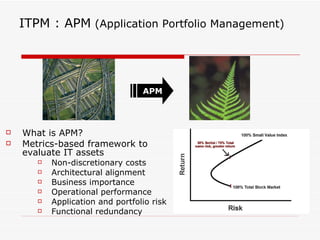
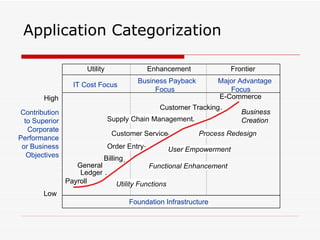
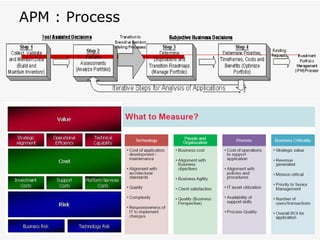
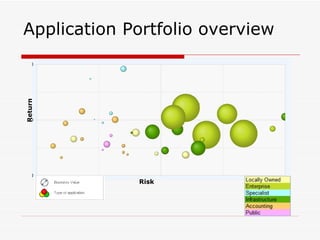
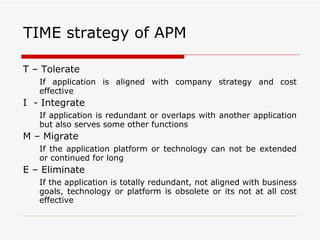
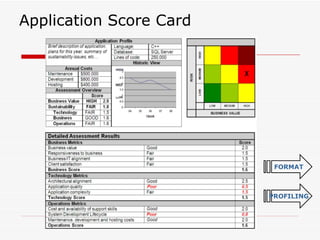
The document discusses consolidating applications to create a library and increase awareness across applications. It outlines advantages like improved portfolio management and resource coordination. It then defines Application Portfolio Management (APM) and the metrics used to evaluate applications. APM involves categorizing applications based on factors like business importance and risk. It presents a TIME strategy for APM - whether to tolerate, integrate, migrate, or eliminate an application. Finally, it mentions using application scorecards to profile applications.