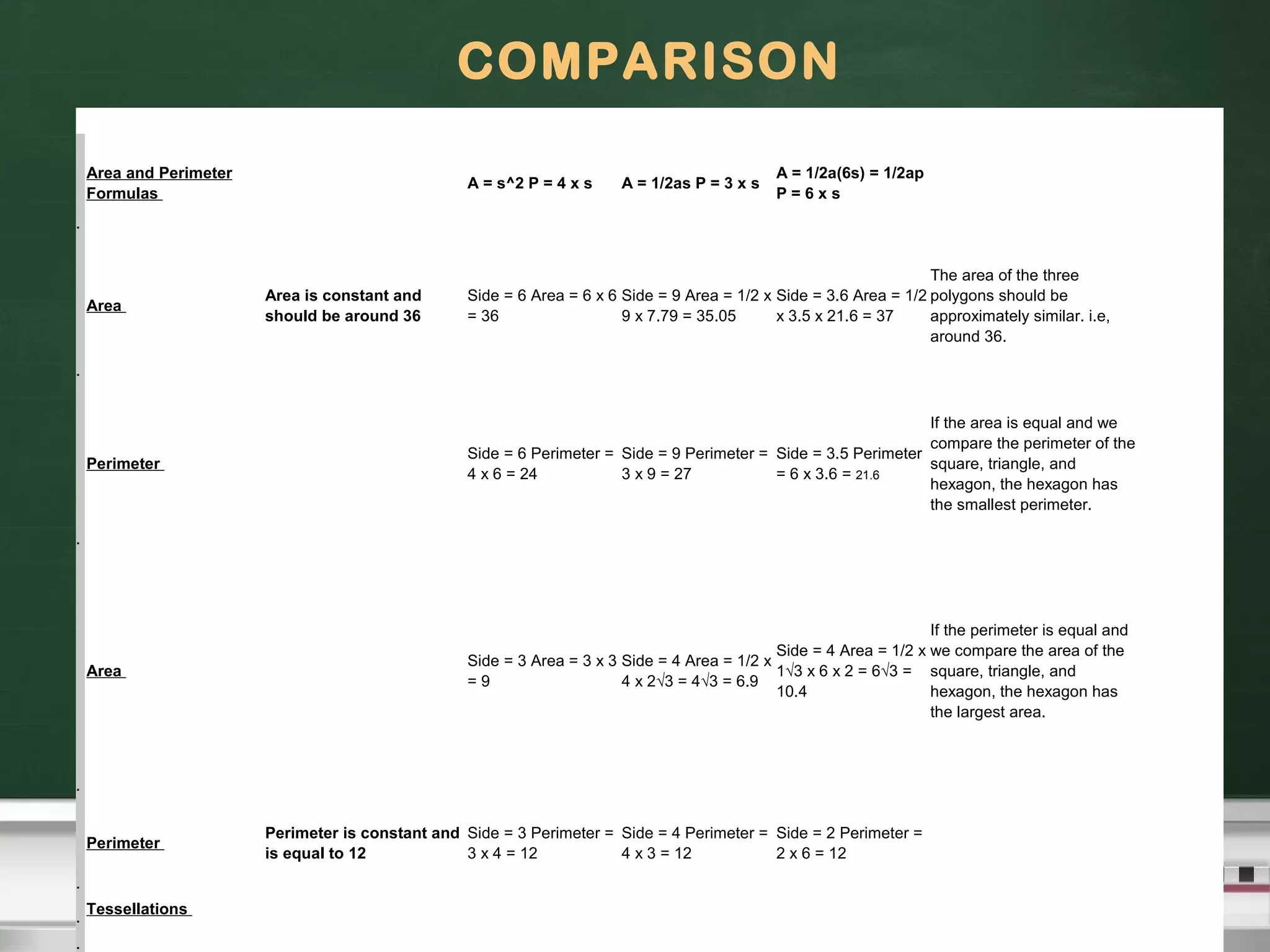
The document discusses communication in social insects like bees and ants. It describes how bees use a waggle dance to communicate distance and direction of food sources to other bees. The dance includes a straight run indicating direction and speed indicating distance - faster dances mean closer food. Experiments with ants in mazes found they can adapt routes using pheromones when paths are blocked, zigzagging to find alternatives. Hexagonal structures in bee hives are also mathematically efficient for enclosing space with less material.