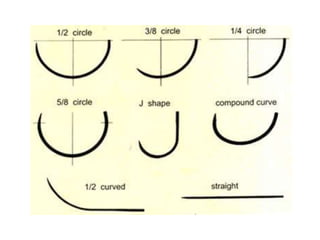
This document provides information about suture training. It discusses suture materials including absorbable materials like surgical catgut and non-absorbable materials like silk. It also covers suture needles, needle holders, and various suture patterns for closing wounds like simple interrupted, simple continuous, and horizontal mattress sutures. Considerations for choosing suture materials include durability, handling ability, and tissue reaction. Suture trainers are described as devices that can be used to simulate skin and practice different suture techniques. References are provided at the end.