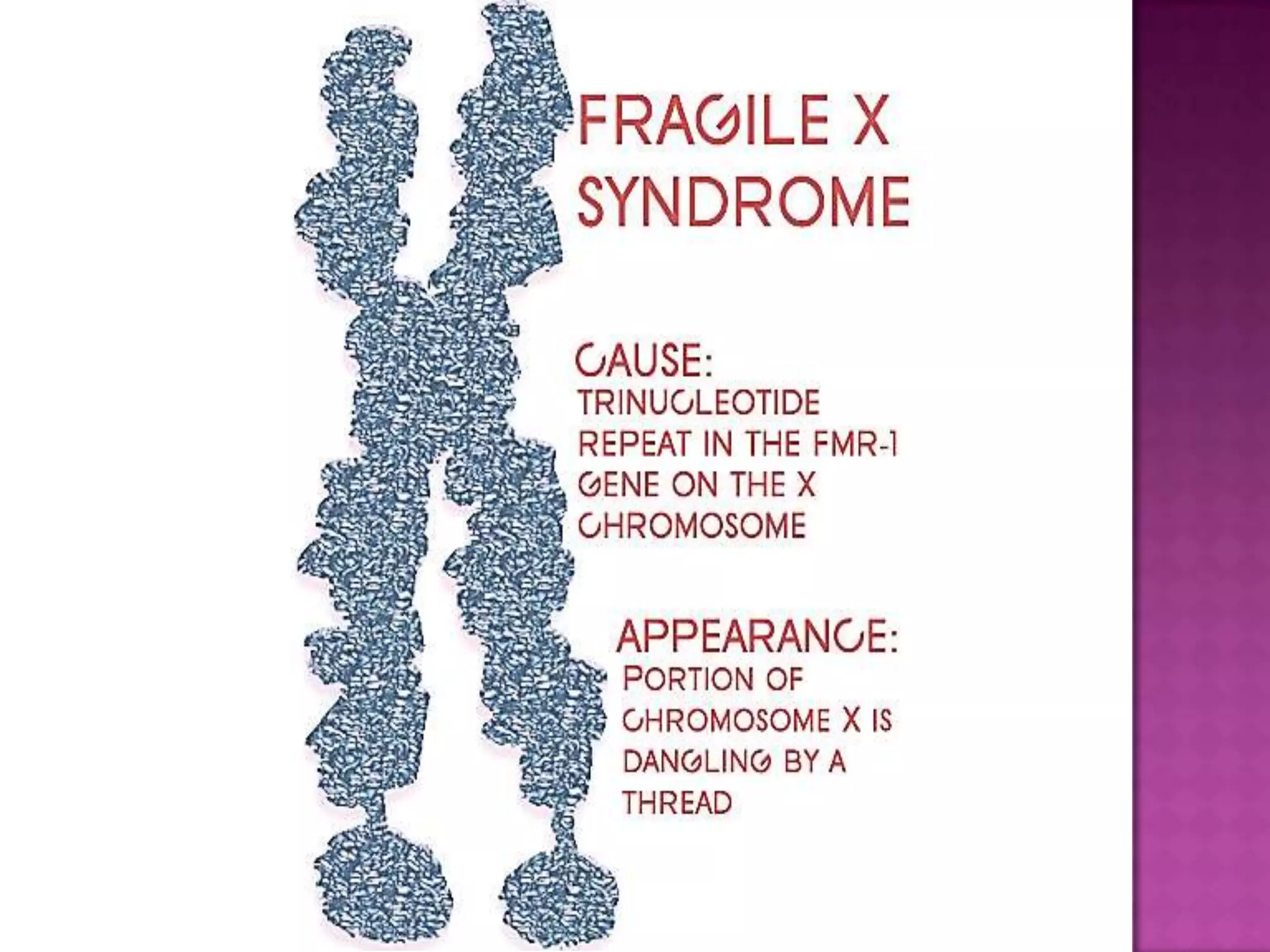
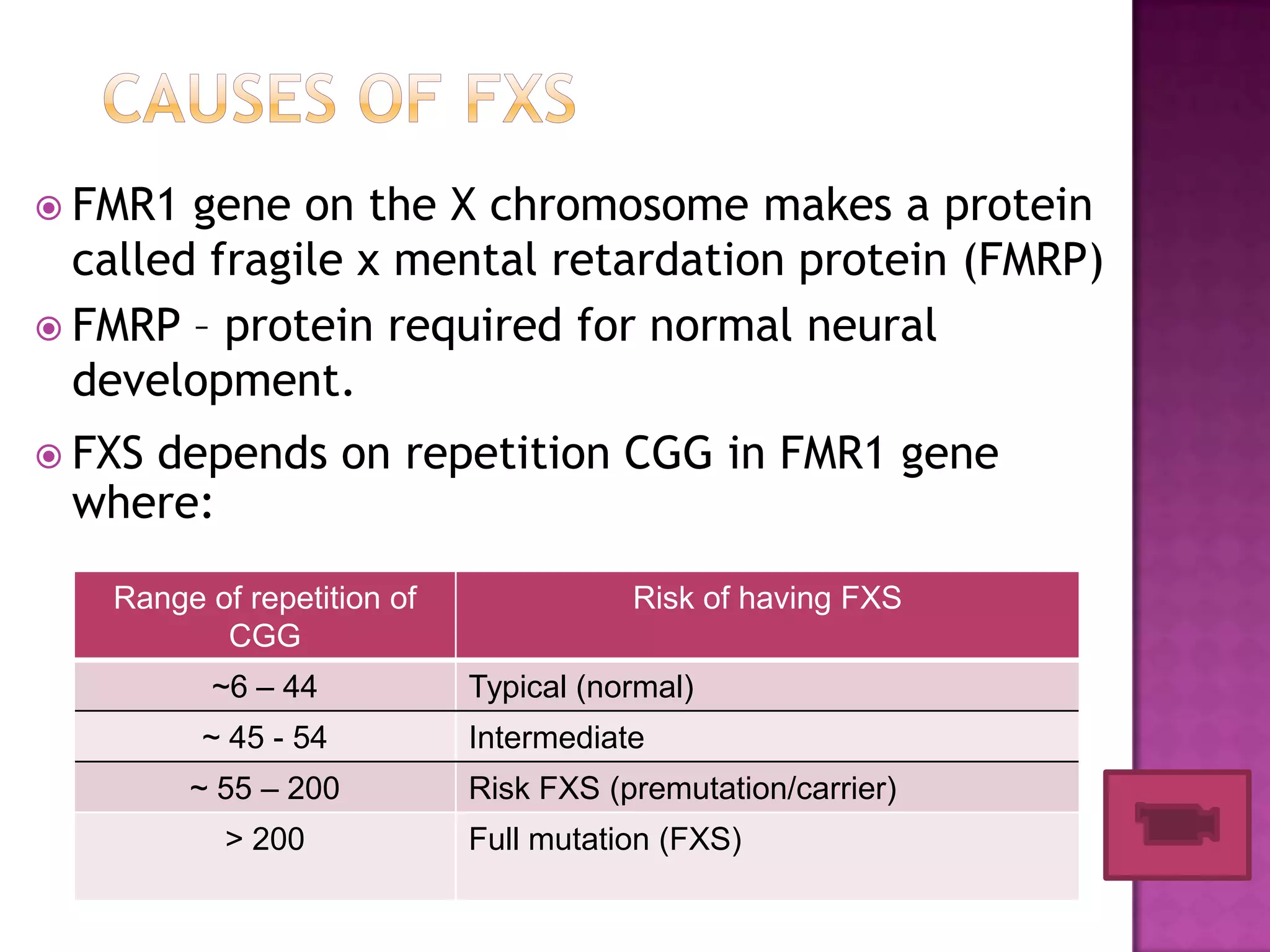
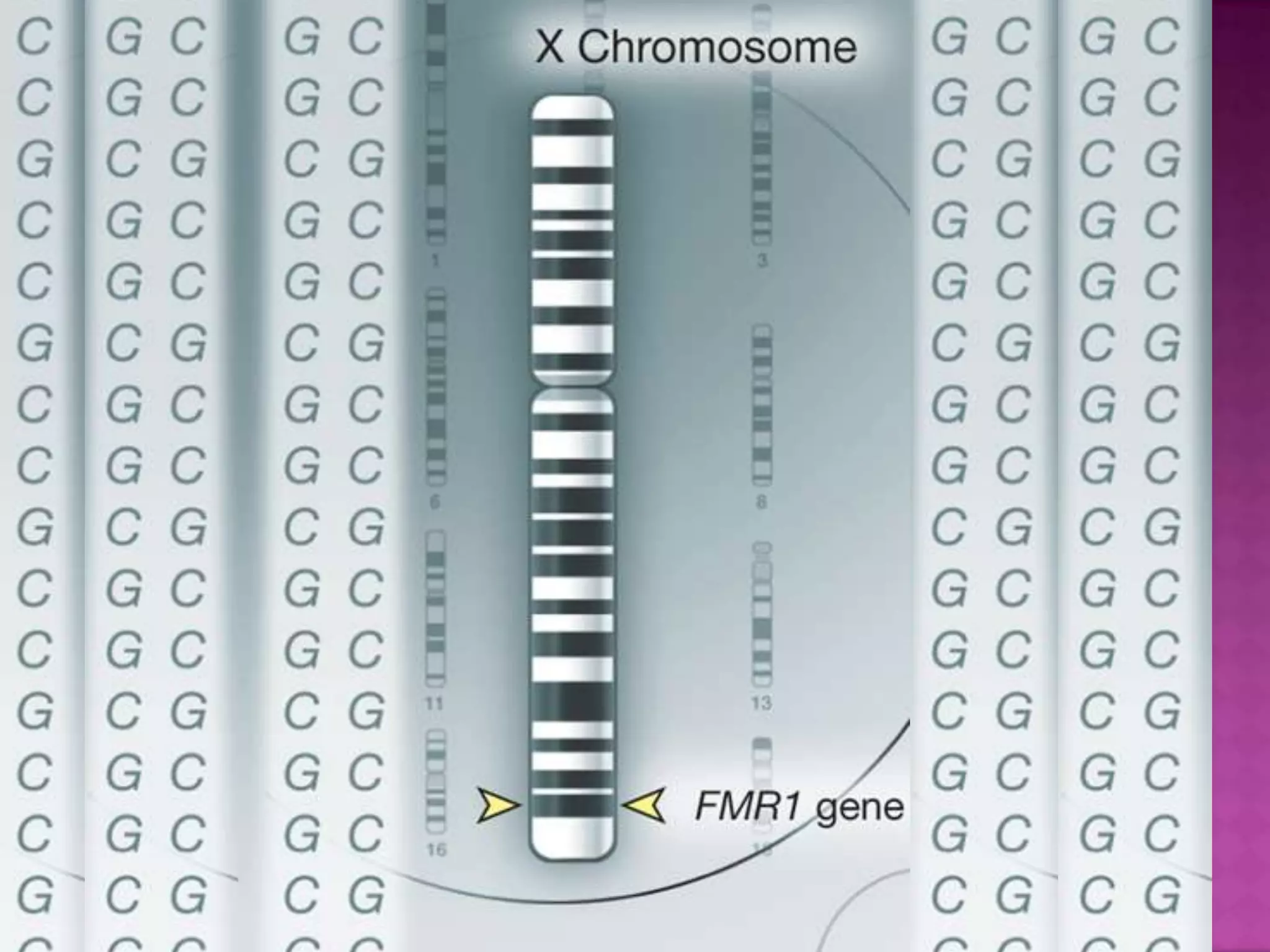
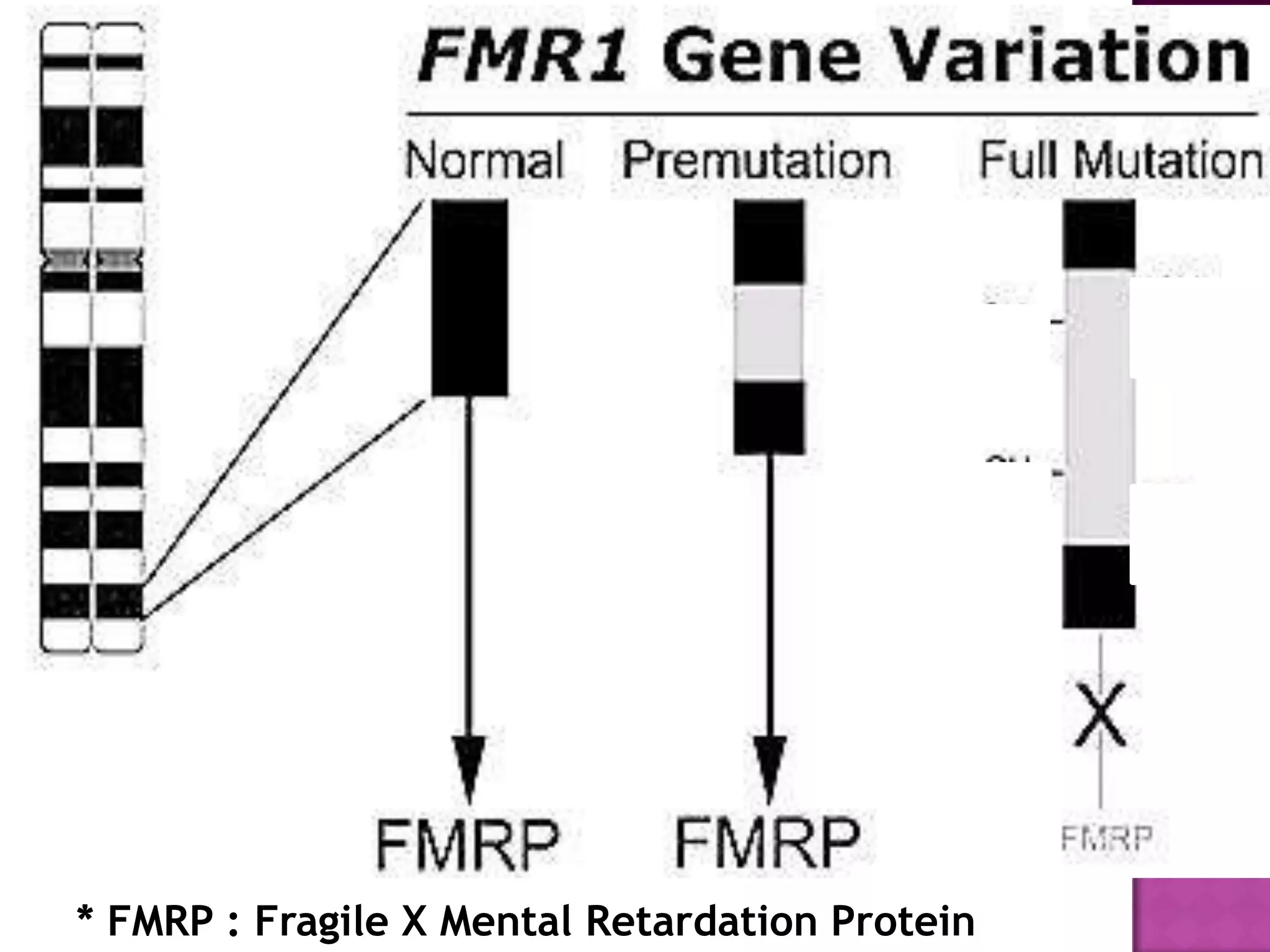
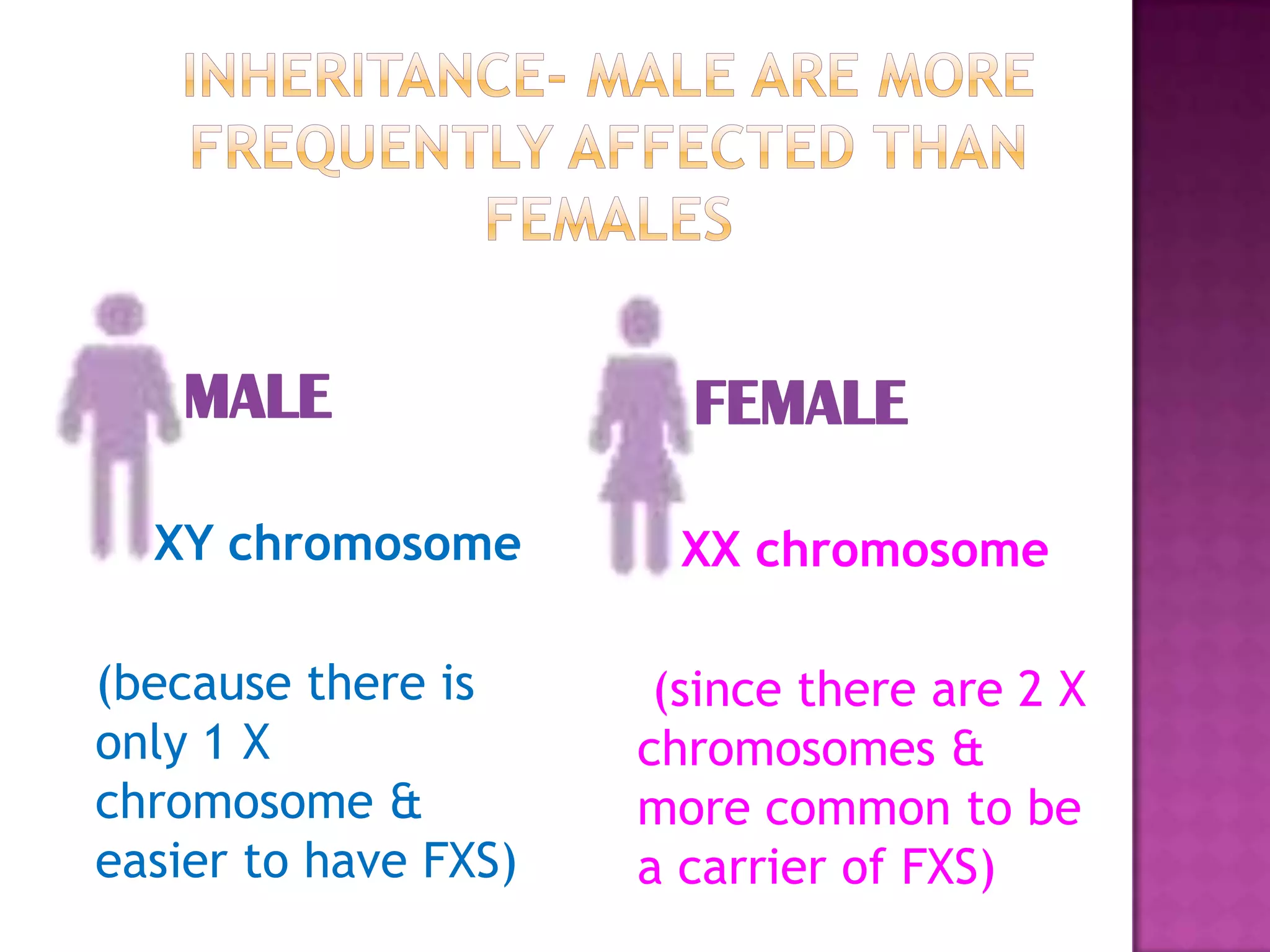
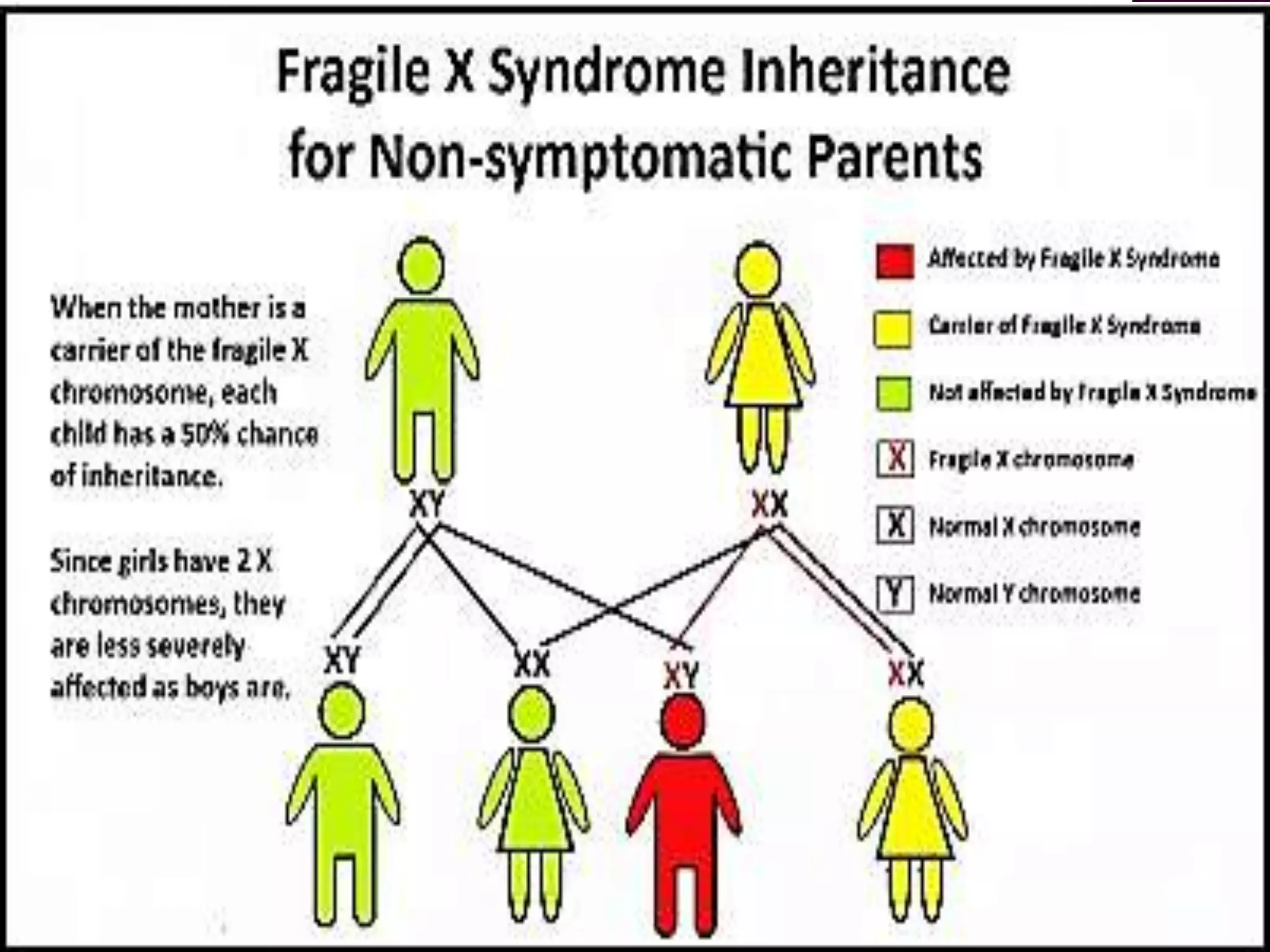
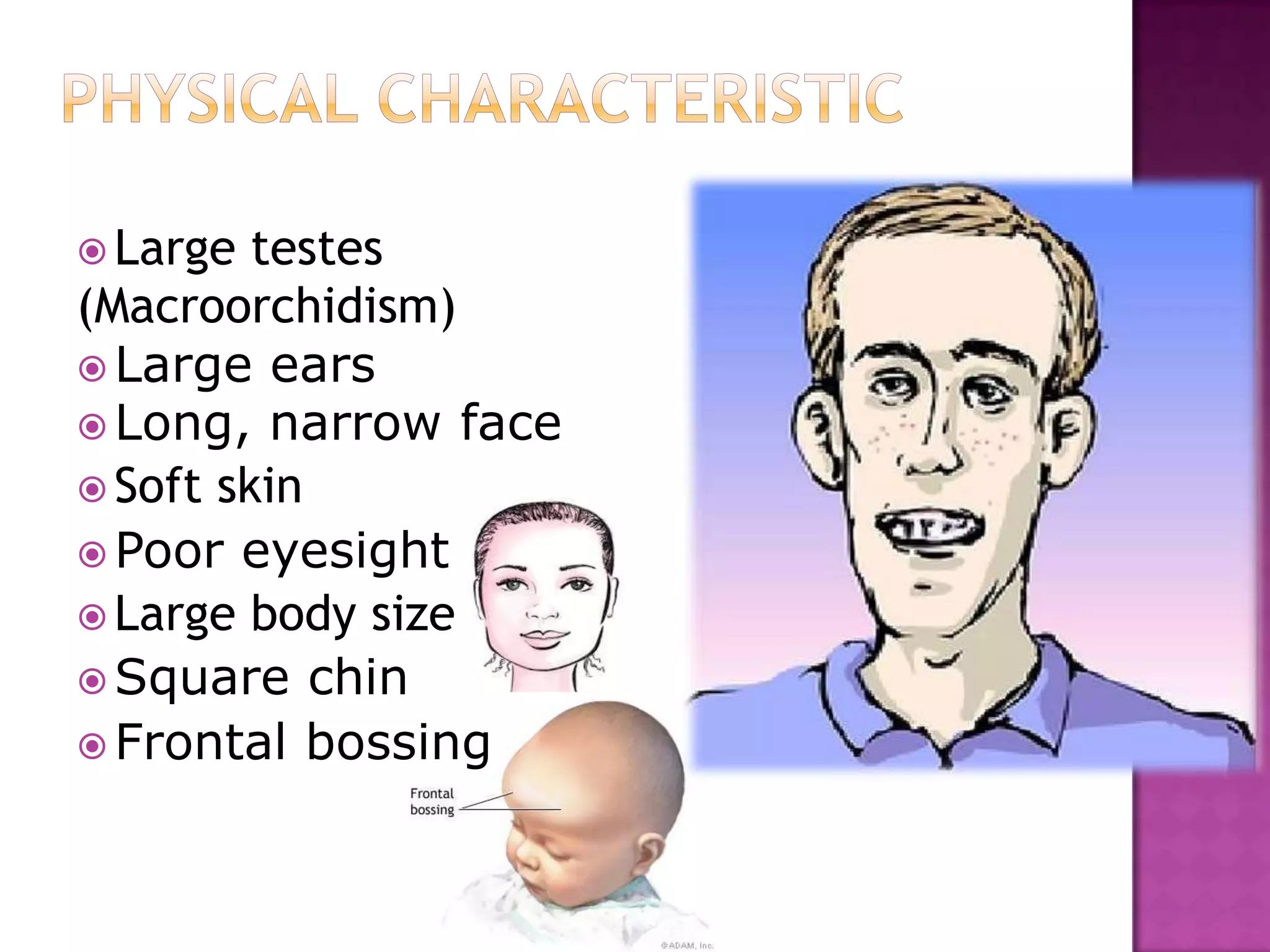
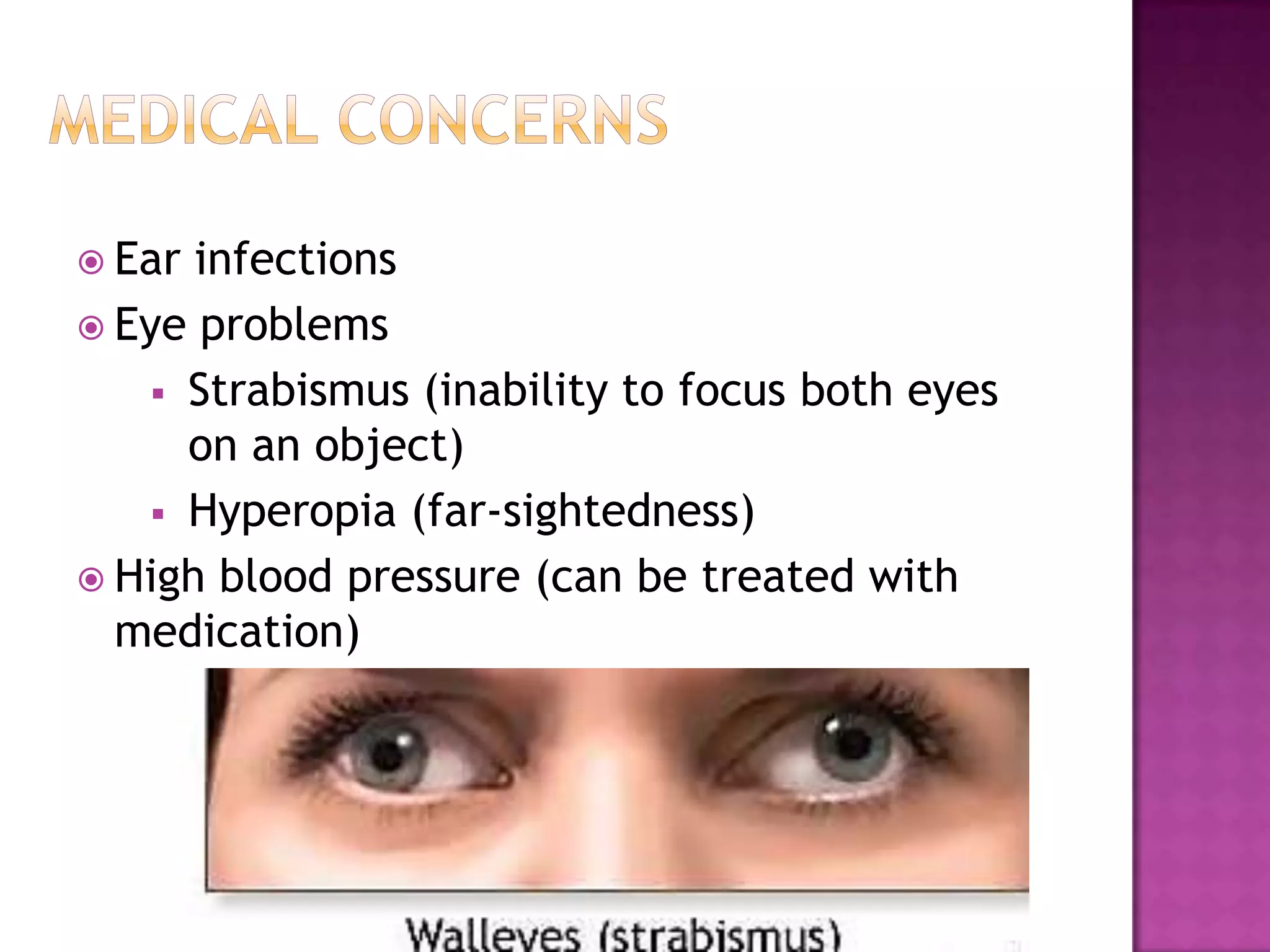
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition caused by a mutation on the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome. This mutation causes the FMR1 gene to produce little to no fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), which is important for neural development. Those with over 200 CGG repeats on the FMR1 gene have the full mutation and typically experience intellectual disabilities and distinctive physical features. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms through therapies and medications that target issues like attention deficits or anxiety. Genetic counseling is recommended for families with a history of the syndrome.