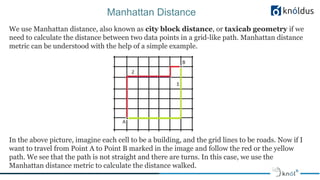
Machine learning is presented by Pranay Rajput. The agenda includes an introduction to machine learning, basics, classification, regression, clustering, distance metrics, and use cases. ML allows computer programs to learn from experience to improve performance on tasks. Supervised learning predicts labels or targets while unsupervised learning finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data. Popular algorithms include classification, regression, and clustering. Classification predicts class labels, regression predicts continuous values, and clustering groups similar data points. Distance metrics like Euclidean, Manhattan, and cosine are used in ML models to measure similarity between data points. Common applications involve recommendation systems, computer vision, natural language processing, and fraud detection. Popular frameworks for ML include scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras