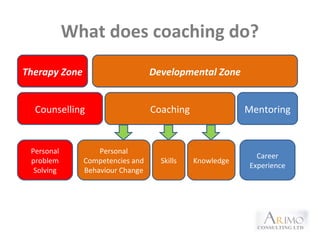
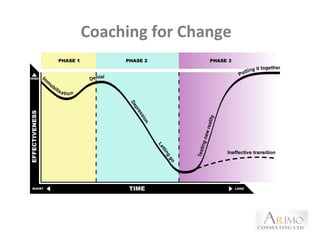
This document outlines an executive coaching program. It discusses that executive coaching involves one-on-one development between a coach and client to set goals and enhance personal and organizational performance. Coaching helps clients become more self-aware through action learning methods. The aims of coaching include skill development, performance improvement, and career development. Coaching is appropriate when there is a steep learning curve, performance is critical, and there are relevant people skills issues. A coach can help by focusing attention, improving self-discipline, validating data, sharing new ideas, and supporting the learning process. The roles of HR, client, boss, and coach in the coaching process are also outlined.