The document summarizes Karsten Dambekalns' presentation on persistence in FLOW3 using Doctrine 2. It discusses [1] how Doctrine 2 is seamlessly integrated and provides object persistence in FLOW3, [2] the basic usage of repositories to perform CRUD operations, and [3] advanced querying capabilities using both the Query Object Mapper and DQL. It also covers modeling associations, schema management through migrations, and checking the migration status.





![Advanced Queries using the QOM
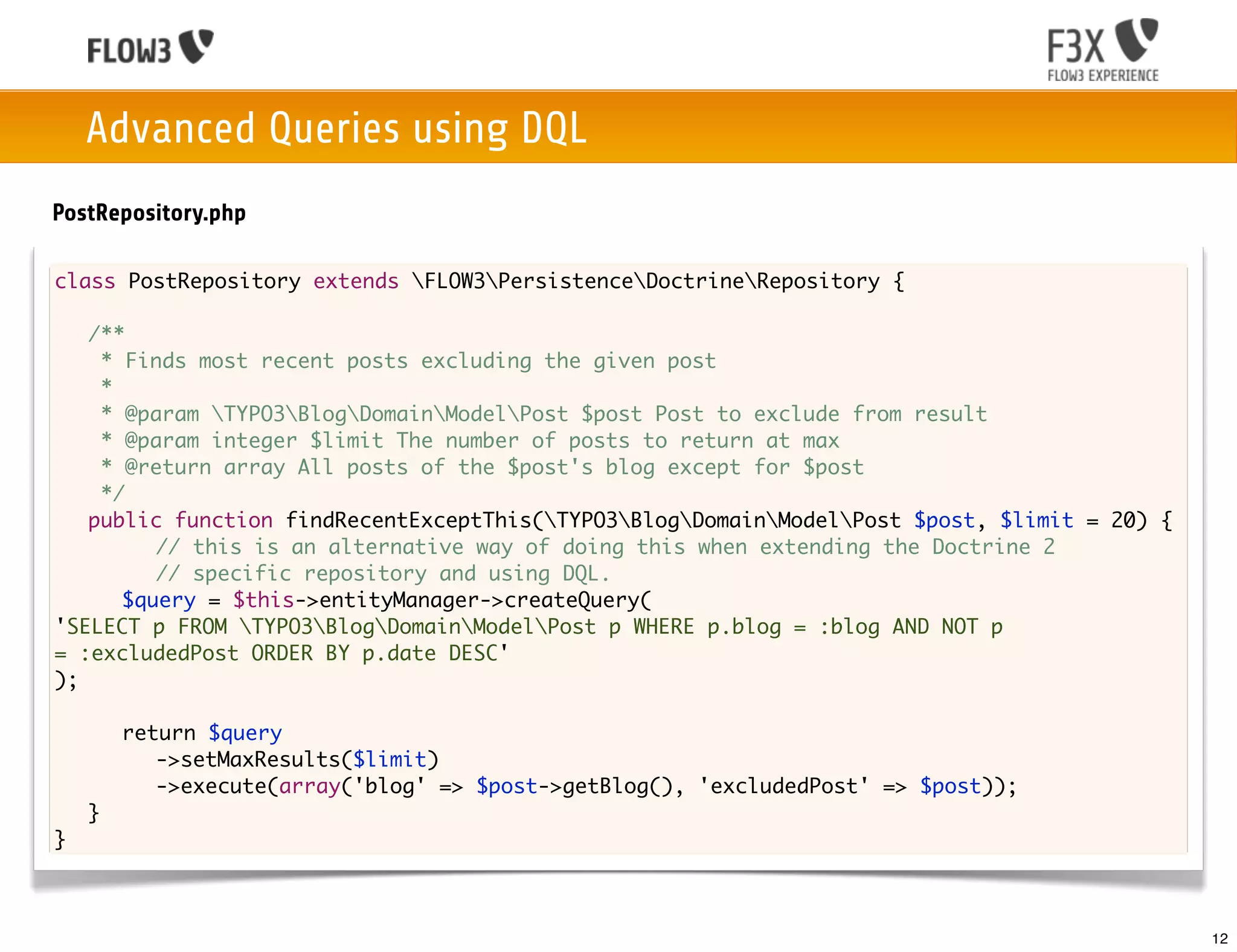
PostRepository.php
class PostRepository extends FLOW3PersistenceRepository {
/**
* Finds most recent posts excluding the given post
*
* @param TYPO3BlogDomainModelPost $post Post to exclude from result
* @param integer $limit The number of posts to return at max
* @return array All posts of the $post's blog except for $post
*/
public function findRecentExceptThis(TYPO3BlogDomainModelPost $post, $limit = 20) {
$query = $this->createQuery();
$posts = $query->matching($query->equals('blog', $post->getBlog()))
->setOrderings(array(
'date' => TYPO3FLOW3PersistenceQueryInterface::ORDER_DESCENDING
))
->setLimit($limit)
->execute()
->toArray();
unset($posts[array_search($post, $posts)]);
return $posts;
}
}
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doctrineinflow3-120401145549-phpapp01/75/Doctrine-in-FLOW3-11-2048.jpg)