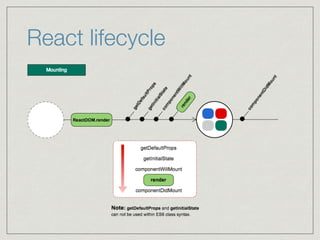
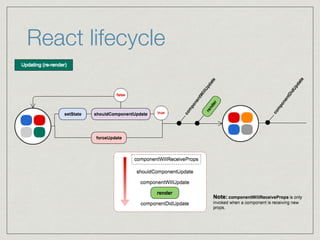
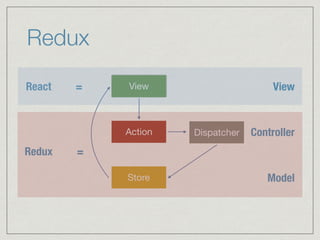
The document discusses React, Redux, and ES6/7 features. It begins with an overview of React lifecycles and class components. It then provides a brief introduction to Redux, including core concepts like actions, reducers, and unidirectional data flow. The document also includes an example to demonstrate how React and Redux can work together, with Redux managing application state in the store and React components interacting via container components.












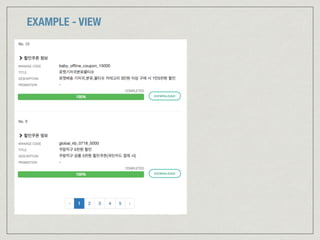
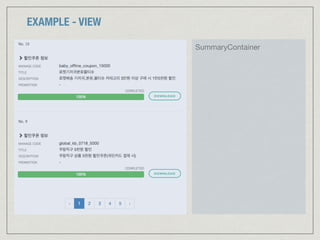
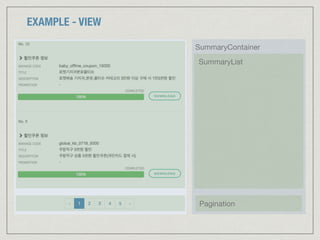
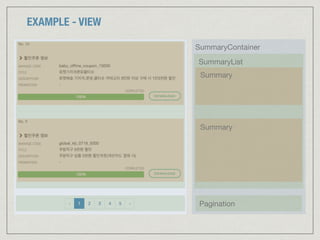
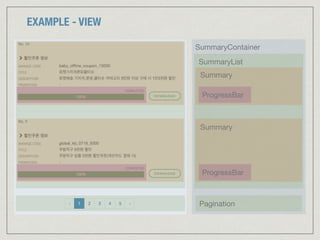
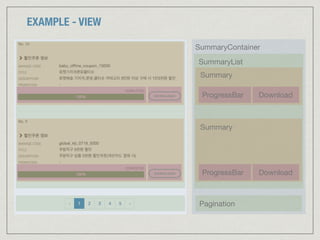
![EXAMPLE - MODEL (APPLICATION STATE)
{
summaries: [
{
id: 10,
manageCode: 'baby_offline_coupon_15000',
title: '로켓배송기저귀분유물티슈',
description: '로켓배송 기저귀,분유,물티슈 카테고리 3만원 이상 구매 시 1만5천원 할인',
progress {
status: 'COMPLETED',
progress: 100
}
},
{ /* ... */ },
],
paging: {
page: 1,
size: 2,
totalPage: 5
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-23-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE - REDUX
export function fetchSummary(params) {
return {
thunk: async(dispatch, getState, { repositories: { summary: repository } }) => {
const { data: summaries } = await repository.getSummaries(params);
const action = { type: 'UPDATE_SUMMARY', payload: summaries };
return dispatch(action);
}
};
}
summaryAction.js
const initialState = {
summaries: []
};
export default function summaryReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'UPDATE_SUMMARY':
return {
...state,
summaries: action.payload.contents
}
}
}
summaryReducer.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-24-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE - REDUX
export function fetchSummary(params) {
return {
thunk: async(dispatch, getState, { repositories: { summary: repository } }) => {
const { data: summaries } = await repository.getSummaries(params);
const action = { type: 'UPDATE_SUMMARY', payload: summaries };
return dispatch(action);
}
};
}
summaryAction.js
const initialState = {
summaries: []
};
export default function summaryReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'UPDATE_SUMMARY':
return {
...state,
summaries: action.payload.contents
}
}
}
summaryReducer.js
import { combineReducers, createStore } from 'redux';
import summaryReducer from './summaryReducer';
import paginationReducer from './paginationReducer';
import otherReducer from './otherReducer';
const reducer = combineReducers({
summary: summaryReducer,
pagination: paginationReducer,
other: otherReducer
});
const store = createStore(reducer);
store.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-25-320.jpg)
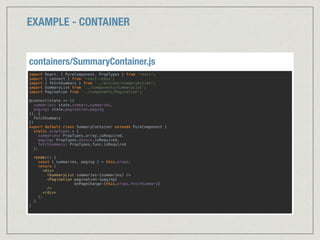
![EXAMPLE - COMPONENT
import React, { PureComponent, PropTypes } from 'react';
import Summary from './Summary';
export default class SummaryList extends PureComponent {
static propTypes = {
summaries: PropTypes.array.isRequired,
fetchSummary: PropTypes.func.isRequired
};
static defaultProps = {
summaries: []
};
render() {
const { summaries } = this.props;
return (
<div>
{ summaries.map(summary => <Summary summary={summary} />) }
</div>
);
}
}
components/SummaryList.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-27-320.jpg)
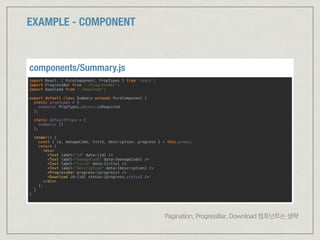

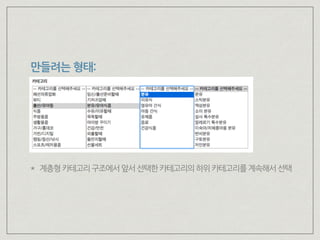
![잘못된 예
export function fetchCategory(code) {
return {
thunk: async(dispatch, getState, { repositories: { category: repository } }) => {
const { data: categories } = await repository.getCategoriesByCode({code});
const action = { type: 'UPDATE_CATEGORY', payload: categories };
return dispatch(action);
}
};
}
categoryAction.js
const initialState = {
categories: []
};
export default function categoryReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'UPDATE_CATEGORY':
return {
...state,
categories: action.payload
}
}
}
categoryReducer.js
[
{ code: 1010, name: ‘패션/의류잡화’ },
{ code: 1011, name: ‘뷰티’ },
{ code: 1012, name: ‘출산/유아동’ },
]
request: { code: 0 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-31-320.jpg)



![REDUCER 개선
categories: [
{ code: 1010, name: ‘패션/의류잡화’ },
{ code: 1011, name: ‘뷰티’ },
{ code: 1012, name: ‘출산/유아동’ },
]
categories: [
[
{ code: 1010, name: ‘패션/의류잡화’, selected: false },
{ code: 1011, name: ‘뷰티’, selected: false },
{ code: 1012, name: ‘출산/유아동’, selected: true },
],
[
{ code: 2010, name: ‘임신/출산준비할때’, selected: false },
{ code: 2011, name: ‘기저귀갈때’, selected: true },
{ code: 2012, name: ‘분유/유아식품’, selected: false },
],
[ /* .. */ ]
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-35-320.jpg)
![import { REQUEST_CATEGORIES, RECEIVE_CATEGORIES } from '../actions/categoryAction';
const initialState = {
categories: []
};
export default function reducer(state = initialState, { type, request, payload }) {
switch (type) {
case REQUEST_CATEGORIES:
return {
...state,
isFetching: true
};
case RECEIVE_CATEGORIES:
const { depth, code } = request;
const categories = state.categories.slice(0, depth);
if (depth > 0) {
categories[depth - 1] = categories[depth - 1].map(o => ({
code: o.code,
name: o.name,
selected: `${o.code}` === `${code}`
}));
}
return {
...state,
categories: [...categories, payload],
isFetching: false
};
default:
return state;
}
}
categoryReducer.js
REDUCER 개선](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-36-320.jpg)
![const prefix = 'CATEGORY/';
export const REQUEST_CATEGORIES = `${prefix}REQUEST_CATEGORIES`;
export const RECEIVE_CATEGORIES = `${prefix}RECEIVE_CATEGORIES`;
export function fetchCategory(depth = 0, code = 0) {
return {
thunk: async(dispatch, getState, { repositories: { category: repository } }) => {
dispatch(requestCategory(code));
const having = getState().category.categories;
if (having.length > depth && !code) {
const requestDepth = depth > 1 ? depth - 1 : 0;
const categories = having[requestDepth].map(o => ({ code: o.code, name: o.name }));
const requestCode = requestDepth > 0 ? having[requestDepth - 1].find(o => o.selected).code : 0;
return dispatch(receiveCategory({ depth: requestDepth, code: requestCode }, categories));
}
const { data: categories } = await repository.getCategories(code);
return dispatch(receiveCategory({ depth, code }, categories));
}
};
}
const requestCategory = (params) => ({
type: REQUEST_CATEGORIES
});
const receiveCategory = (request, categories) => ({
type: RECEIVE_CATEGORIES,
request,
payload: categories
});
categoryAction.js
REDUCER 개선](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-37-320.jpg)


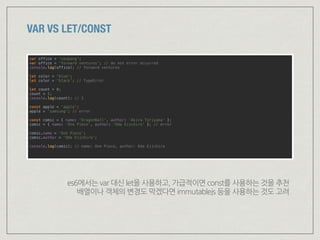
![ARROW FUNCTION
// function
[ 1, 3, 7 ].map(function(value) {
return value * 2;
});
// arrow function
[ 1, 3, 7 ].map(value => value * 2);
// object를 반환하는 arrow function
const toMap = name => {
return { name: name };
};
// object를 반환하는 arrow function 간략 표기
const toMap = name => ({ name: name });
// compare ‘this’ with arrow function and function
const object = {
f1: function() {
console.log('f1', this);
function f1_1() { console.log('f1_1', this) }
setTimeout(f1_1, 1000);
setTimeout(() => { console.log('f1_2', this) }, 1000);
},
f2: () => {
console.log('f2', this);
function f2_1() { console.log('f2_1', this) }
setTimeout(f2_1, 1000);
setTimeout(() => { console.log('f2_2', this) }, 1000);
}
};
object.f1(); // Object, Window, Window
object.f2(); // Window, Window, Window
arrowfunction에서의this는arrowfunction이정의된지점의this값과같다](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-41-320.jpg)
![DEFAULT PARAMETERS
// 파라미터 기본값이 없는 경우
function increase(number) {
if (typeof number === 'undefined') return '[ERROR] number is undefined’;
return number + 1;
}
console.log(increase()); // [ERROR] number is undefined
console.log(increase(undefined)); // [ERROR] number is undefined
console.log(increase(10)); // 11
// 파라미터 기본값을 할당한 경우
function increase(number = 0) {
return number + 1;
}
console.log(increase()); // 1
console.log(increase(undefined)); // 1
console.log(increase(10)); // 11
OBJECT LITERAL : SHORTHAND
// es5
var x = 1;
var y = 2;
var object = {
x: x, y: y
};
// es6
const x = 1;
const x = 2;
const object = { x, y };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-42-320.jpg)
![SPREAD SYNTAX
// spread syntax
function myFunction(x, y, z) {
console.log(`x: ${x}, y: ${y}, z: ${z}`);
}
const args1 = [ 1, 3, 5 ];
const args2 = [ 'foo', 'bar' ];
myFunction(...args1); // x: 1, y: 3, z: 5
myFunction(...args2); // x: foo, y: bar, z: undefuned
// rest parameters
function restSyntax(x, y, z, ...rest) {
console.log(`x: ${x}, y: ${y}, z: ${z}, rest: ${rest}`);
}
restSyntax(...args1); // x: 1, y: 3, z: 5, rest:
restSyntax(...args1, ...args2); // x: 1, y: 3, z: 5, rest: foo, bar
restSyntax(9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1); // x: 9, y: 8, z: 7, rest: 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
// assign
const arr1 = [ 1, 2 ];
const arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6 ];
const arr3 = [ ...arr1, 3, ...arr2 ];
console.log(arr1); // 1, 2
console.log(arr2); // 4, 5, 6
console.log(arr3); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-43-320.jpg)
![DESTRUCTURING ASSIGNMENT : ARRAY
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ];
// assign
const [ first, second ] = arr;
console.log(first); // 1
console.log(second); // 2
// assign with pass some value
const [ first, , , fourth ] = arr;
console.log(first, fourth); // 1, 4
// assign rest
const [ first, second, ...rest ] = arr;
console.log(first, second); // 1, 2
console.log(rest); // [ 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
// assign with default value
const [ x, y = 999 ] = [ 1 ];
console.log(x); // 1
console.log(y); // 999
// nested array
const [ a, [ b ]] = [ 1, [ 2 ]];
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 2
// function
function myFunction([ x, y, z = 999]) {
console.log(`x: ${x}, y: ${y}, z: ${z}`);
}
myFunction([ 1, 2, 3 ]); // x: 1, y: 2, z: 3
myFunction([ 1, 2 ]); // x: 1, y: 2, z: 999
myFunction(undefined); // Error
// function with default value
function myFunctionWithDefault([ x, y, z = 999] = []) {
console.log(`x: ${x}, y: ${y}, z: ${z}`);
}
myFunctionWithDefault(undefined); // x: undefined, y: undefined, z: 999](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-44-320.jpg)
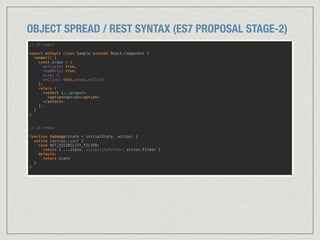

![알아두면 좋을 ES6 문법
Promise
Set / Map
yield / generator
비동기관련하여자주쓰이므로흐름정도는알아두면좋음
new Set([1,2,3]).has(2), new Map({foo:’bar’}).has(‘foo’)
javascript에 대해 좀 더 파고 싶다면. ( #MDN / Ben Nadel's blog )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactreduxes6-2ndmpocop-160908180543/85/React-Redux-and-es6-7-49-320.jpg)







