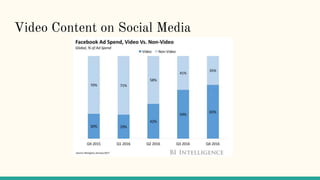
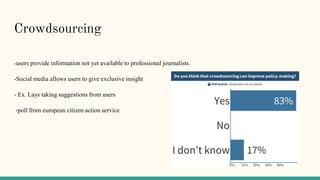
The document discusses how social media has fundamentally changed journalism by allowing easier public and private discussions between journalists, public officials, and the public. It also describes how social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram have helped journalists more easily achieve the five democratic needs of informing, analyzing, investigating, creating public conversation, and encouraging accountability. Additionally, the rise of smartphones and social media has increased the sharing of rich media like videos and photos which can attract advertisers.