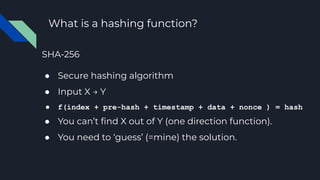
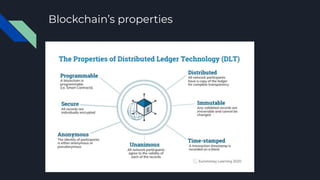
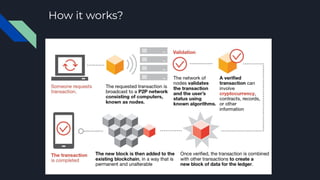
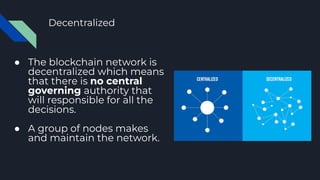
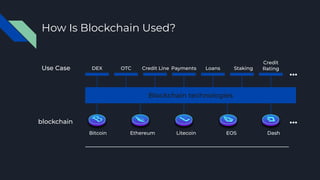
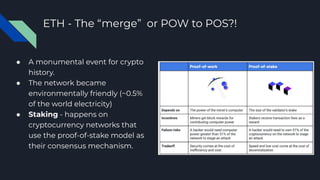
The document explains blockchain technology, emphasizing its properties such as immutability, decentralization, and security, which allow secure and verifiable transactions without a central authority. It outlines the use cases of blockchain in cryptocurrency, banking, and asset transfers, highlighting the growing application of this technology. Additionally, it discusses Ethereum's transition to proof-of-stake to enhance sustainability and reduce its carbon footprint.