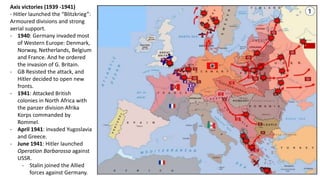
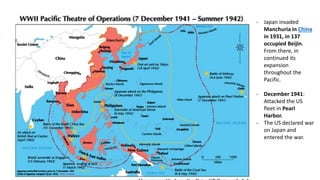
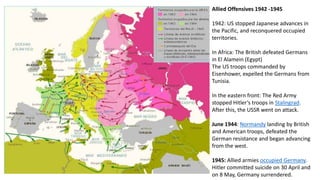
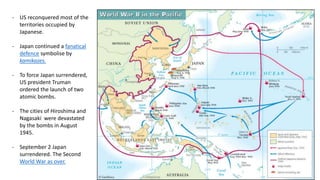
The Second World War was caused by the expansionist policies of totalitarian regimes like Germany, Italy, and Japan. It began in 1939 when Germany invaded Poland. Germany and Italy formed the Rome-Berlin Axis alliance, and Japan later allied with Germany. By 1941, Germany and Italy controlled much of Europe while Japan controlled parts of Asia. The United States entered the war after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Through major Allied offensives from 1942-1945, the Allies regained ground and defeated Germany and Japan. The war resulted in over 50 million deaths and massive destruction and human rights violations. It also led to the division of Europe and start of the Cold War between the Western allies and the Soviet Union.