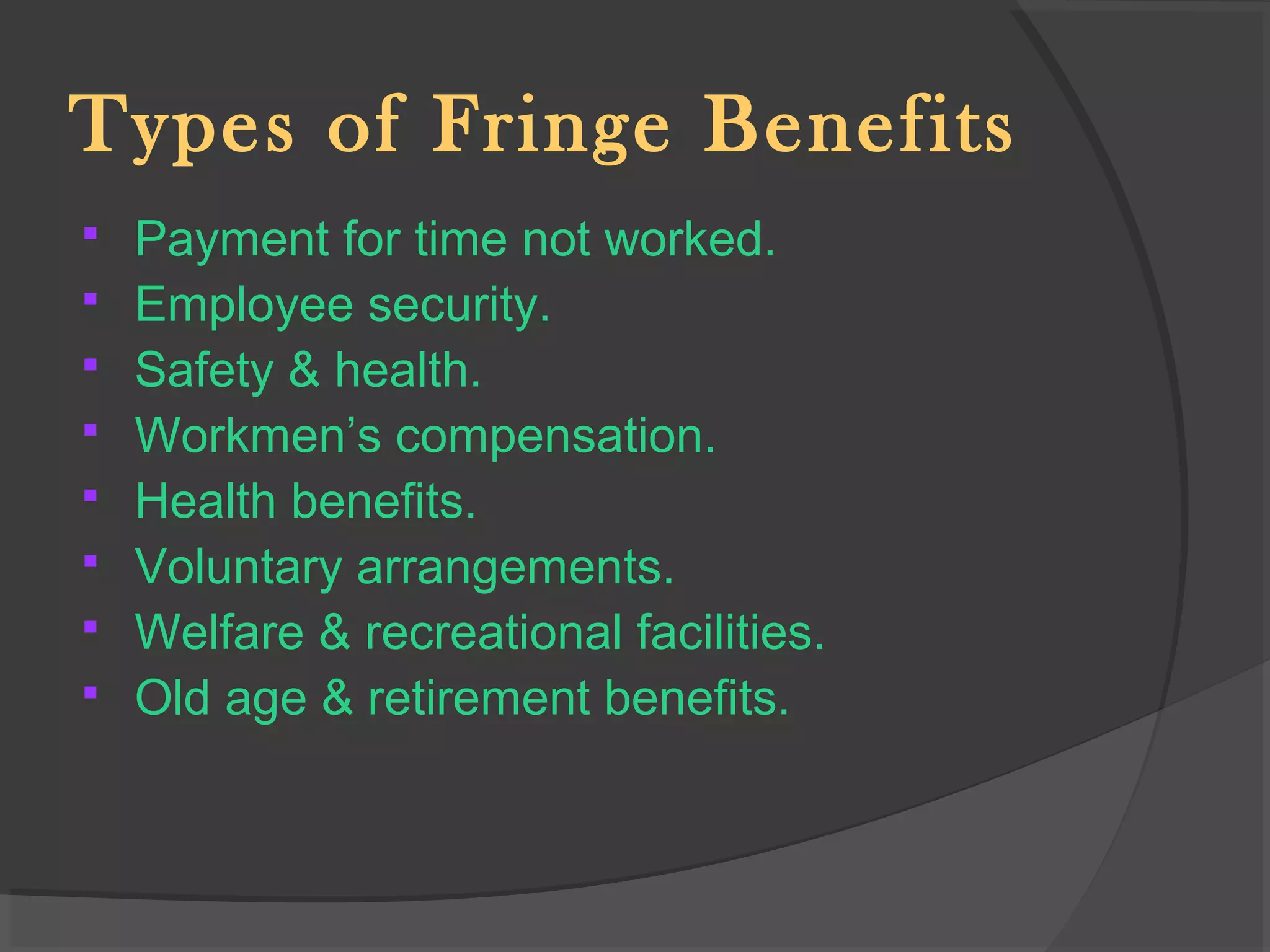
This document defines and discusses fringe benefits provided to employees. It notes that fringe benefits are non-monetary benefits given to employees in addition to their salary, such as a company car or health insurance. The document outlines several examples of fringe benefits and discusses the objectives, needs, importance, principles, types, advantages, and disadvantages of providing fringe benefits to employees.