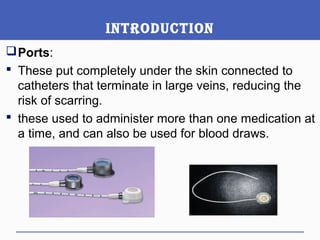
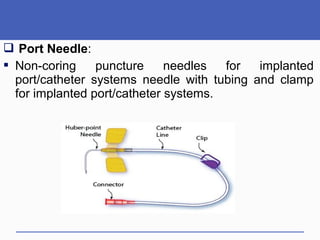
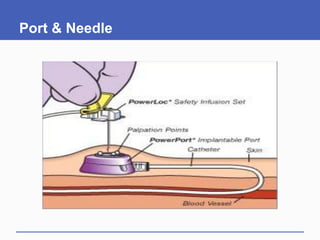
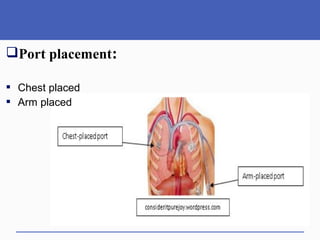
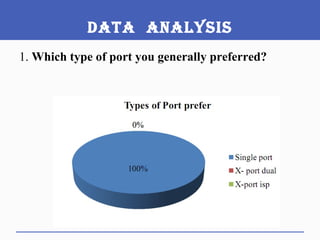
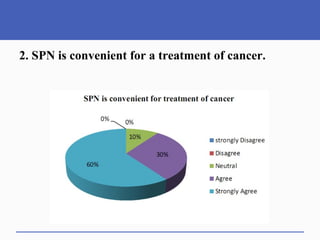
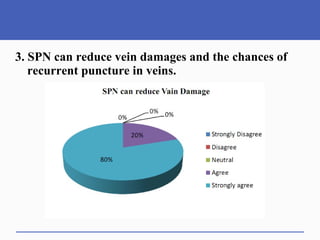
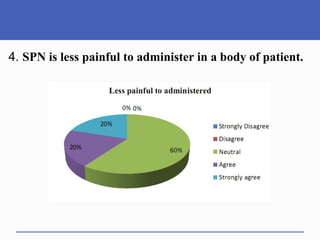
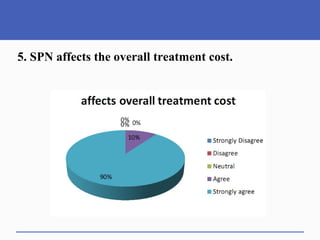
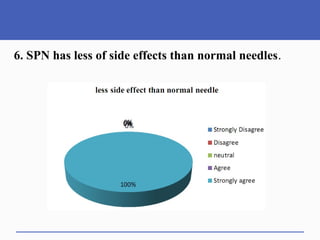
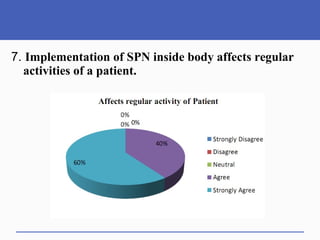
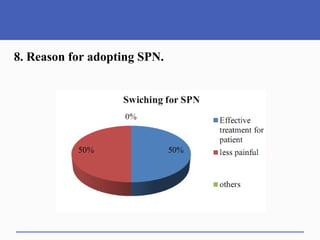
This document presents a study on doctors' perceptions of safety port needles (SPN). A survey was conducted of 50 doctors working in cancer hospitals in Ahmedabad. The results showed that doctors prefer single port needles as they reduce vein damage and recurrent punctures. While SPNs are seen as less painful and having fewer side effects than normal needles, they are also seen as inconvenient and potentially affecting patients' regular activities. However, SPNs are viewed as an effective tool for treating long-term diseases like cancer despite increasing costs.