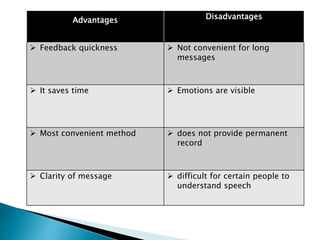
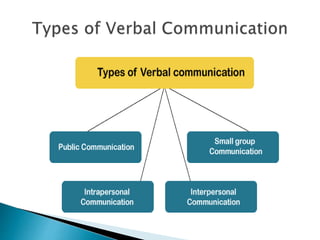
Verbal communication involves expressing views through sound and words. It can be oral, such as discussions or phone calls, or written, as in letters. Advantages of verbal communication include quick feedback, time savings, and clarity, while disadvantages are lack of permanence and difficulty conveying emotions or long messages. Intrapersonal communication is internal and private, involving thoughts, feelings, and decision-making. Interpersonal communication occurs between two or more people through both verbal and nonverbal exchange of information in various contexts like groups, organizations, or different cultures.