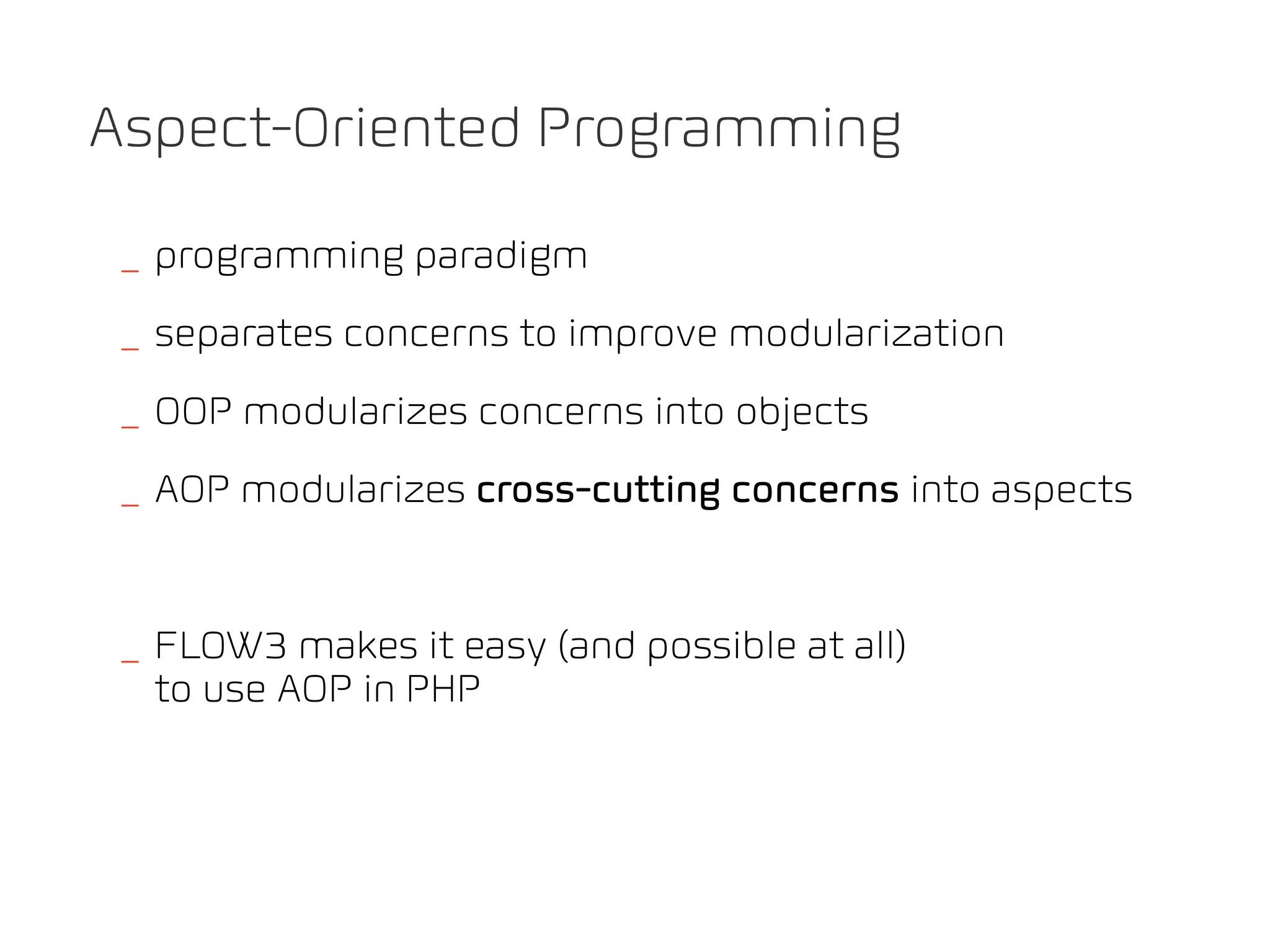
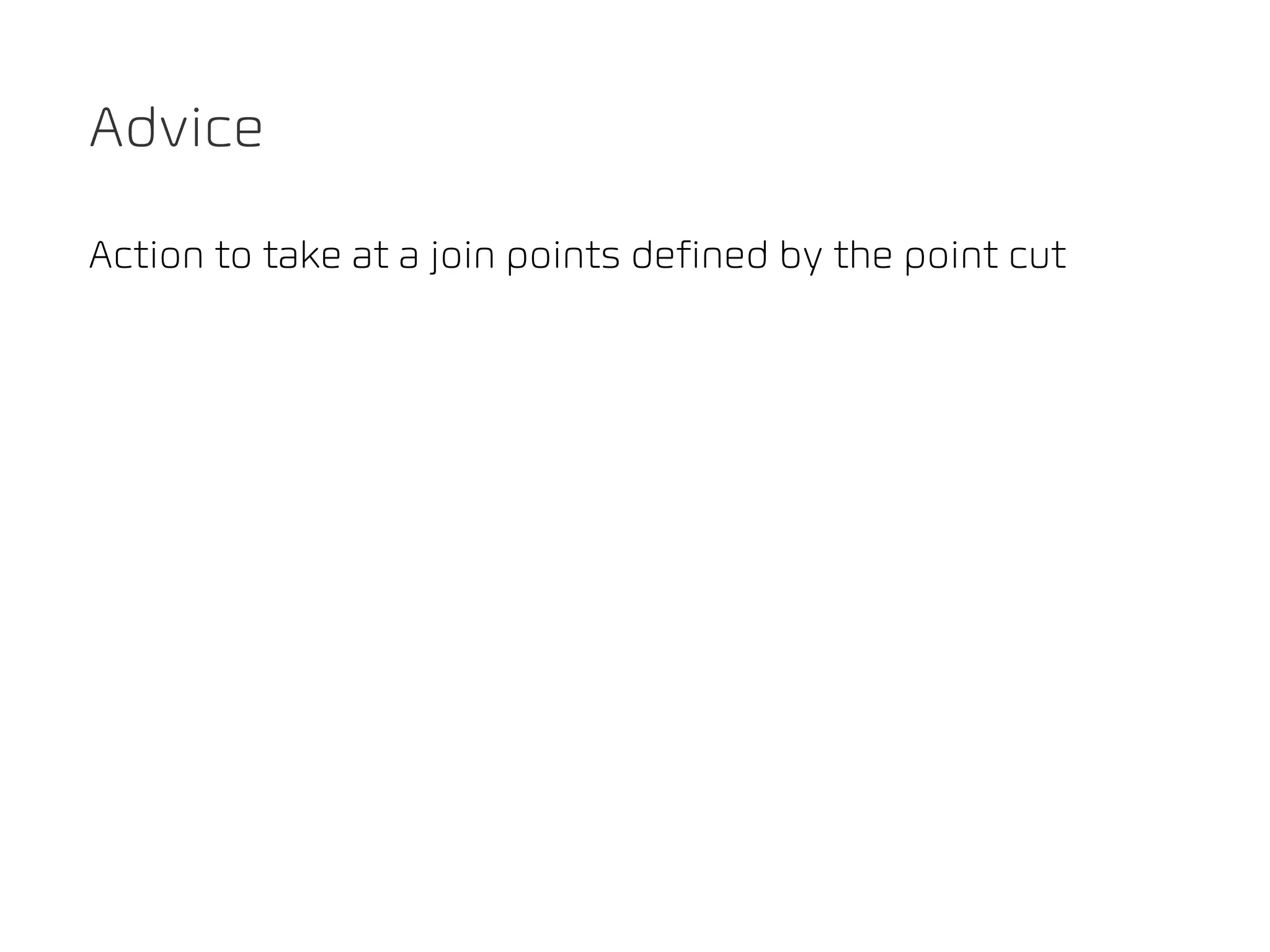
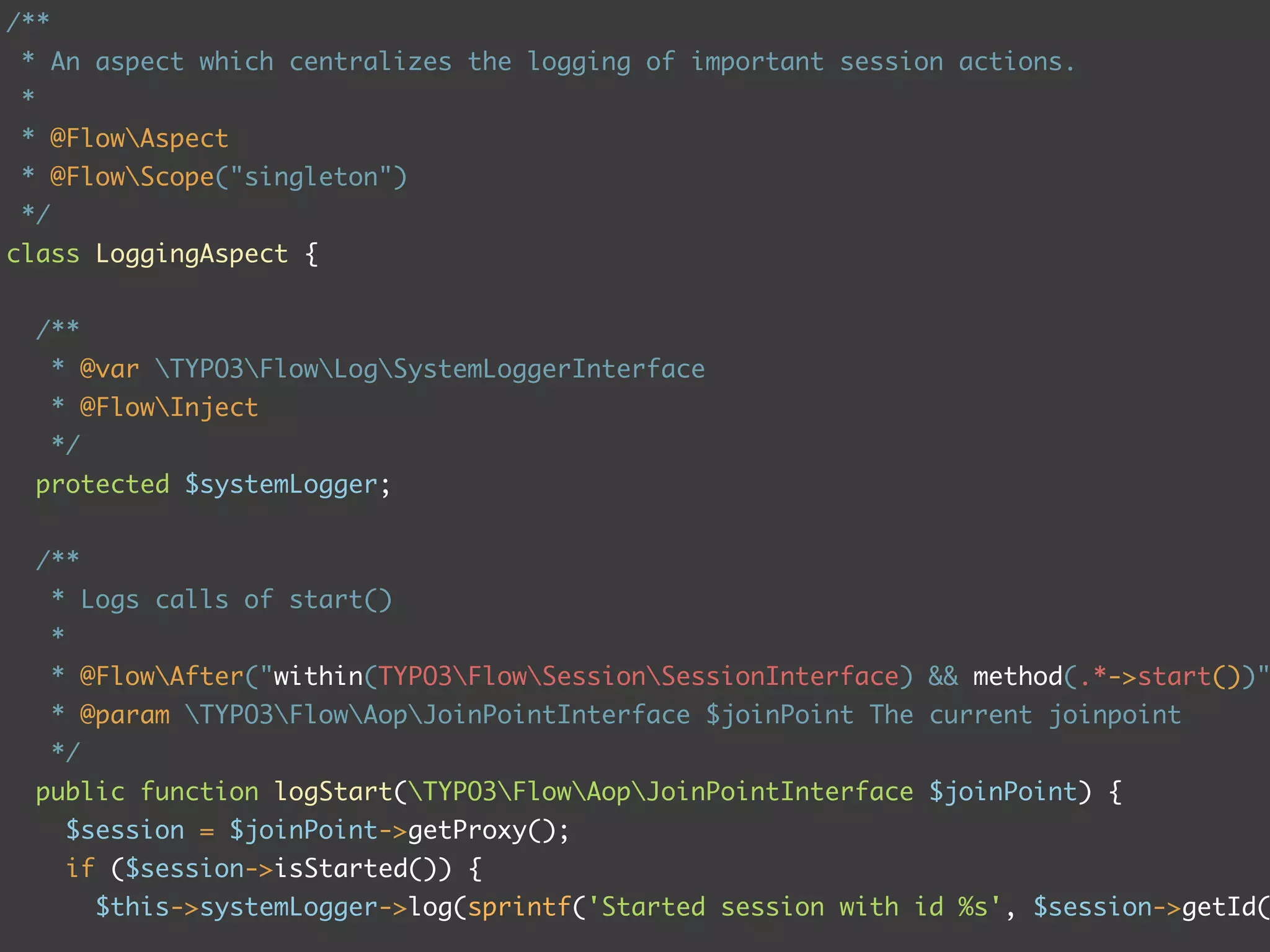
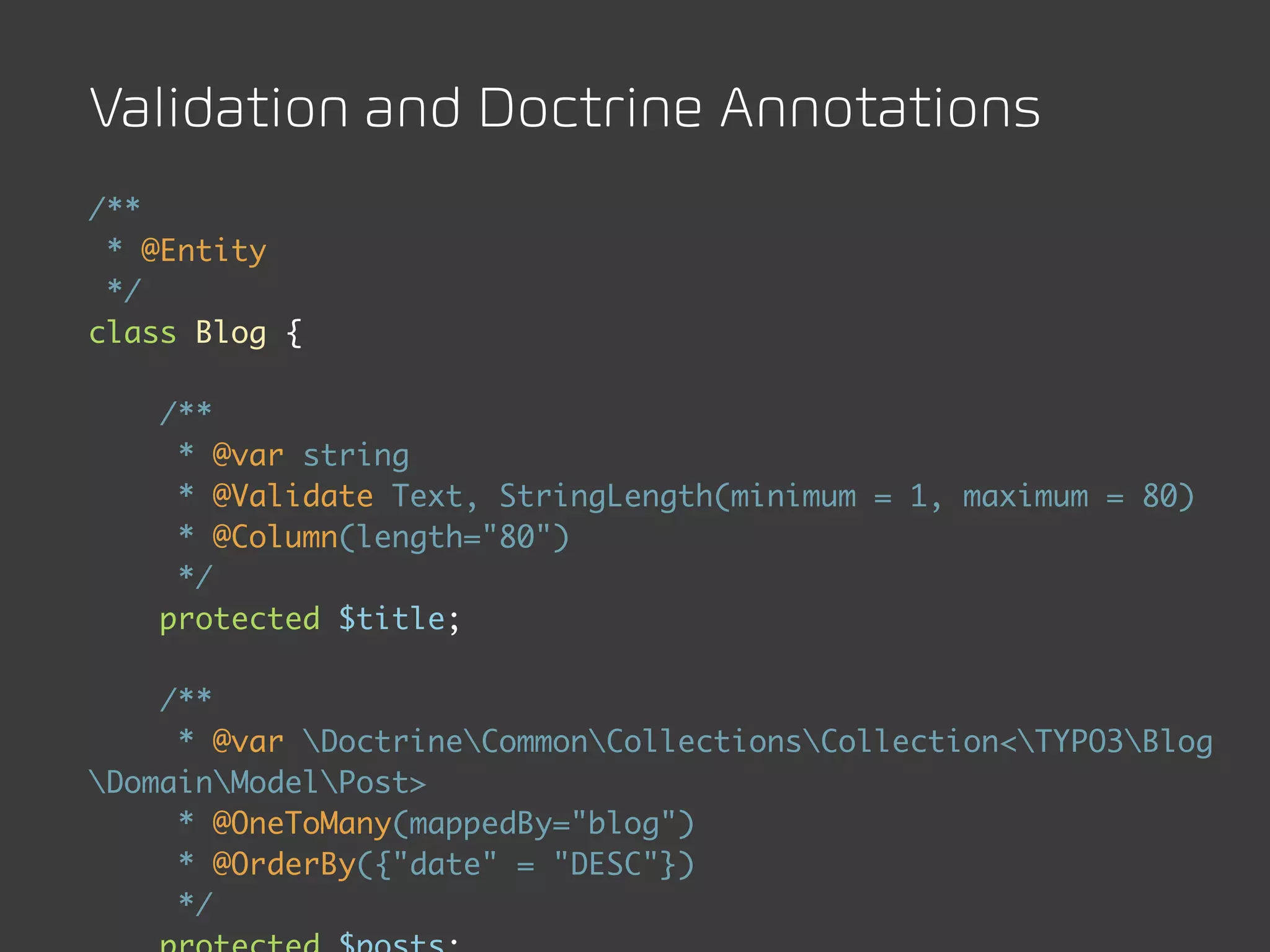
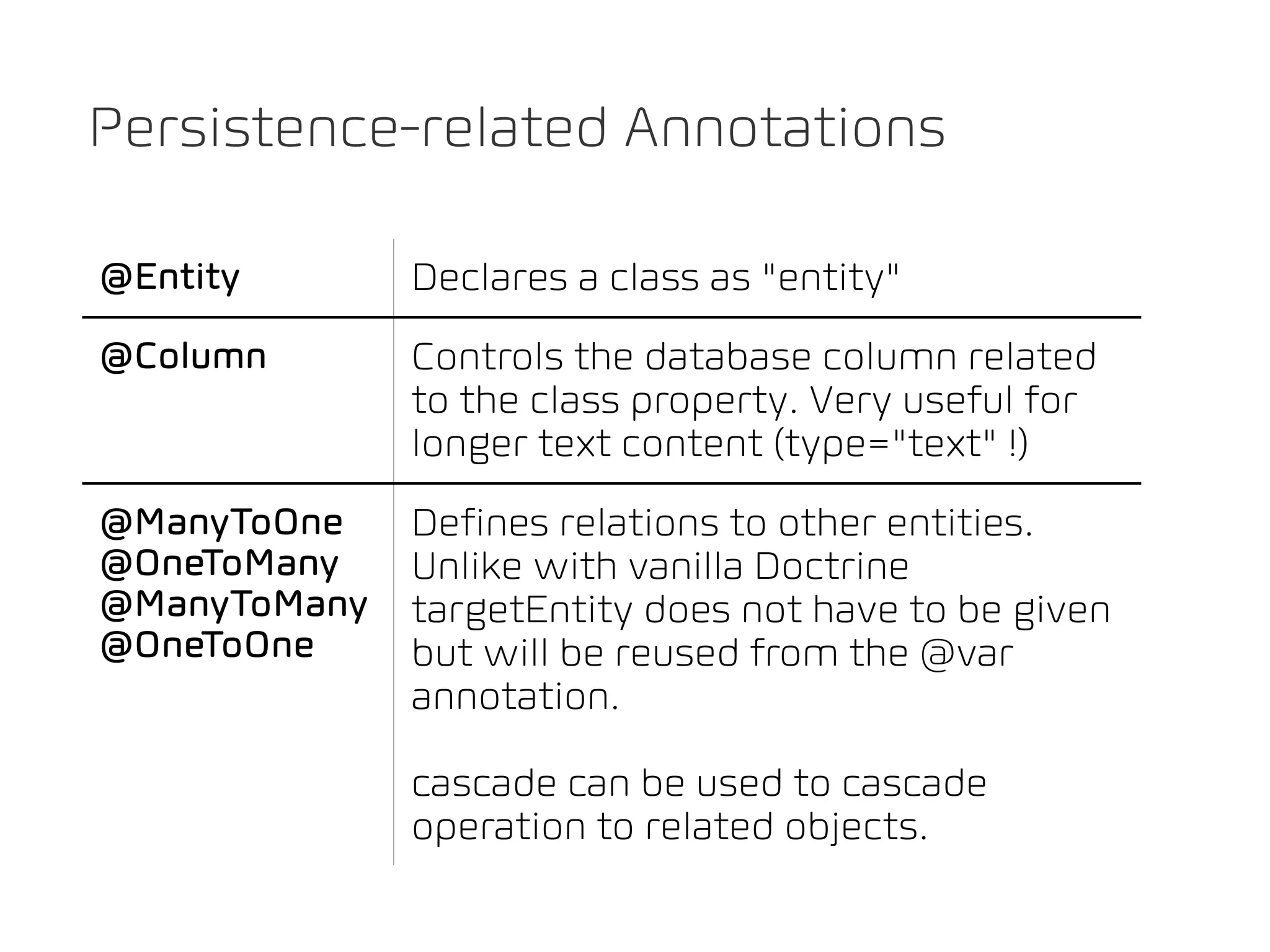
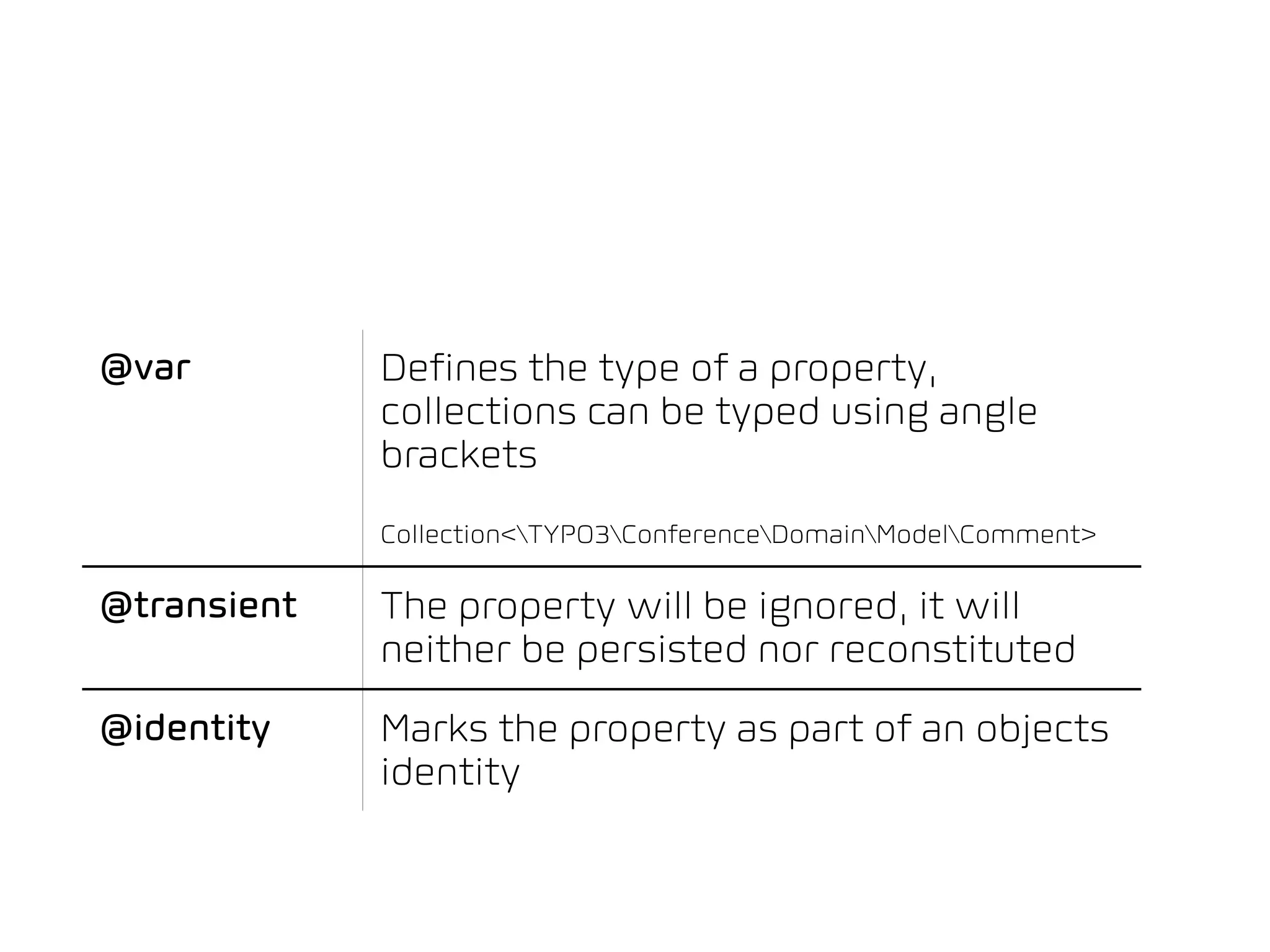
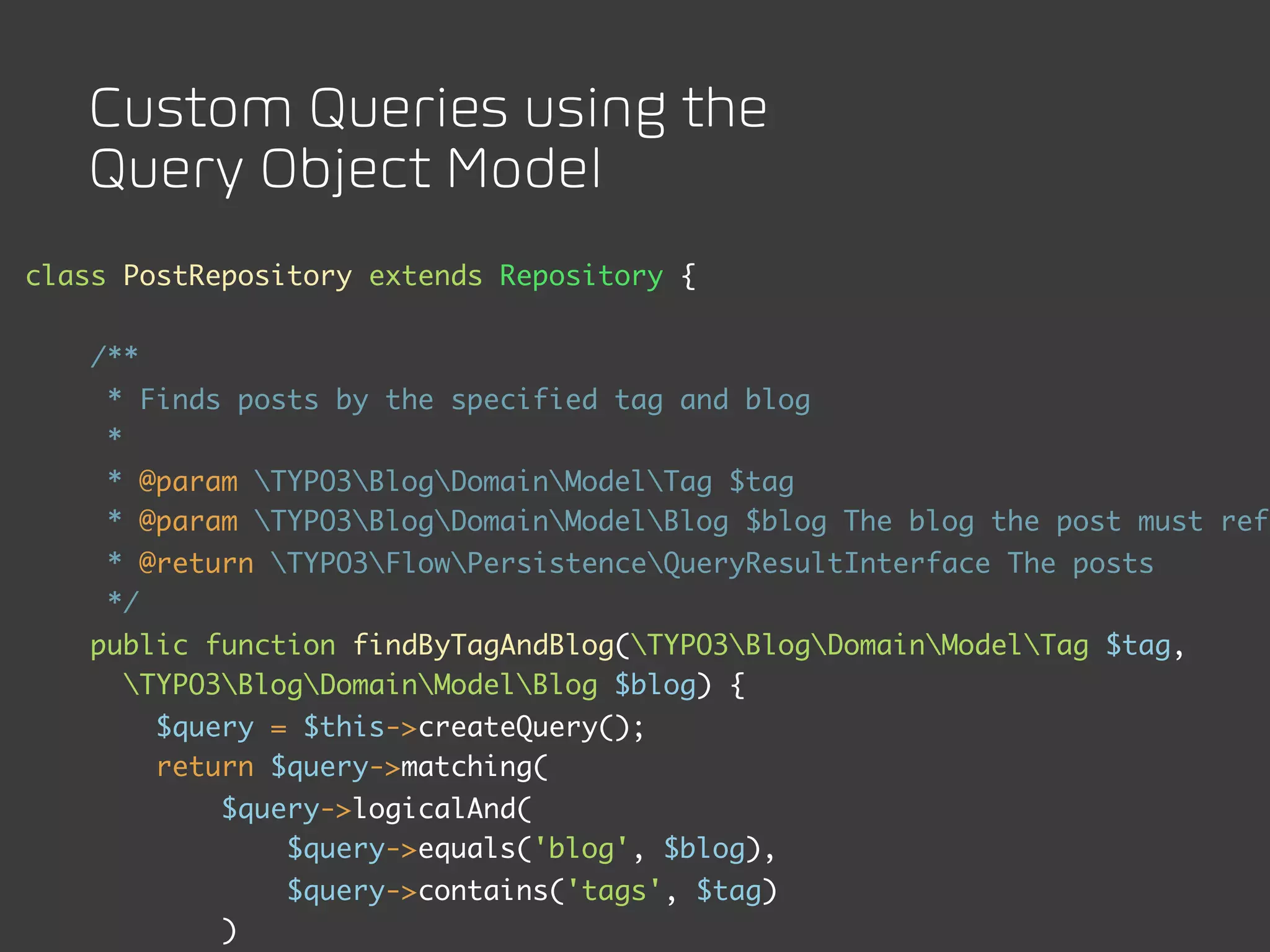
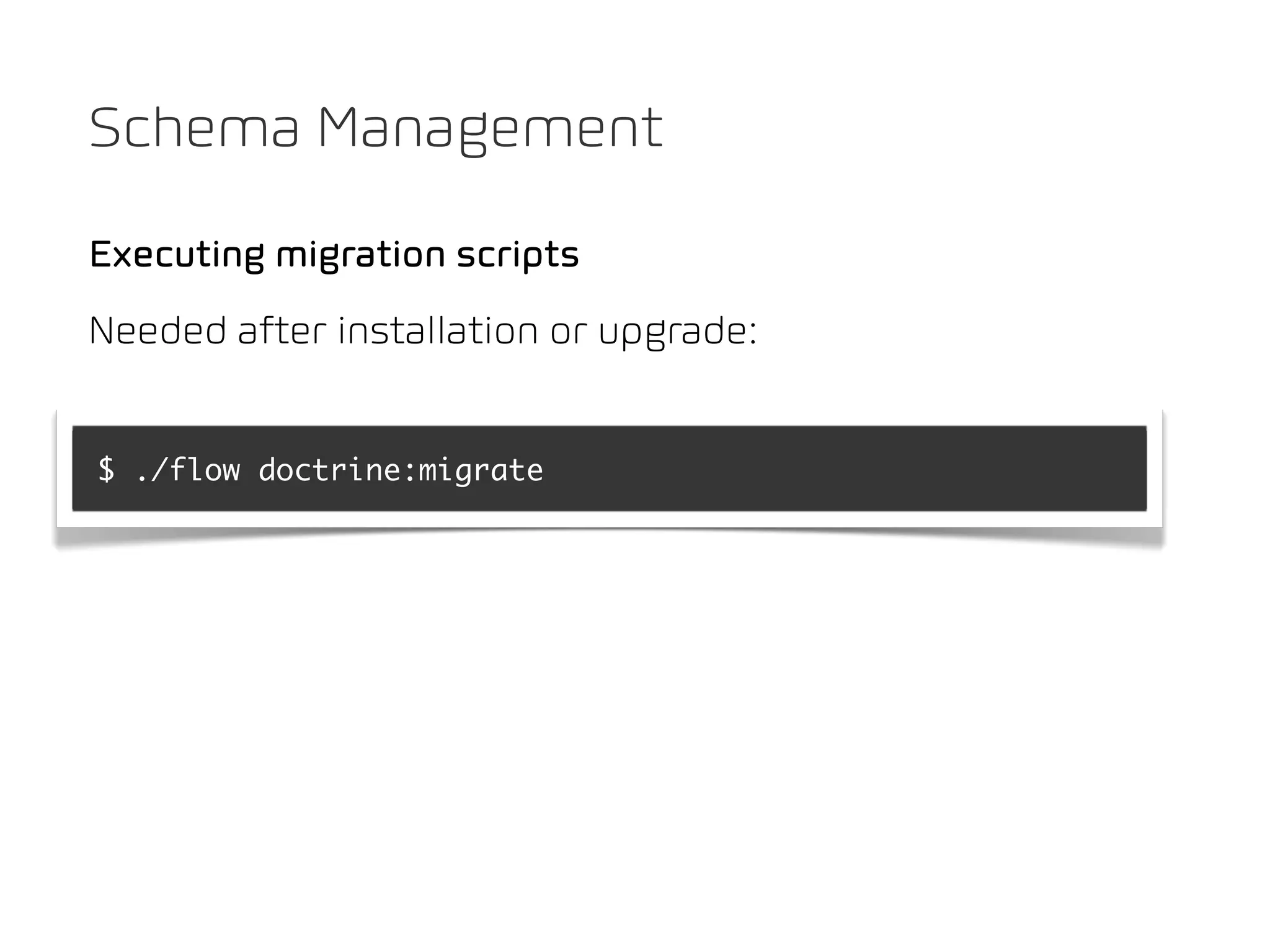
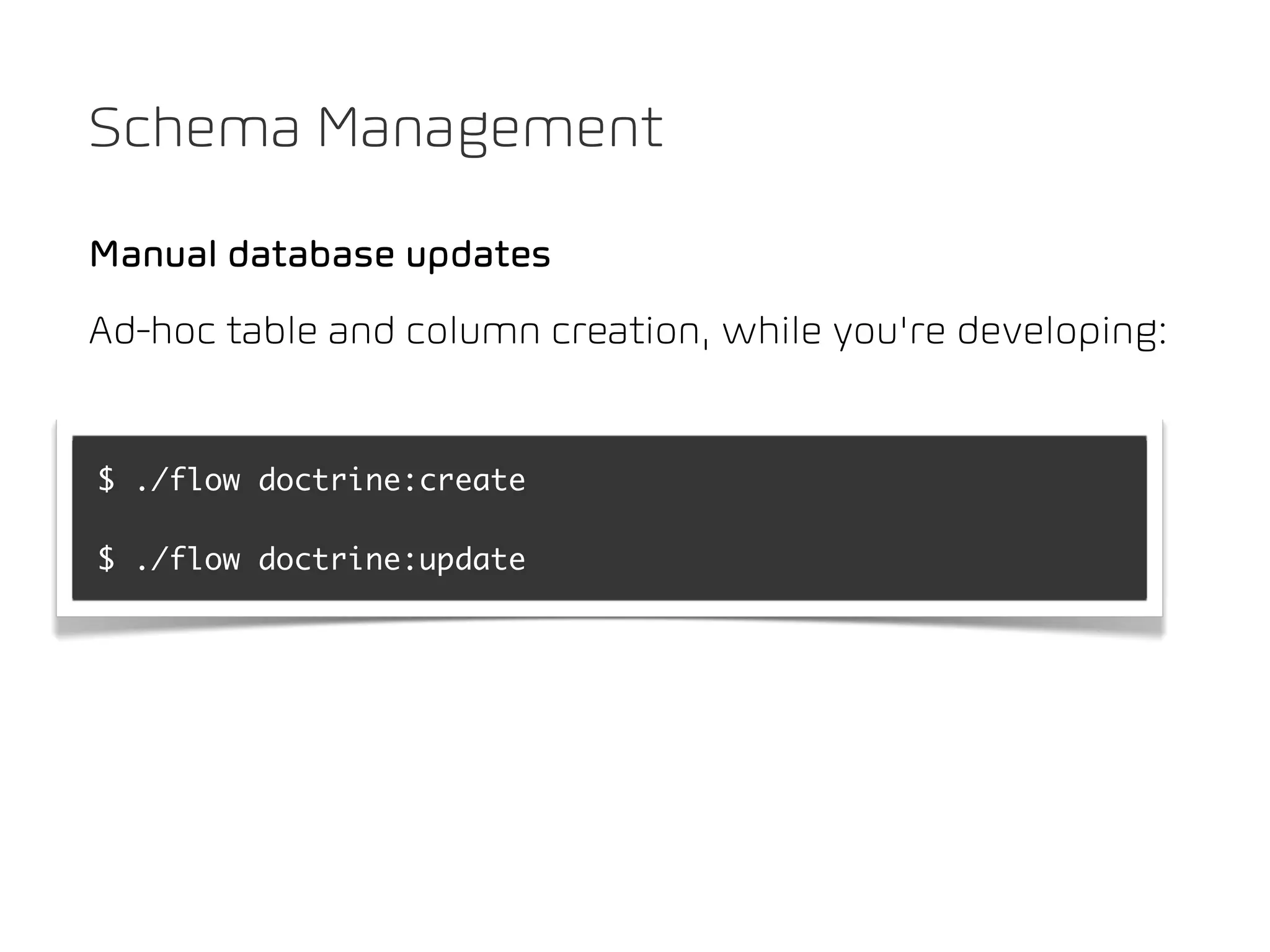
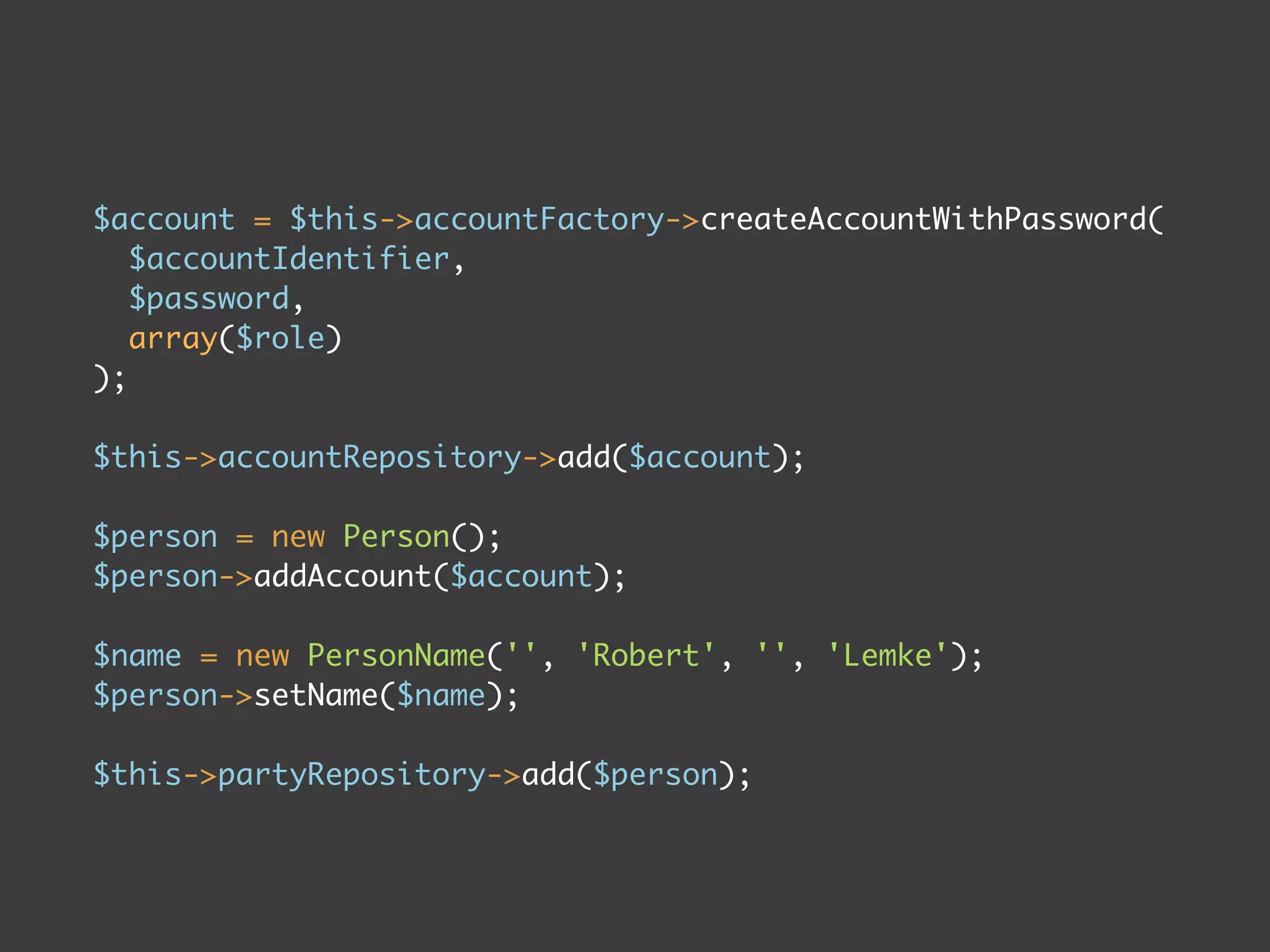
The document discusses TYPO3 Flow and provides instructions for installation, configuration, and various functionalities including setting up database connections and managing file permissions. It also introduces concepts such as dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and security measures, along with examples of creating packages, controllers, and managing entities within the framework. Additionally, it covers advanced topics like schema management and securing against threats like cross-site request forgery.






![Command Line Use
$ ./flow help kickstart:actioncontroller
Kickstart a new action controller
COMMAND:
typo3.kickstart:kickstart:actioncontroller
USAGE:
./flow kickstart:actioncontroller [<options>] <package key> <controller name>
ARGUMENTS:
--package-key The package key of the package for the new controller
with an optional subpackage, (e.g.
"MyCompany.MyPackage/Admin").
--controller-name The name for the new controller. This may also be a
comma separated list of controller names.
OPTIONS:
--generate-actions Also generate index, new, create, edit, update and
delete actions.
--generate-templates Also generate the templates for each action.
--generate-related Also create the mentioned package, related model and
repository if neccessary.
--force Overwrite any existing controller or template code.
Regardless of this flag, the package, model and
repository will never be overwritten.
DESCRIPTION:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typo3flow2-0workshopt3board13-130222120609-phpapp01/75/TYPO3-Flow-2-0-Workshop-T3BOARD13-10-2048.jpg)






![class ServiceLocator {
protected static $services = array();
public function getInstance($name) {
return self::$service[$name];
}
}
class SomeOtherController {
public function action() {
$service = ServiceLocator::getInstance("SomeService");
…
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typo3flow2-0workshopt3board13-130222120609-phpapp01/75/TYPO3-Flow-2-0-Workshop-T3BOARD13-22-2048.jpg)














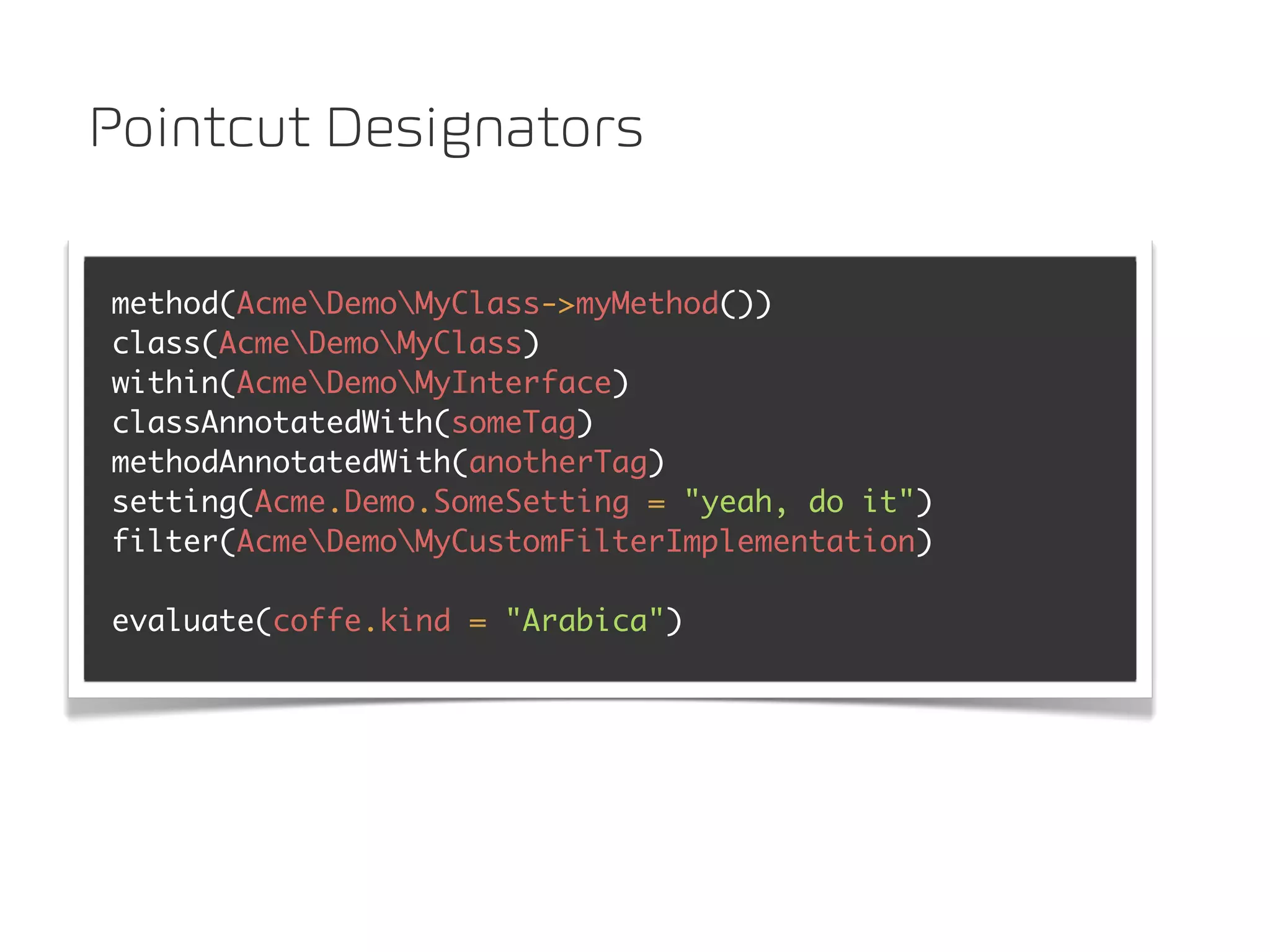








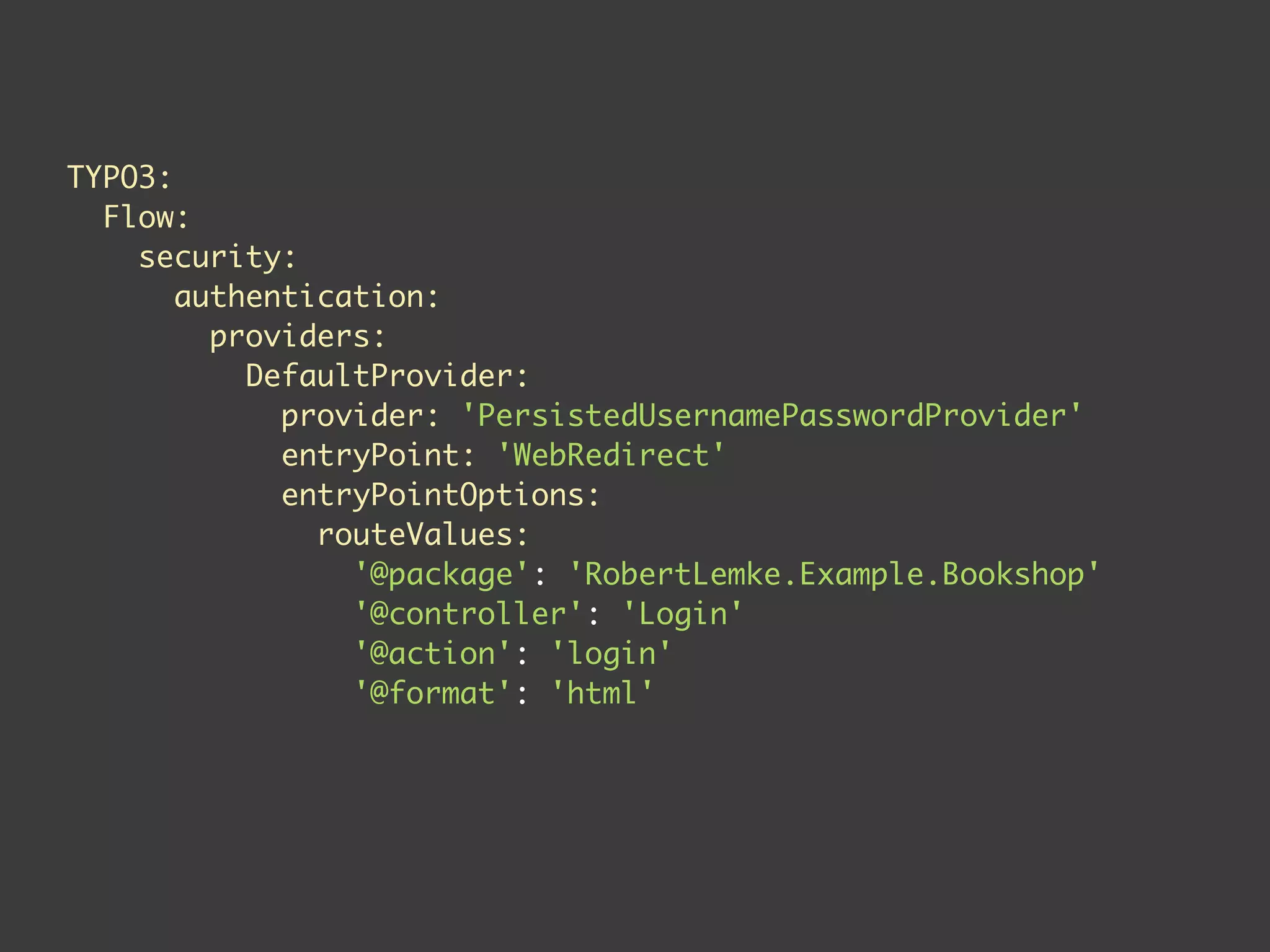

![resources:
methods:
BookManagementMethods: 'method(.*Controller->(new|edit|create|
delete|update)Action())'
BookManagementDelete: 'method(.*BookController->deleteAction())'
roles:
Administrator: []
acls:
methods:
Administrator:
BookManagementMethods: GRANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typo3flow2-0workshopt3board13-130222120609-phpapp01/75/TYPO3-Flow-2-0-Workshop-T3BOARD13-62-2048.jpg)

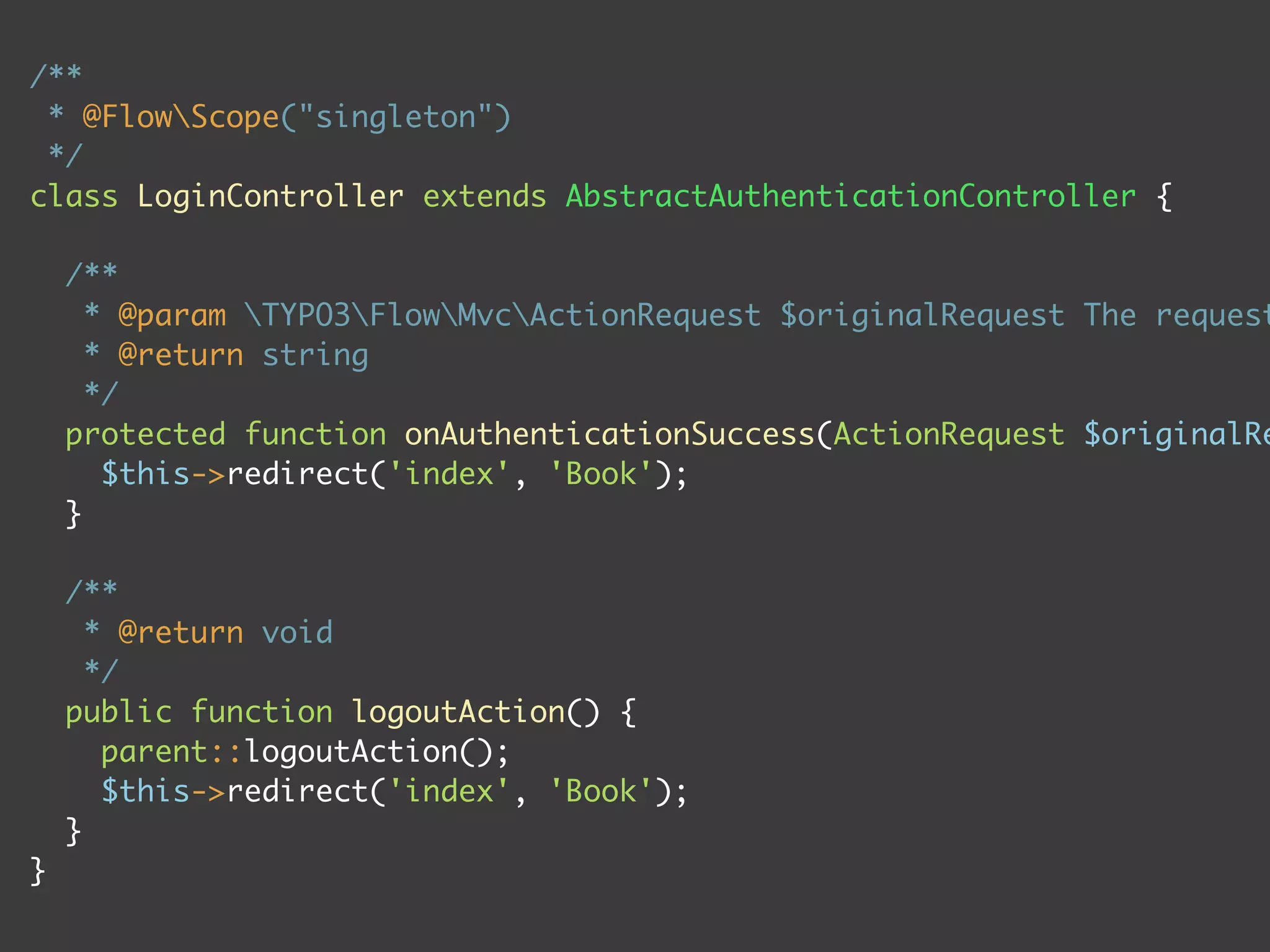
![<f:base/>
<f:flashMessages />
<f:form action="authenticate">
<f:form.textfield name="__authentication[TYPO3][Flow][Security]
[Authentication][Token][UsernamePassword][username]" />
<f:form.password name="__authentication[TYPO3][Flow][Security]
[Authentication][Token][UsernamePassword][password]" />
<f:form.submit value="login" />
</f:form>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typo3flow2-0workshopt3board13-130222120609-phpapp01/75/TYPO3-Flow-2-0-Workshop-T3BOARD13-65-2048.jpg)