May have sensors attached.
• May have actuator attached.
• Can communicate with other Things.
• Can be involved in the information
exchange between real/physical and
``digital/virtual’’ world. [IoTRoadMap]
[IoTRoadMap] De Saint-Exupery, Internet of things, strategic research roadmap, Research report 2009. (URL:
http://ec. europa. eu/information—society/policy/rfid/documents/in—. cerp. Pdf )
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-2-2048.jpg)
![Internet of Things (IoT)
``A global network infrastructure that connects physical and virtual
things” [CASAGRAS Project].
[CASAGRAS Project] : http://www.rfidglobal.eu/userfiles/documents/CASAGRAS26022009.pdf
Figure credit : http://www.leaderstudio.net/iot/images/internet-of-things.jpg
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-3-2048.jpg)



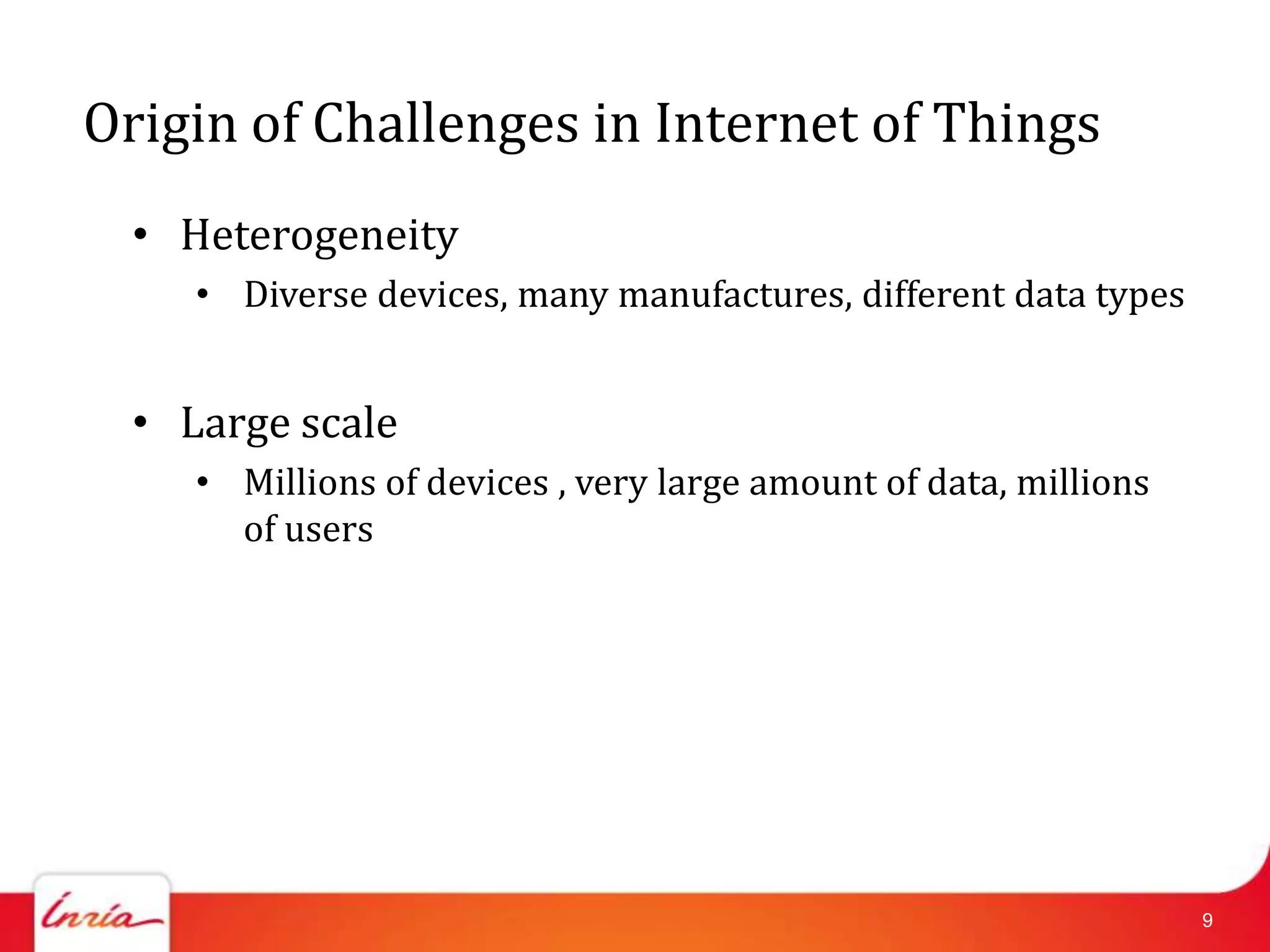

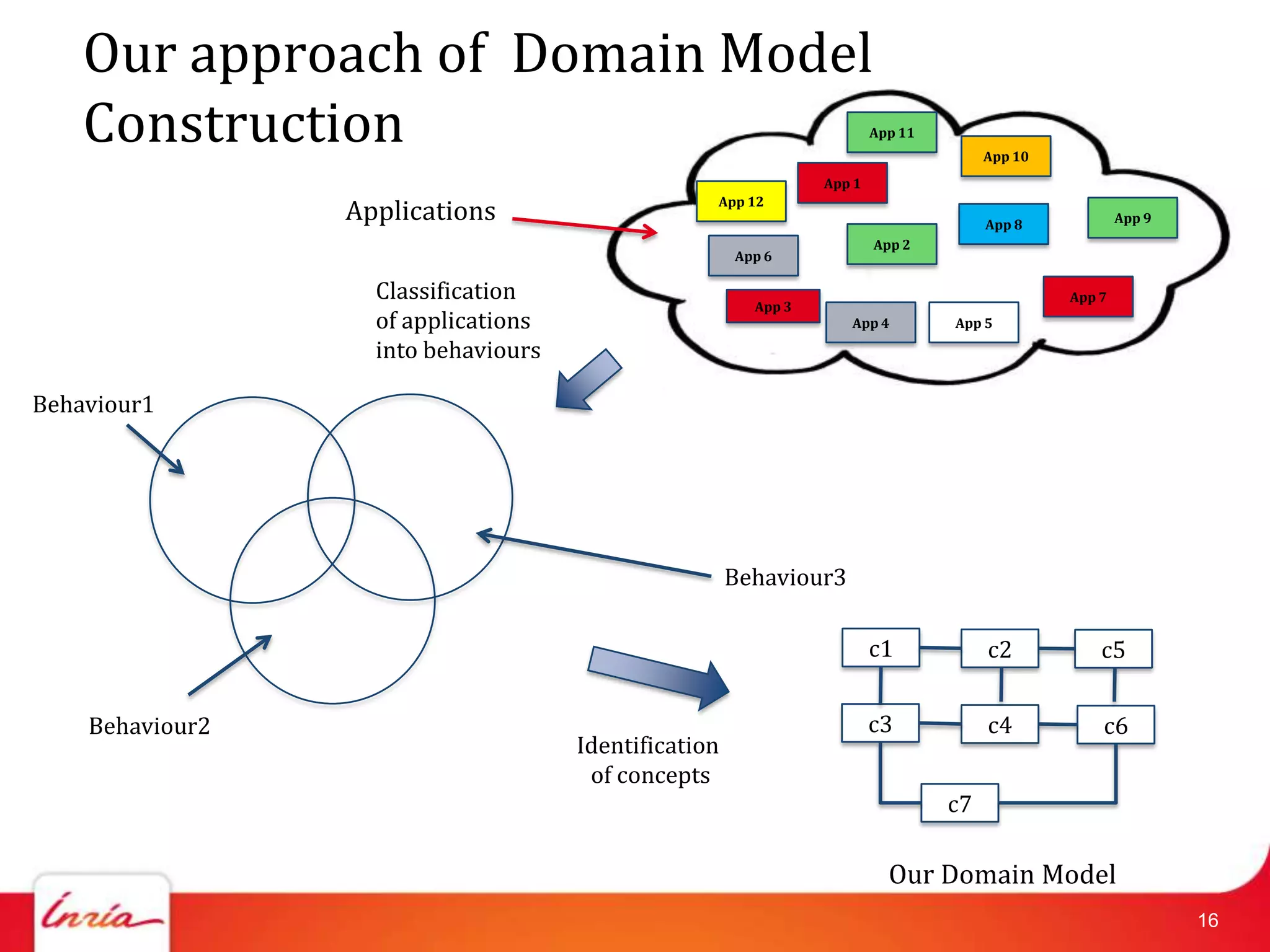
![First step : Important Initial Questions
1. What are the key concepts in the domain ?
2. What are the associations (or relationships)
among identified concepts?
Answer : Domain Model (DM)[OldeldDM]
[OldeldDM] P. Oldeld. Domain Modelling. Technical report, Appropriate Process
Group, 2002.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-11-2048.jpg)
![DM Benefits :
Creates Common Understanding
• IoT terms - with different meaning by different people
• leads to confusion and hinders scientific discourse
[Haller2010, IoTA]
• DM provides common lexicon
• Useful to domain experts, programmers , researchers.
[Haller2010] S. Haller. The Things in the Internet of Things. IoT 2010 Poster Session.
Tokyo, Japan, November, 2010.
[IoTA] IoT-A Project: http://www.iot-a.eu
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-12-2048.jpg)
![DM Benefits :
Enables Modular Design
• DM clearly identifies capabilities of each concepts.
• Application requirements tend to arrive in terms of
behaviour [OldeldDM]. They can be broken down into
concepts.
Computational
Sensor Physical entity
and Actuation
Sense the temeprature of a room and keep it steady
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-13-2048.jpg)
![DM Benefits :
Models Invariant Properties
• Models invariant associations [IoTA, SENSEI] – not
change from one application to other.
1 Hosts *
Device: Sensor:
Application 1 Smart Phone Light Sensor
Device: 1 Hosts * Sensor:
Application 2 sunSPOT
Temperature
Sensor
Invariant
Association
[IoTA] IoT-A Project: http://www.iot-a.eu/
[SENSEI] SENSEI project: http://www.sensei-project.eu/
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-14-2048.jpg)

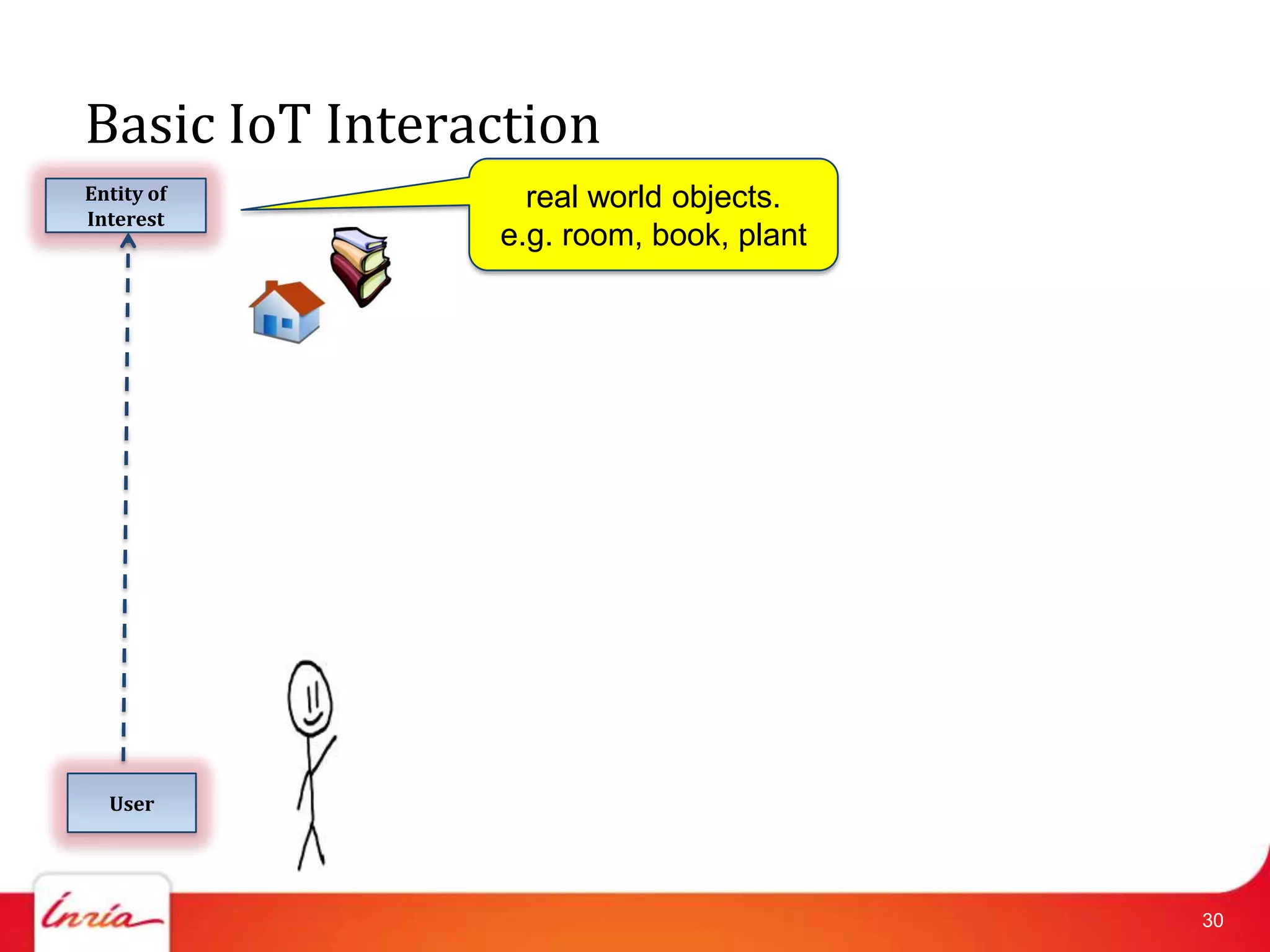
![Data Collection
• Smart things interact with user by stating information
about themselves.
• Periodically
• on event
• on demand
• Found in
• Patient monitoring [Niyato2009]
• Food supply chain [Dada2008]
• …
[Niyato2009] D. Niyato, E. Hossain, and S. Camorlinga. Remote patient monitoring service using heterogeneous wireless access
networks: architecture and optimization. Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on, 27(4):412-423, may 2009.
[Dada2008] A. Dada and F. Thiesse. Sensor applications in the supply chain: The example of quality-based issuing of perishables.
In Proceedings of the 1st international conference on The internet of things, pages 140-154. Springer-Verlag, 2008.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-17-2048.jpg)
![Example: Talking with Plants [Botanicalls]
• Plant notifies a user on his cell phone about
whether it needs water.
• Moisture sensor, Botanicalls device, Botanicalls
service, Mobile phone, Twitter service, User
• Also, precision agriculture [PresAg]
[Botanicall] http://www.botanicalls.com/
[PresAg] http://www.precisionagriculture.com.au/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-18-2048.jpg)
![Sense - Compute - Actuate
• Smart things interact with each other at either in the
local network or through the Internet.
• They take corrective actions [Mattern2010] with no human
originator, recipient or intermediary.
• It may prompt users as required.
• Found in
• Optimizing power consumption costs [Buckl2009]
• Work place safety [SENSEI]
• …
[Mattern2010] F. Mattern and C. Floerkemeier. From the Internet of Computers to the Internet of Things.
From active data management to event-based systems and more, Springer pages 242- 259, 2010.
[Buckl209] C. Buckl, S. Sommer, A. Scholz, A. Knoll, A. Kemper, J. Heuer, and A. Schmitt. Services to
the eld: An approach for resource constrained sensor/actor networks. In International Conference on
Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, pages 476-481. IEEE, 2009.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-19-2048.jpg)
![Sense-Compute-Actuate Example:
maintain temperature in room.[ParaHVAC]
Temperature
node
Heater
User enters
Preferences
[ParaHVAC] M. Feldmeier and J. Paradiso. Personalized HVAC control system.
In Internet of Things (IOT), pages 1 -8, 29-dec., 2010.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-20-2048.jpg)
![Intermittent Sensing
• Centred around tag
• RFID
• (1D) Barcode
• QR- code
• Mostly in applications where things have an information
shadow[ValhoIoT] on the Internet
• Found in
• Tourist information[RellTourist ]
• Mobile ticketing[BroPerci]
• ...
[ValhoIoT] C. A. Valhouli. The Internet of Things: Networked Objects and Smart Devices. Technical report, the hammersmithgroup, February
2011.
[RellTourist D. Reilly, M. Welsman-Dinelle, C. Bate, and K. Inkpen. Just point and click?: using handhelds to interact with paper maps. In
Proceedings of the 7th international conference on Human computer interaction with mobile devices & services, pages 239-242.
ACM, 2005.
[BroPerci] G. Broll, E. Rukzio, M. Paolucci, M. Wagner, A. Schmidt, and H. Humann. Perci: Pervasive service interaction with the Internet of
things. Internet Computing, IEEE, 13(6):74- 81, 2009.
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-21-2048.jpg)
![Intermittent Sensing example:
Reviewing consumer’s product [my2cents]
When user wants to When user wants to read
write other users’ comments, scan
comments, writes barcode, queries to storage
and sends to service.
2 storage service 3
1
User scans barcode
through mobile device
[my2cents] S. Karpischek and F. Michahelles. my2cents-Digitizing
consumer opinions and comments about retail products. In
Internet of Things (IOT), 2010, pages 1-7. IEEE, 2010.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-22-2048.jpg)

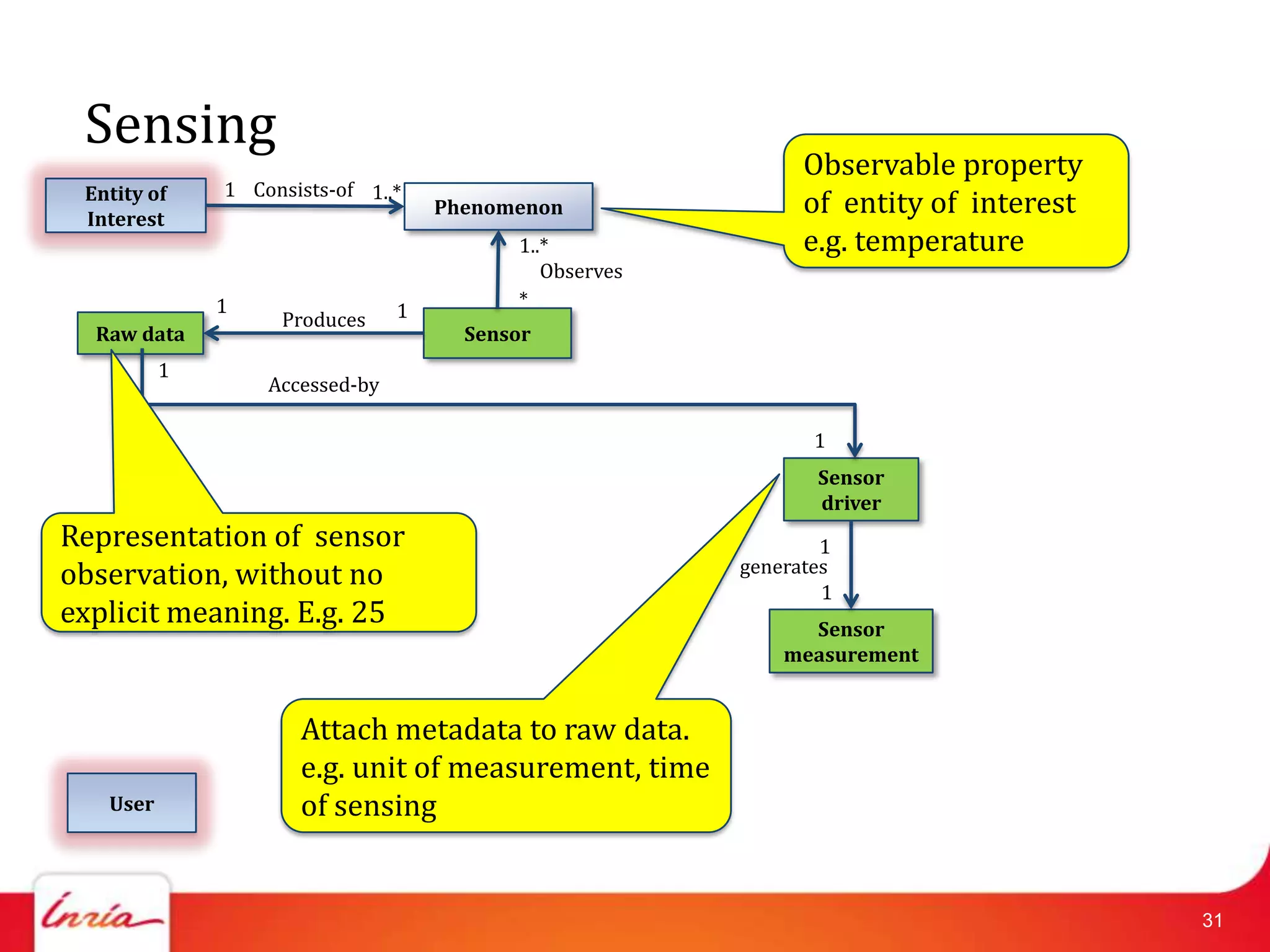
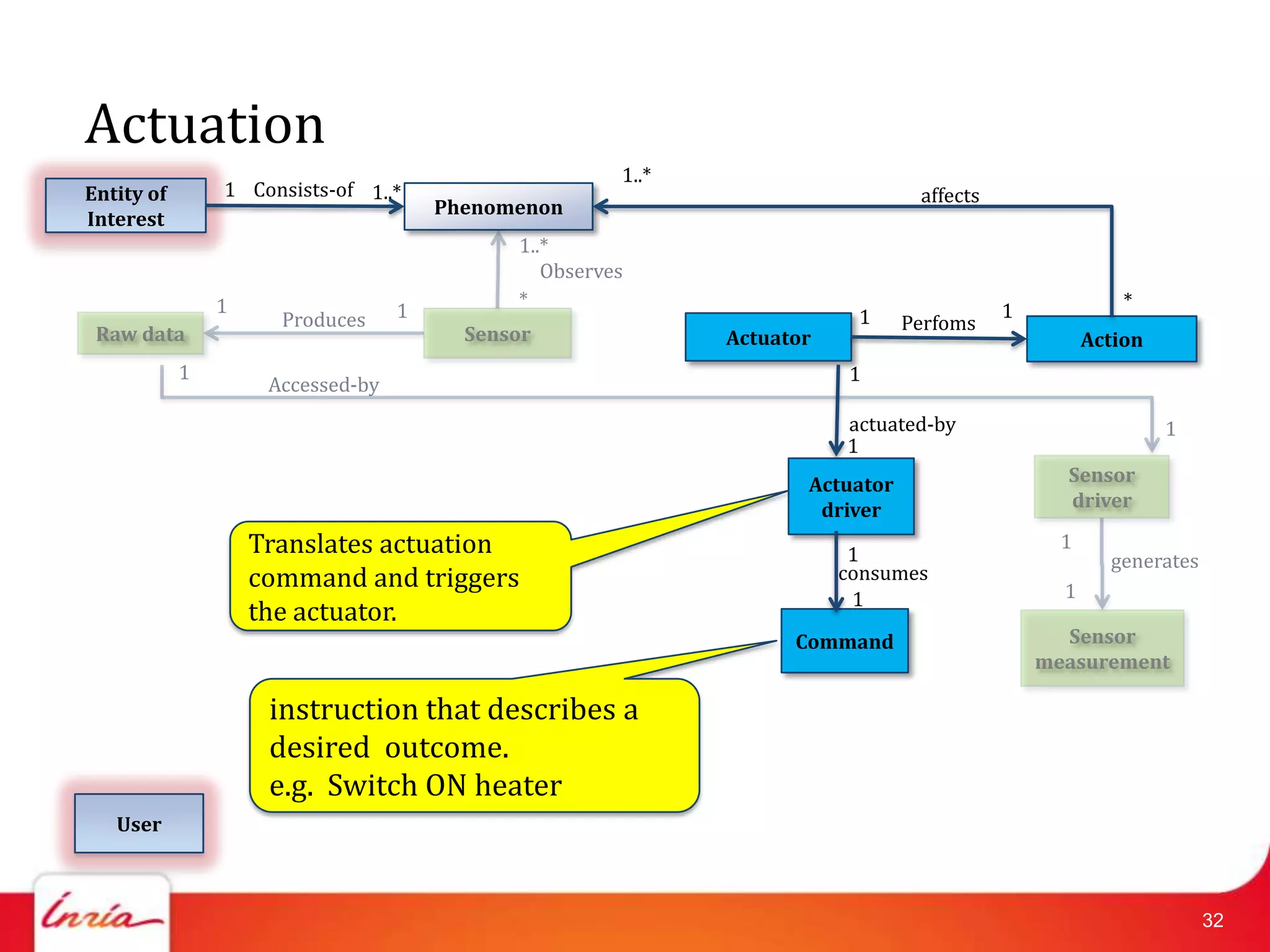
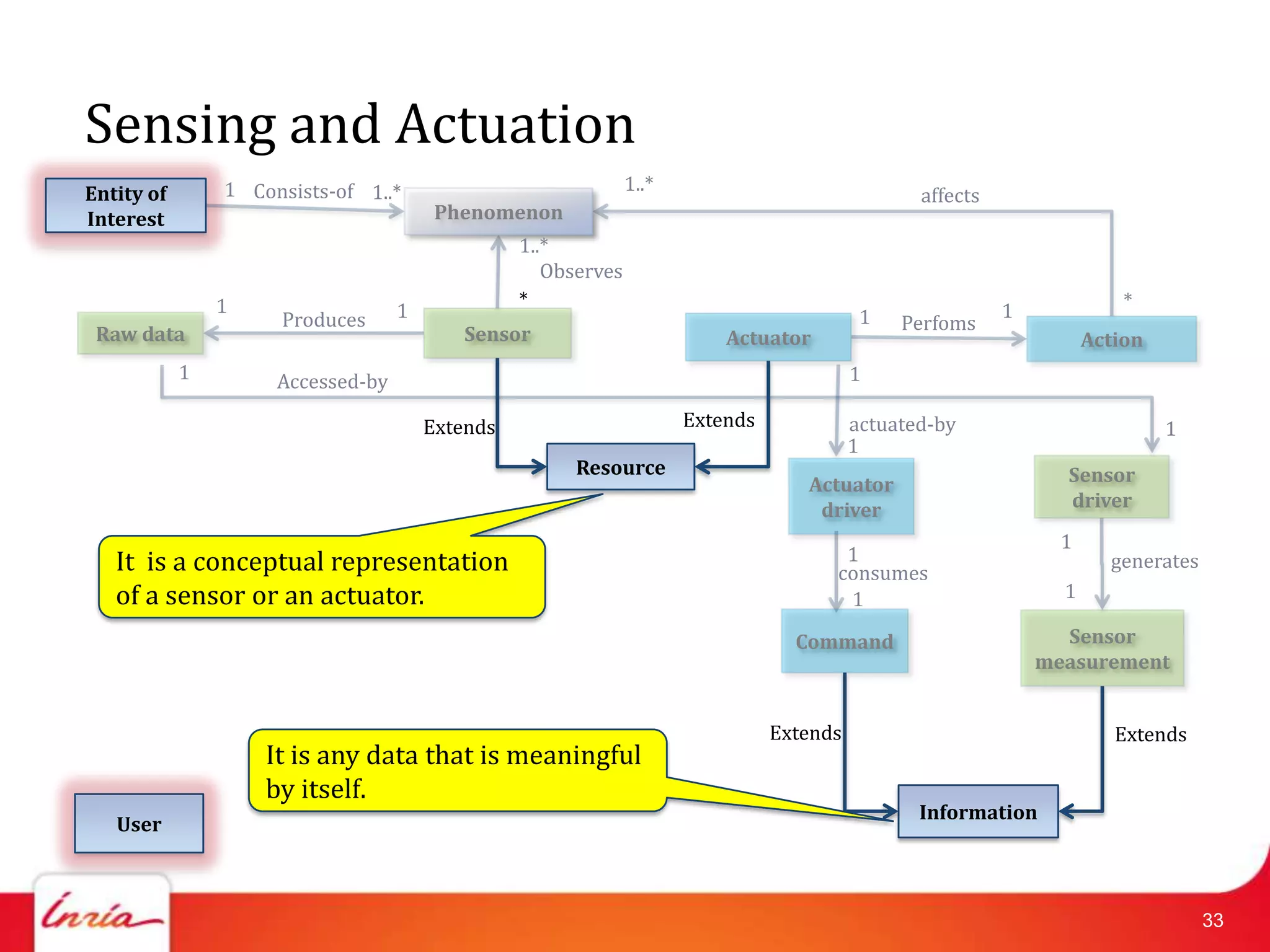
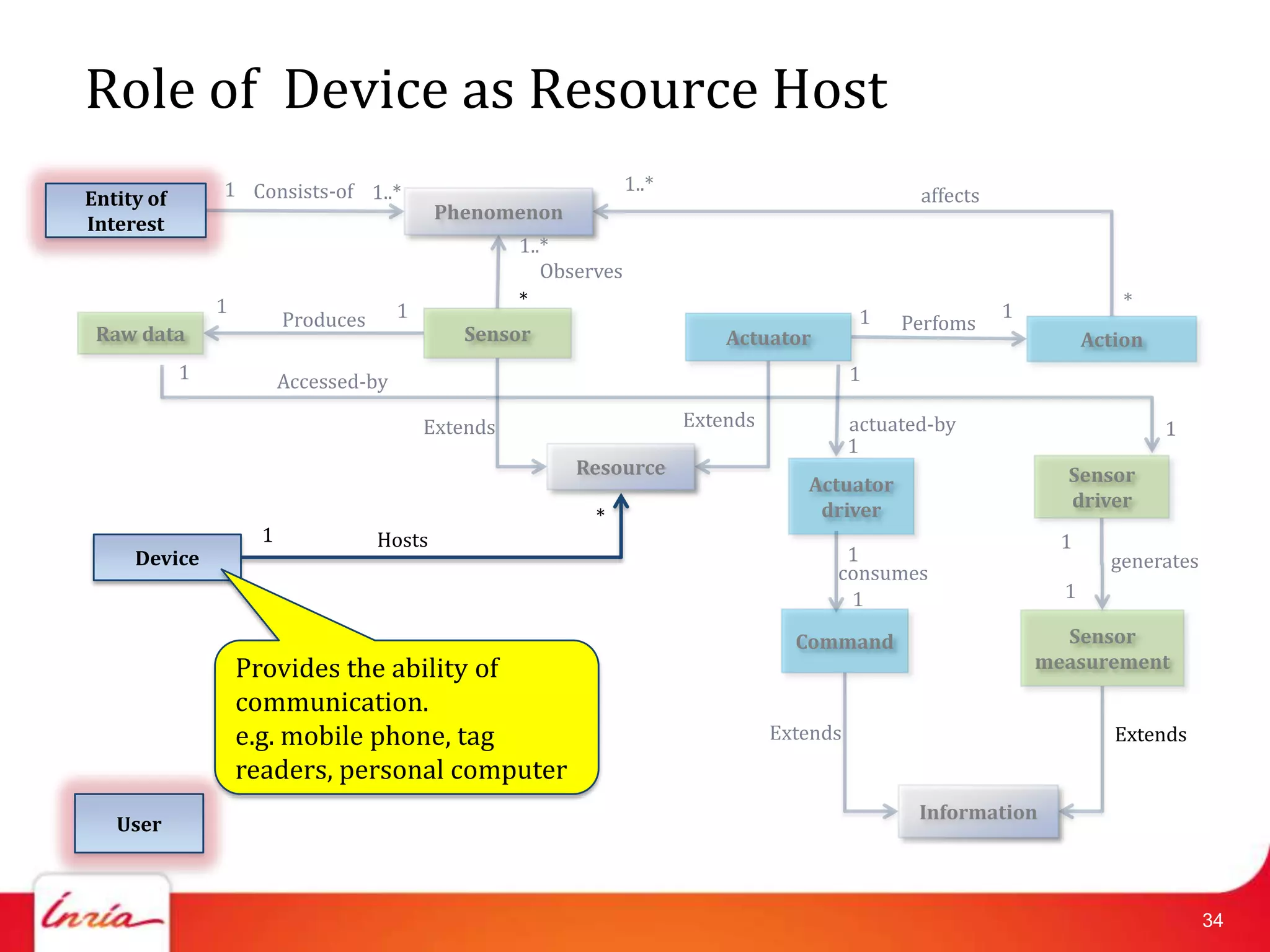
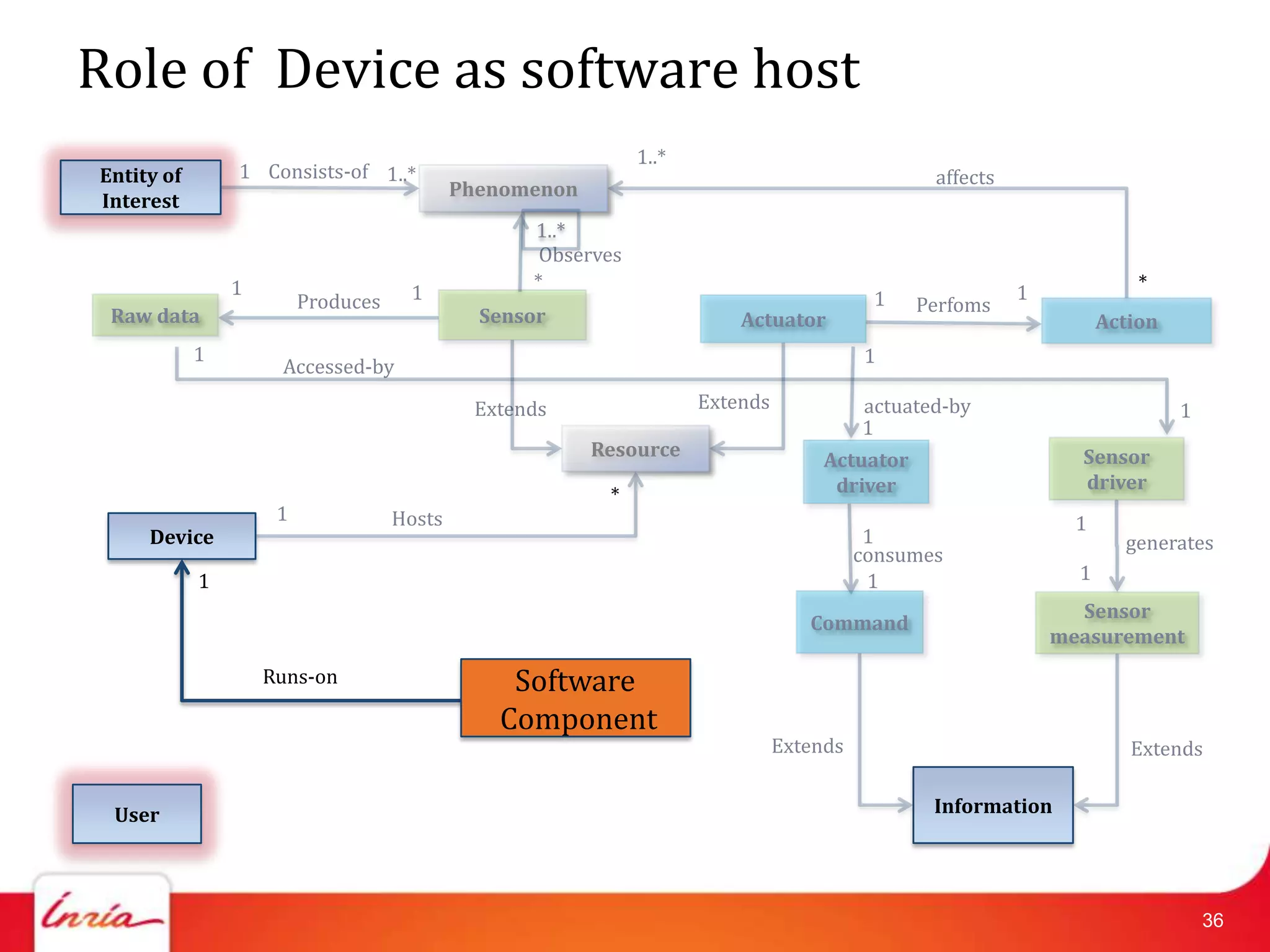
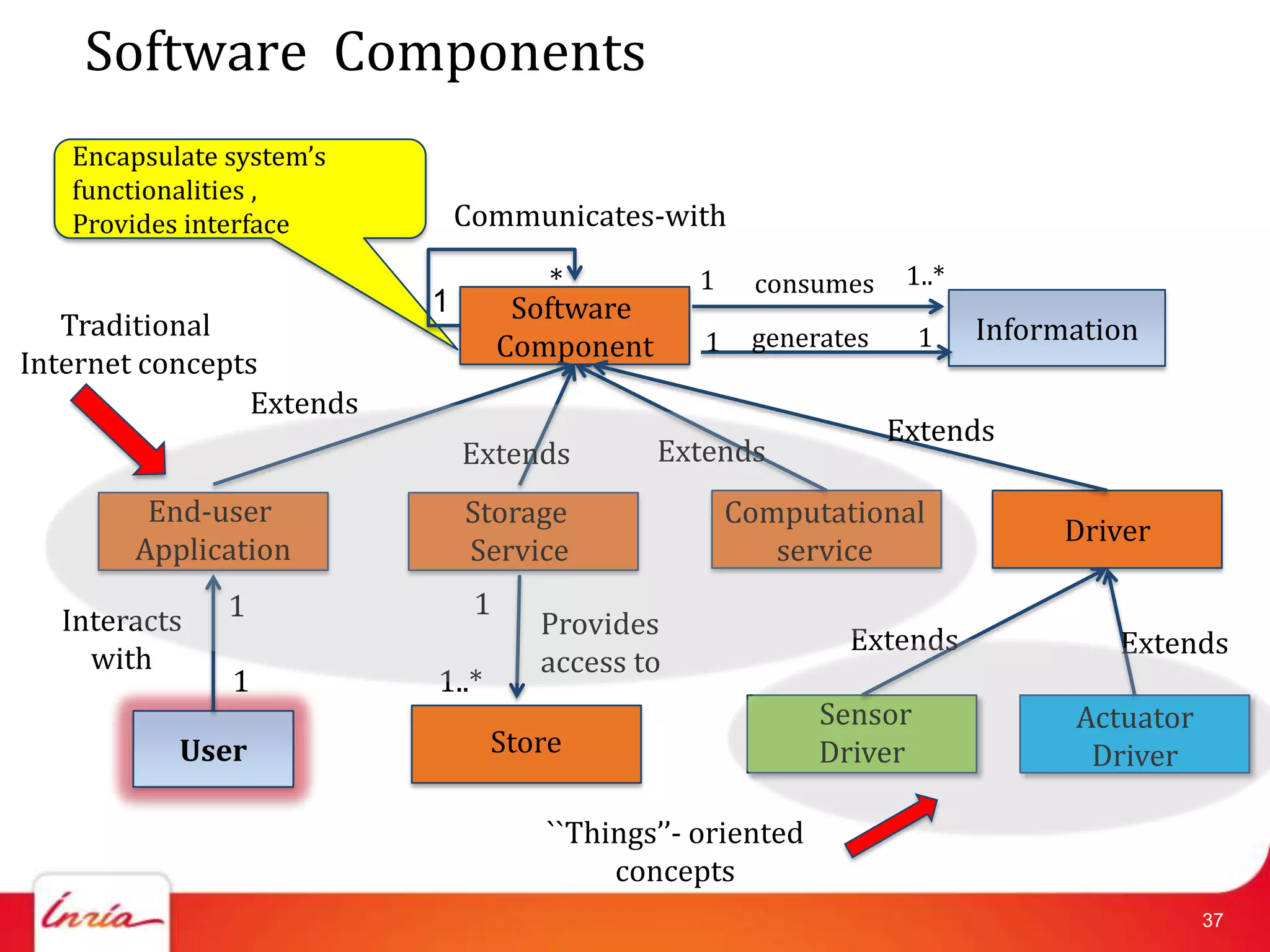
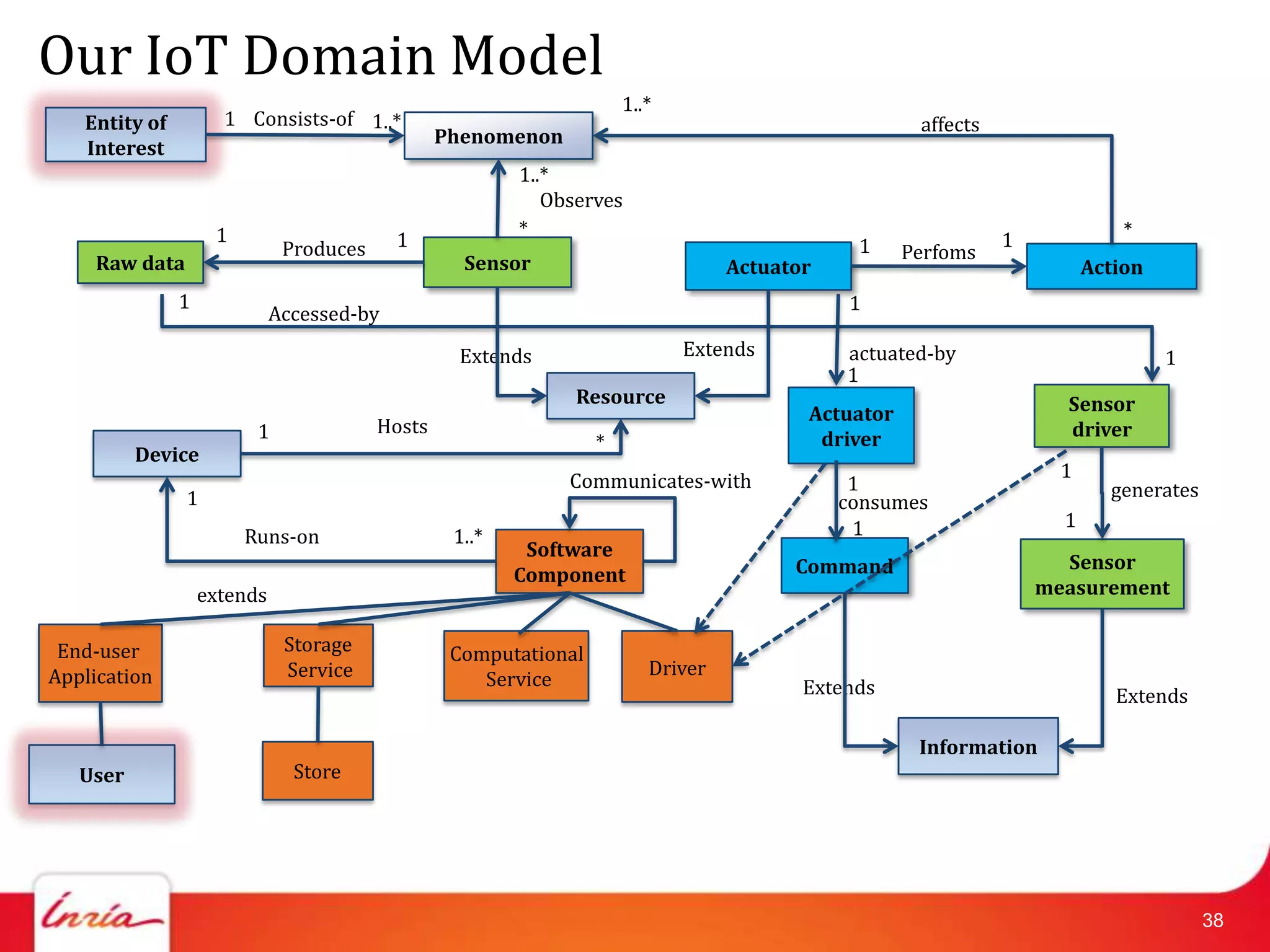
![Related Work on IoT Domain Model
• Haller [Haller2010] has defined the relationship among
things, devices, resources, and services.
• Aim: common understanding
• We add an explicit “user”, traditional internet concepts.
• A more detailed model is in [IoTA2011]
• Direct association between user and physical entity
• We add software components between them
[Haller2010] S. Haller. The Things in the Internet of Things. IoT 2010 Poster
Session. Tokyo, Japan, November, 2010.
[IoTA2011] www.iot-a.eu/
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardsapplicationdevelopmentfortheinternetofthingsupdated-111212112445-phpapp01/75/Towards-application-development-for-the-internet-of-things-updated-32-2048.jpg)