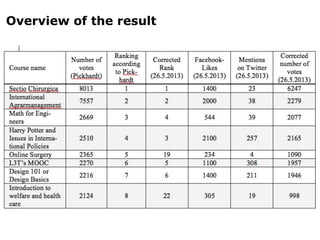
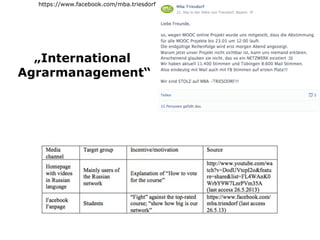
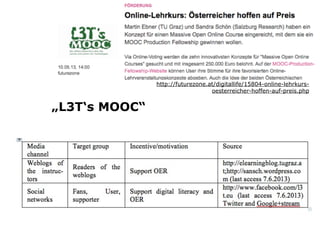
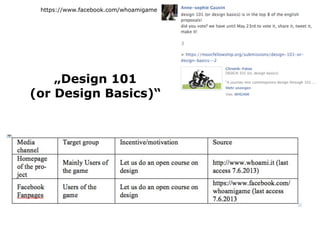
This document summarizes research into a public voting contest held in Germany to award funding for Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs). The researchers analyzed the strategies used by applicants to maximize votes, including harnessing existing online communities and using arguments around open education, topic relevance, and national/institutional pride. They found the top applicants all had large supporting communities before voting began. While the contest intended for the public to decide, the researchers concluded cheating was common and applicants needed to actively campaign within their communities to succeed rather than just waiting for votes.