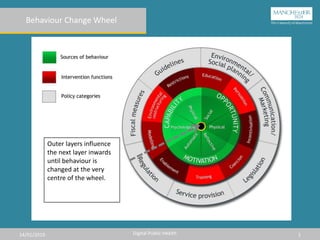
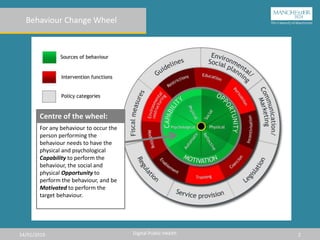
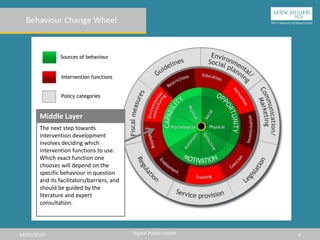
The document describes the Behavior Change Wheel, which is a framework for developing behavior change interventions. It has three layers: the outer layer contains policy categories that can support interventions, the middle layer consists of intervention functions to target specific barriers, and the inner core focuses on the capability, opportunity, and motivation needed for a behavior. An effective intervention must address the relevant precursors like knowledge, skills, or environmental restrictions to influence the target behavior.