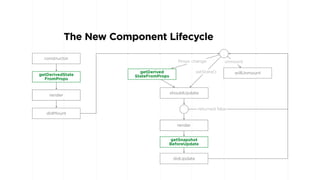
The document is a comprehensive overview of evolving technologies in React, detailing features such as new lifecycle methods, context APIs, error boundaries, and rendering techniques. It also highlights the author's professional background, favorite technologies, and specific coding examples illustrating various React components and practices. Additionally, the document covers advancements in JavaScript, including Babel updates and TypeScript enhancements.






![Render Arrays
import React, { Component }
from 'react';
class Mother extends Component {
render () {
return (
<div>
<span>David</span>
Jovi
<span>Arvid</span>
</div>
);
}
}
import React, { Component }
from 'react';
class Mother extends Component {
render () {
return [
<span key="david">David</span>,
"Jovi",
<span key="arvid">Arvid</span>,
];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2018-05-16evolvingtechnologiesreactbabelwebpack-180517080323/85/2018-05-16-Evolving-Technologies-React-Babel-Webpack-7-320.jpg)
![Render Fragments
import React, { Component }
from 'react';
class Mother extends Component {
render () {
return [
<span key="david">David</span>,
"Jovi",
<span key="arvid">Arvid</span>,
];
}
}
import React, { Component }
from 'react';
class Mother extends Component {
render () {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<span>David</span>
Jovi
<span>Arvid</span>
</React.Fragment>
);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2018-05-16evolvingtechnologiesreactbabelwebpack-180517080323/85/2018-05-16-Evolving-Technologies-React-Babel-Webpack-8-320.jpg)