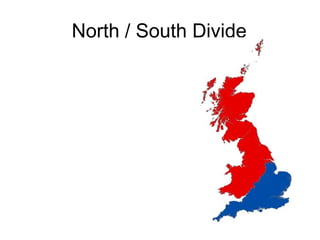
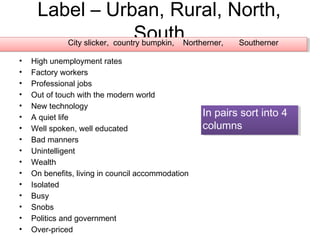
This document discusses regional identity and stereotypes in the United Kingdom. It begins by defining regional identity as being connected to both the country and region one lives in, on a smaller scale than national identity. It then lists common stereotypes associated with different regions of the UK, such as Scots being money-obsessed and drinkers, Welsh people living rurally and being rugby fans, and Northerners being poorer and more working class than Southerners. The document encourages analyzing these stereotypes and considering where they come from and how individuals may subvert them.