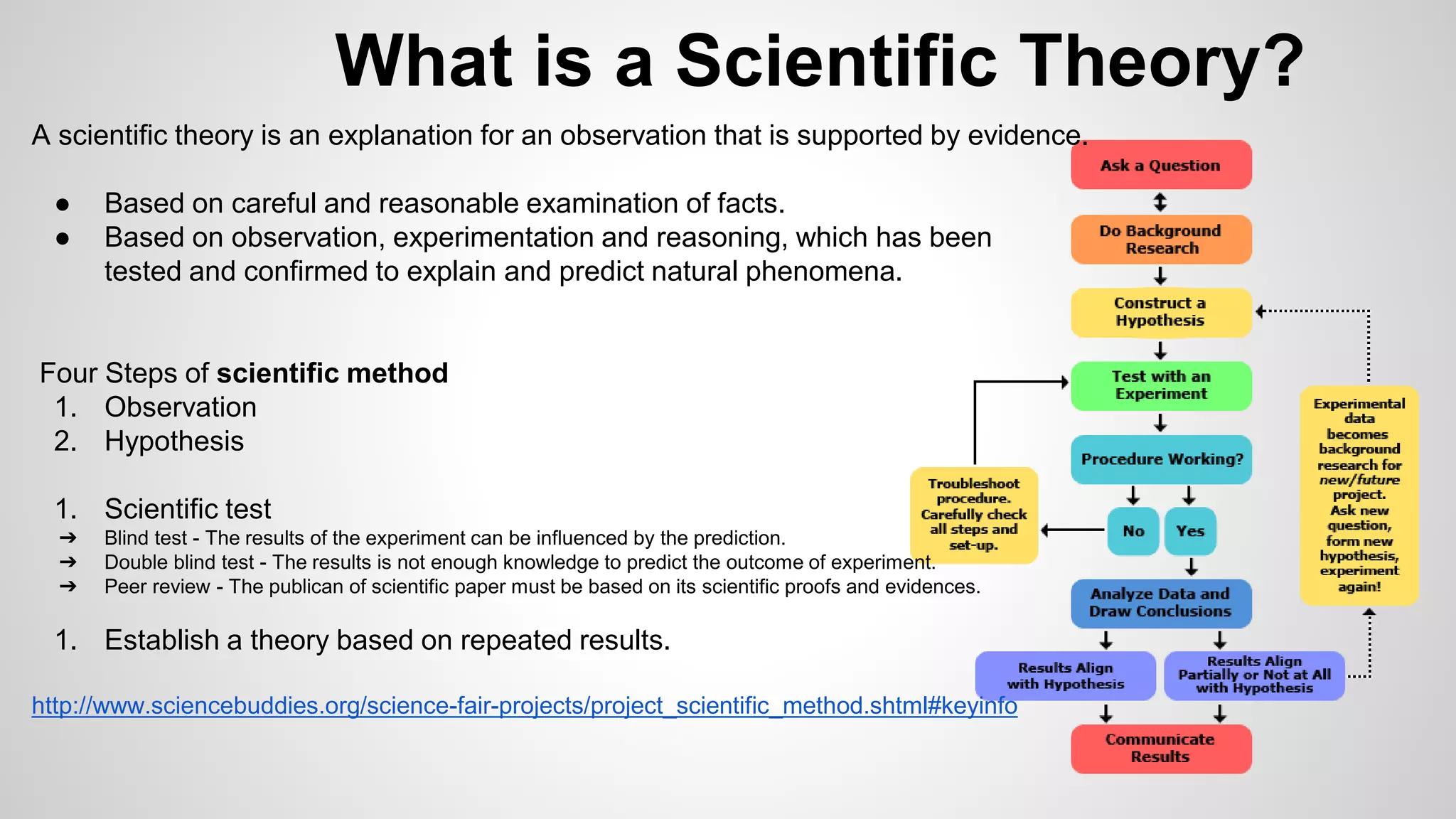
A scientific theory is an explanation for an observation that is supported by evidence obtained through experimentation and testing. The scientific method involves making observations, formulating a hypothesis, conducting experiments to test the hypothesis, and establishing a theory if results are repeatedly confirmed. A key example is the cell theory, which states that all living things are made of cells, cells come from preexisting cells, and they contain DNA. While scientific theories are well-supported, science is an ongoing process, and new evidence can lead to revisions or replacement of existing theories.