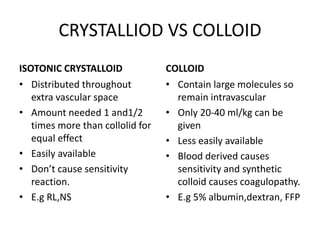
This document defines shock and describes the different types of shock. It discusses:
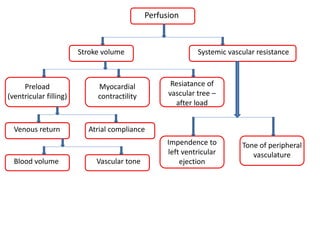
1) Shock is characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion to meet metabolic demand and oxygenation. The main types are hypovolemic, distributive, cardiogenic, and obstructive shock.
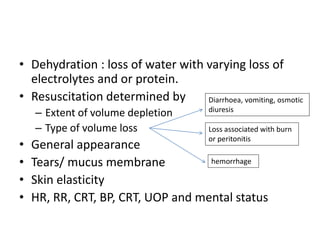
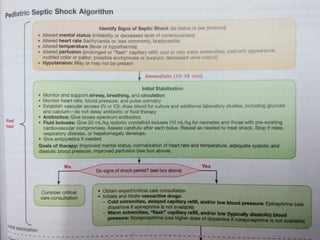
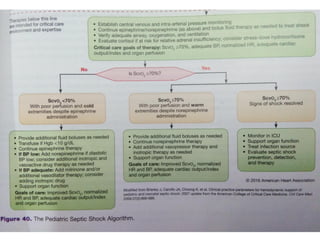
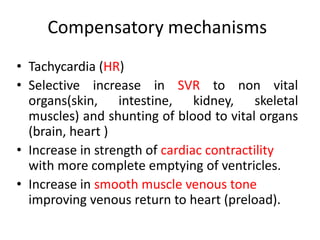
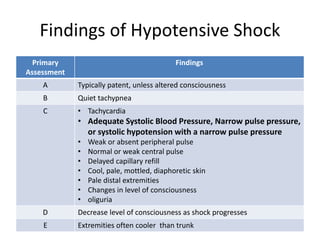
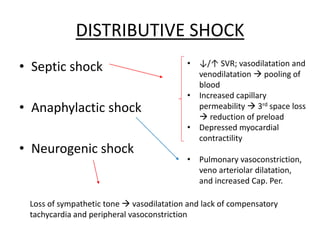
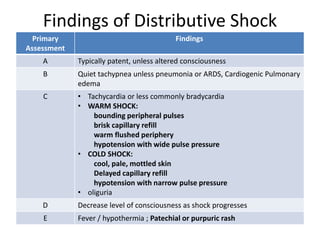
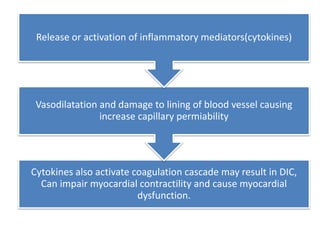
2) Distributive shock includes septic, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock. Signs depend on whether vasodilation or vasoconstriction dominates. Early signs of warm shock are bounding pulses and warm skin while later signs are weak pulses and cool skin.
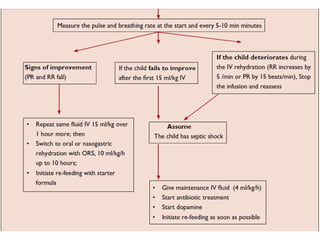
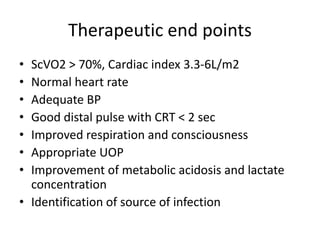
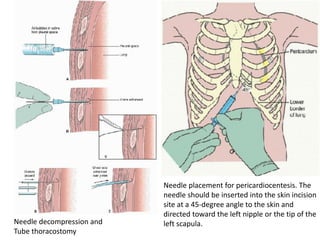
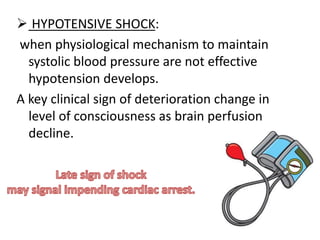
3) Management focuses on optimizing oxygen delivery, improving cardiac output and volume distribution, reducing oxygen demand, and correcting metabolic abnormalities. Positioning



































![Indication of blood transfusion
For replacement of traumatic blood loss if perfusion is inadequate
despite 2-3 bolus of 20ml/kg
• 10ml/kg Packed RBC
– Cross matched
– Type specific
– Type o – ve for female and o [+] or o [-] for male
• Watch for
Hypothermia / myocardial dysfunction/ ionized hypocalcemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock-palsperspective-180413142535/85/Shock-pals-perspective-49-320.jpg)