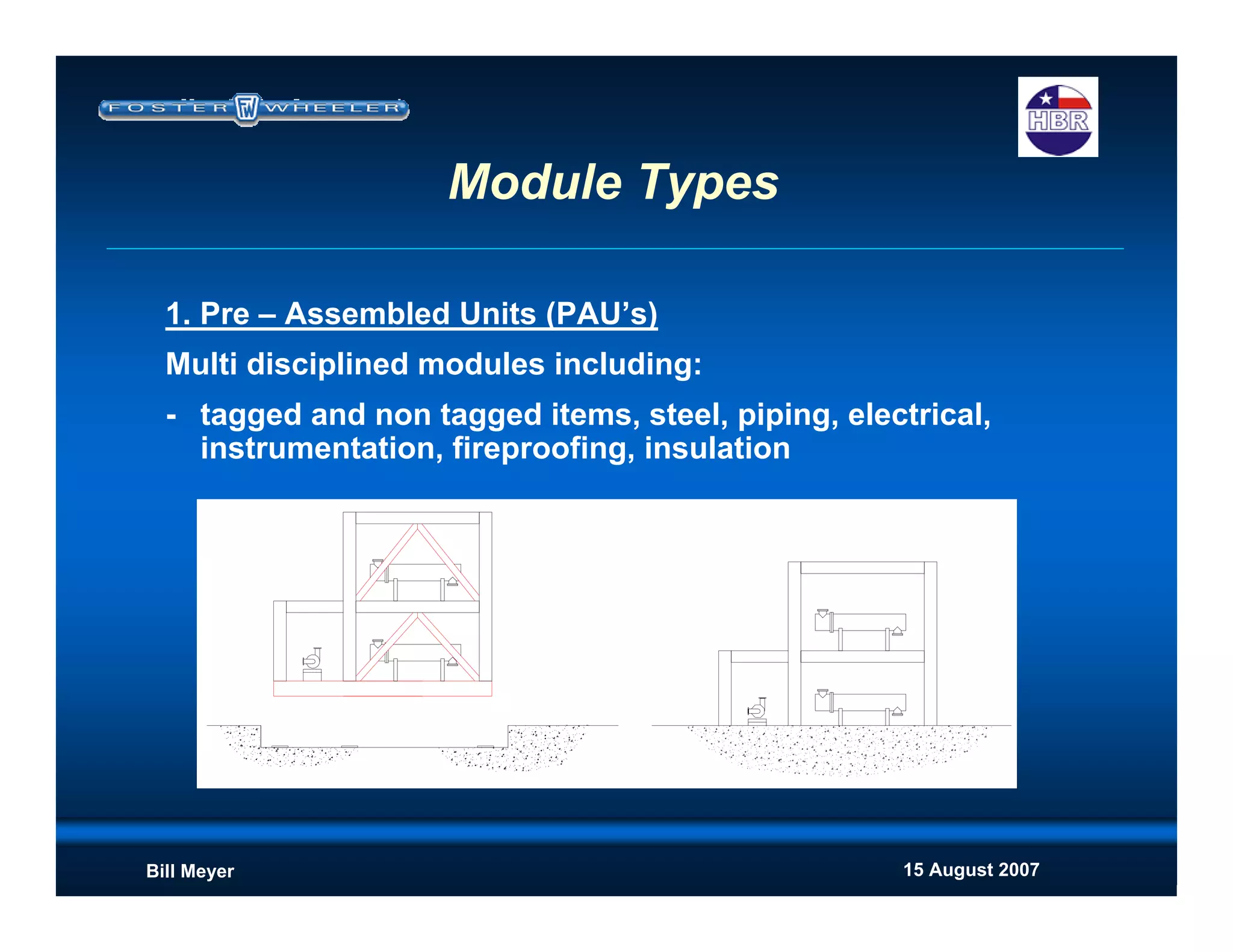
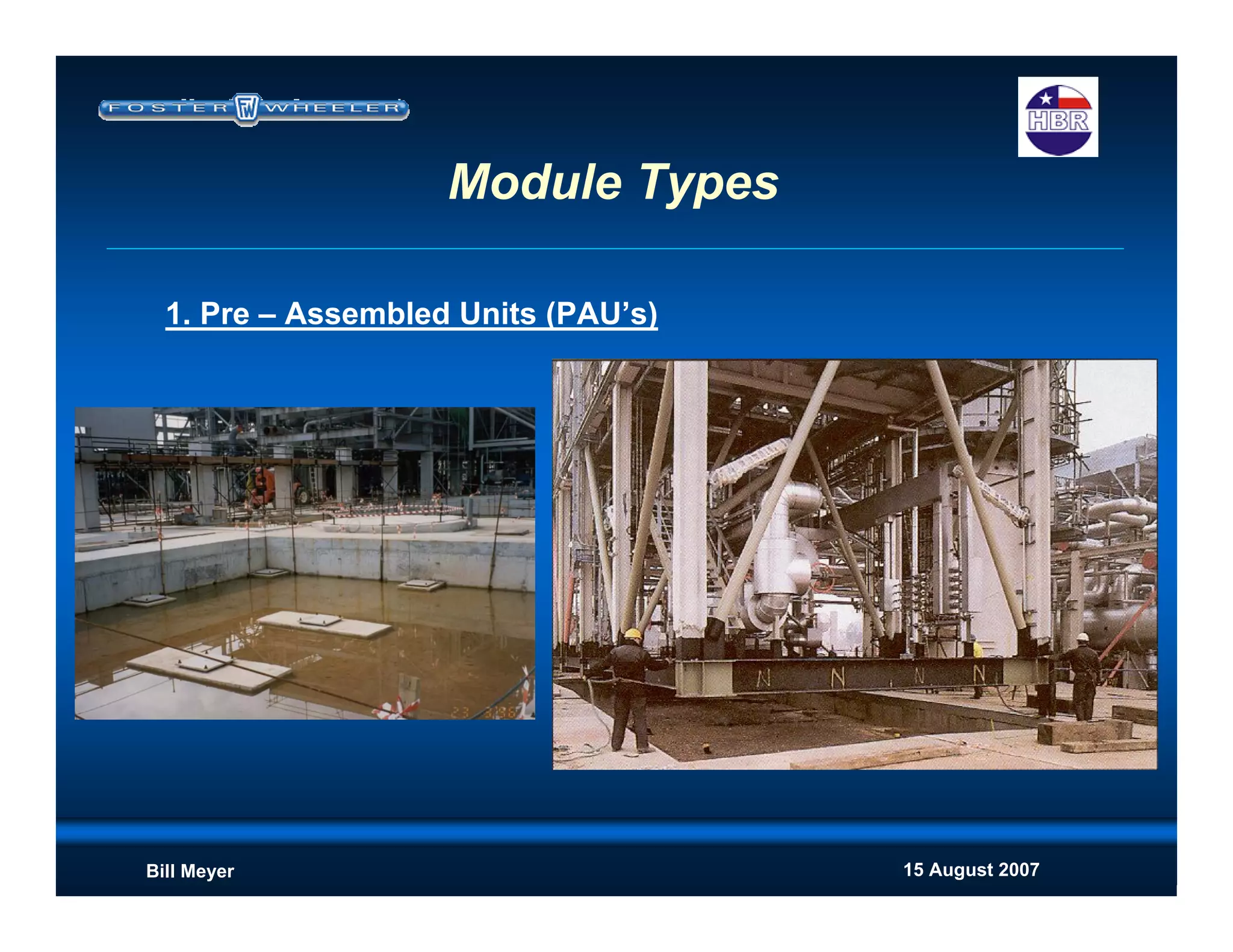
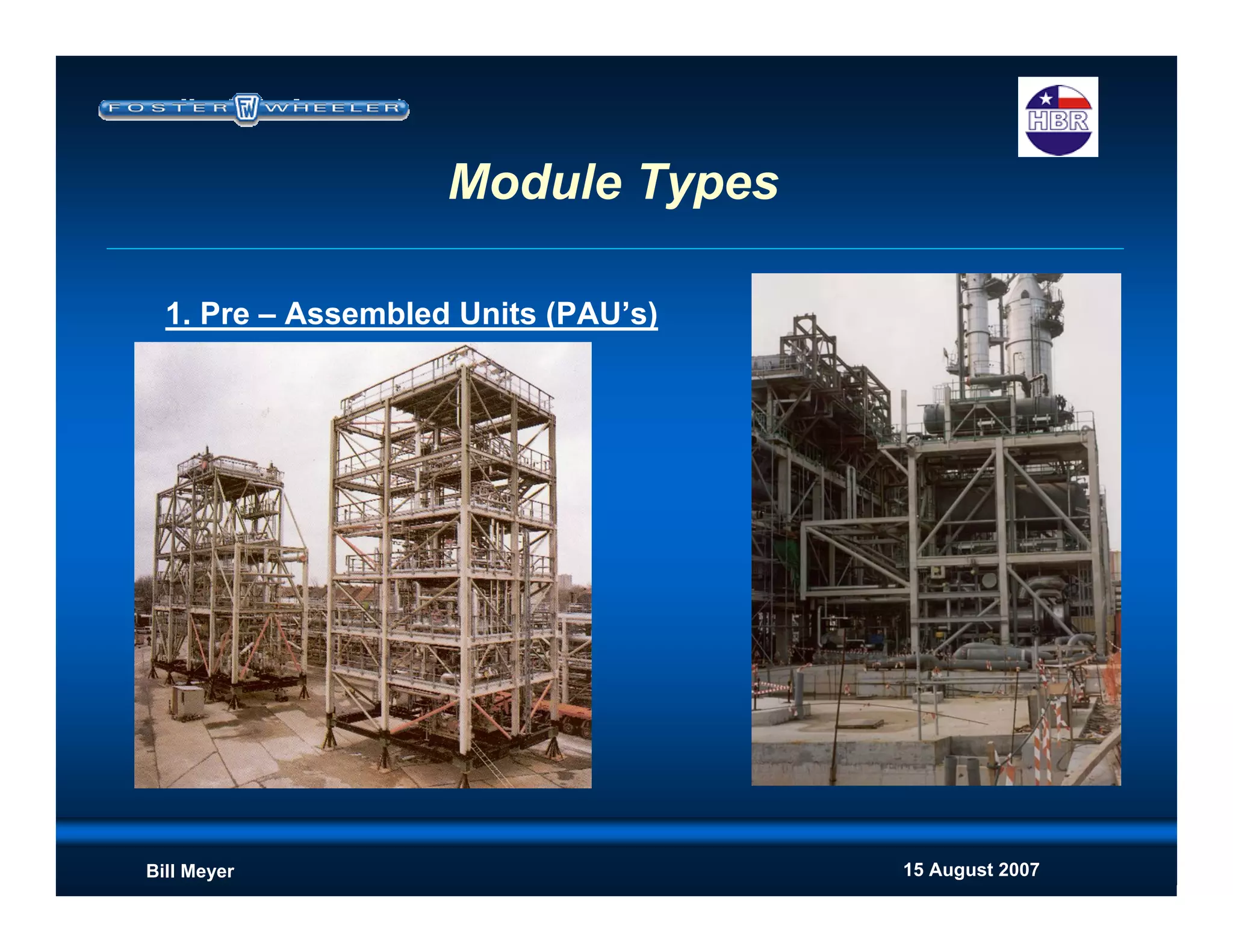
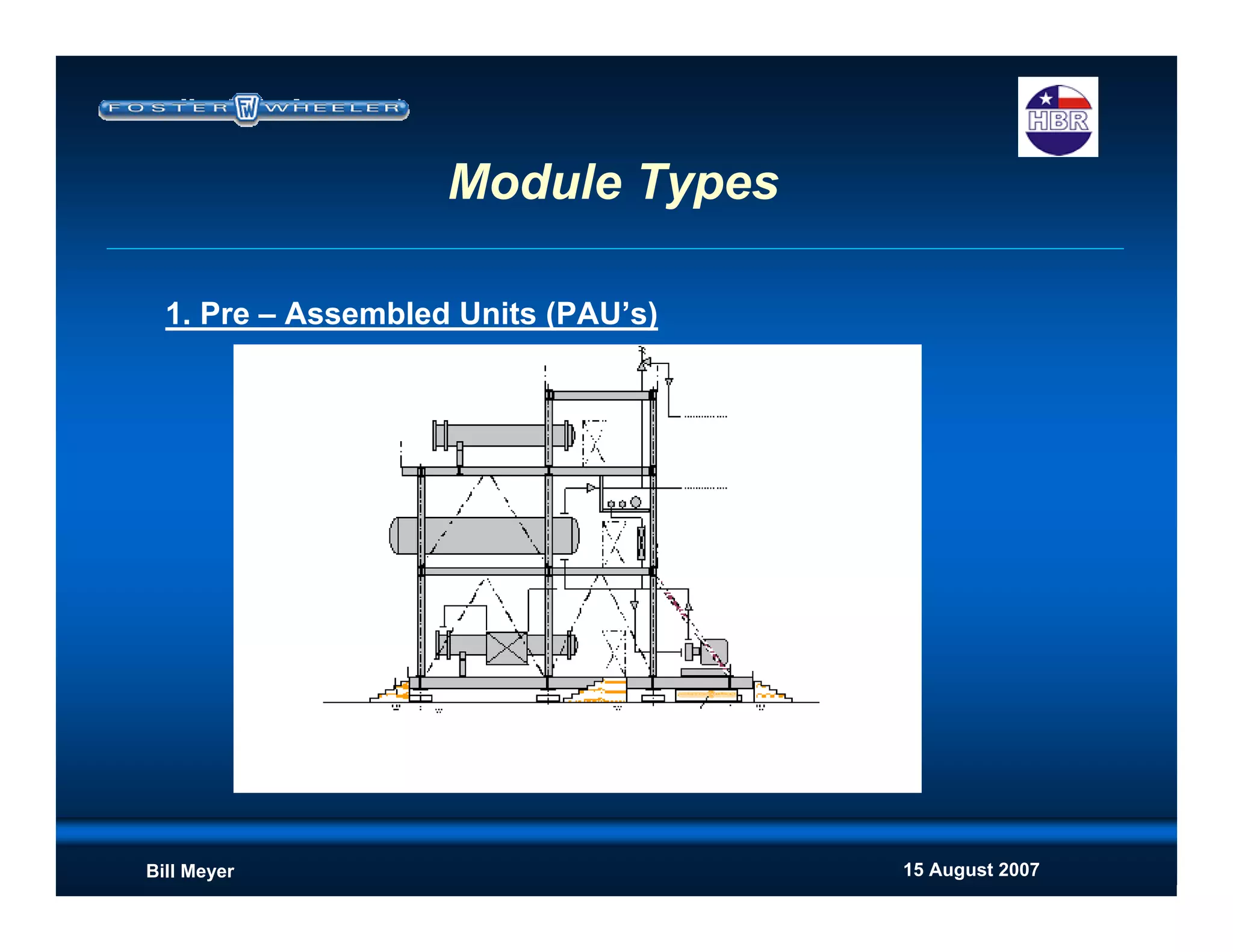
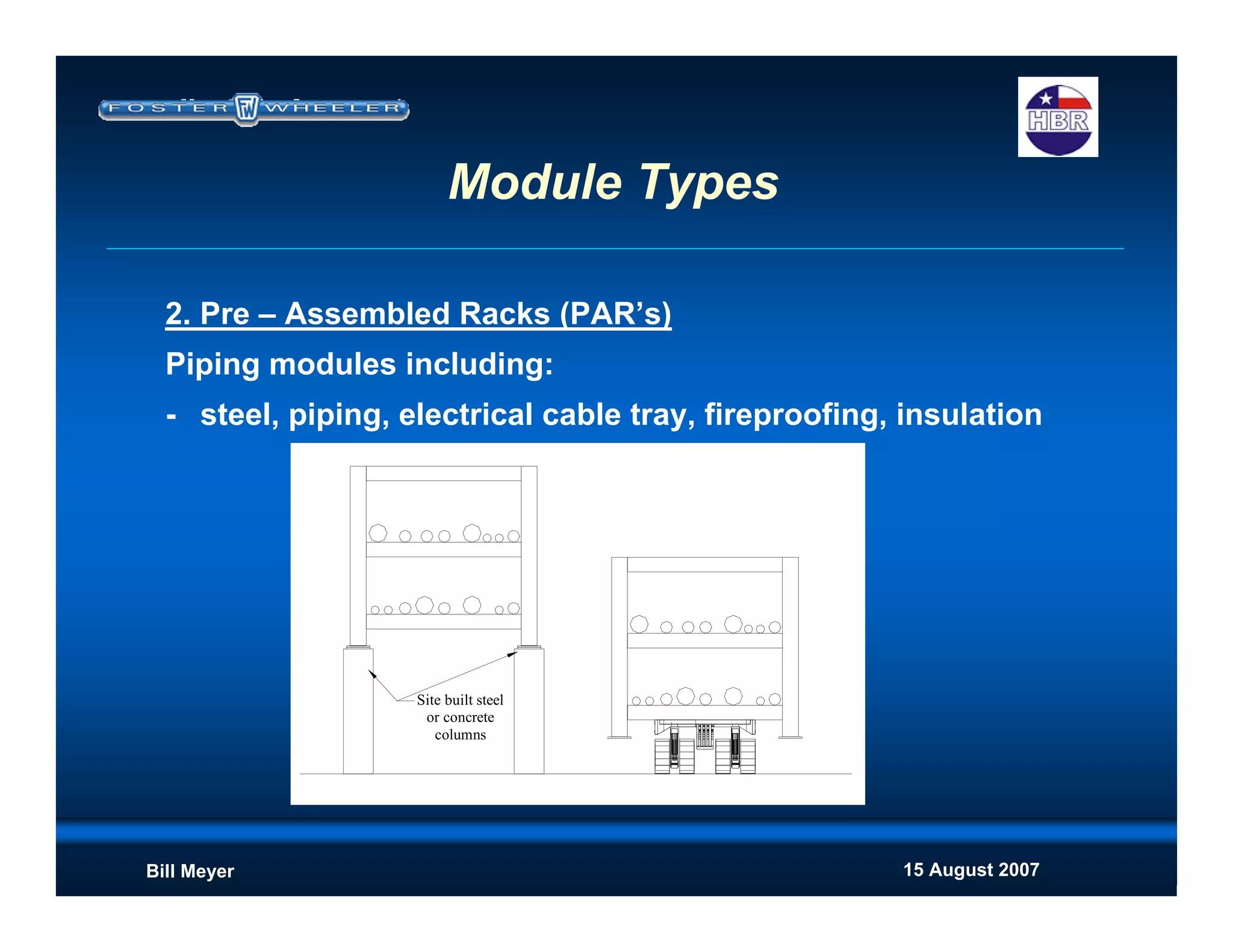
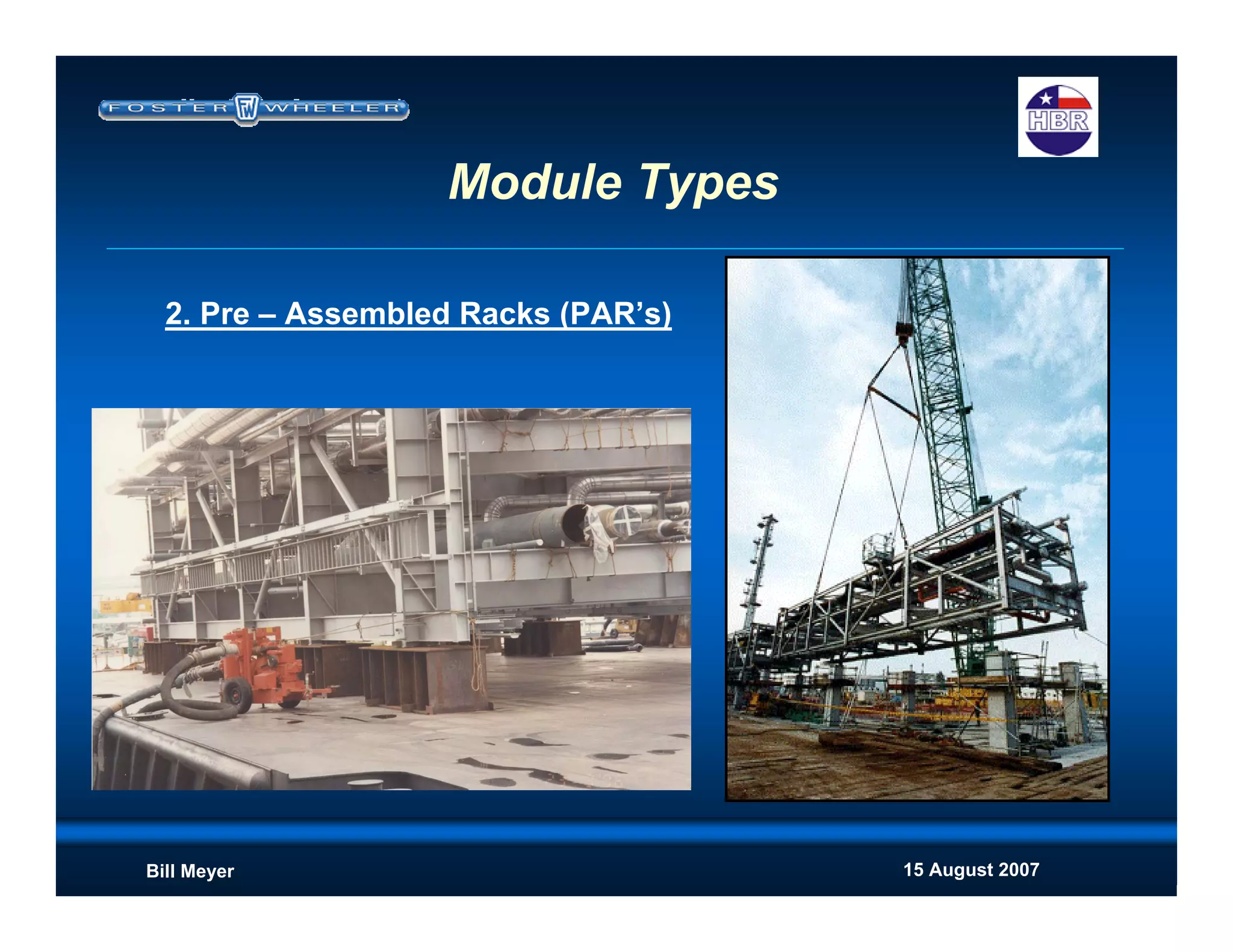
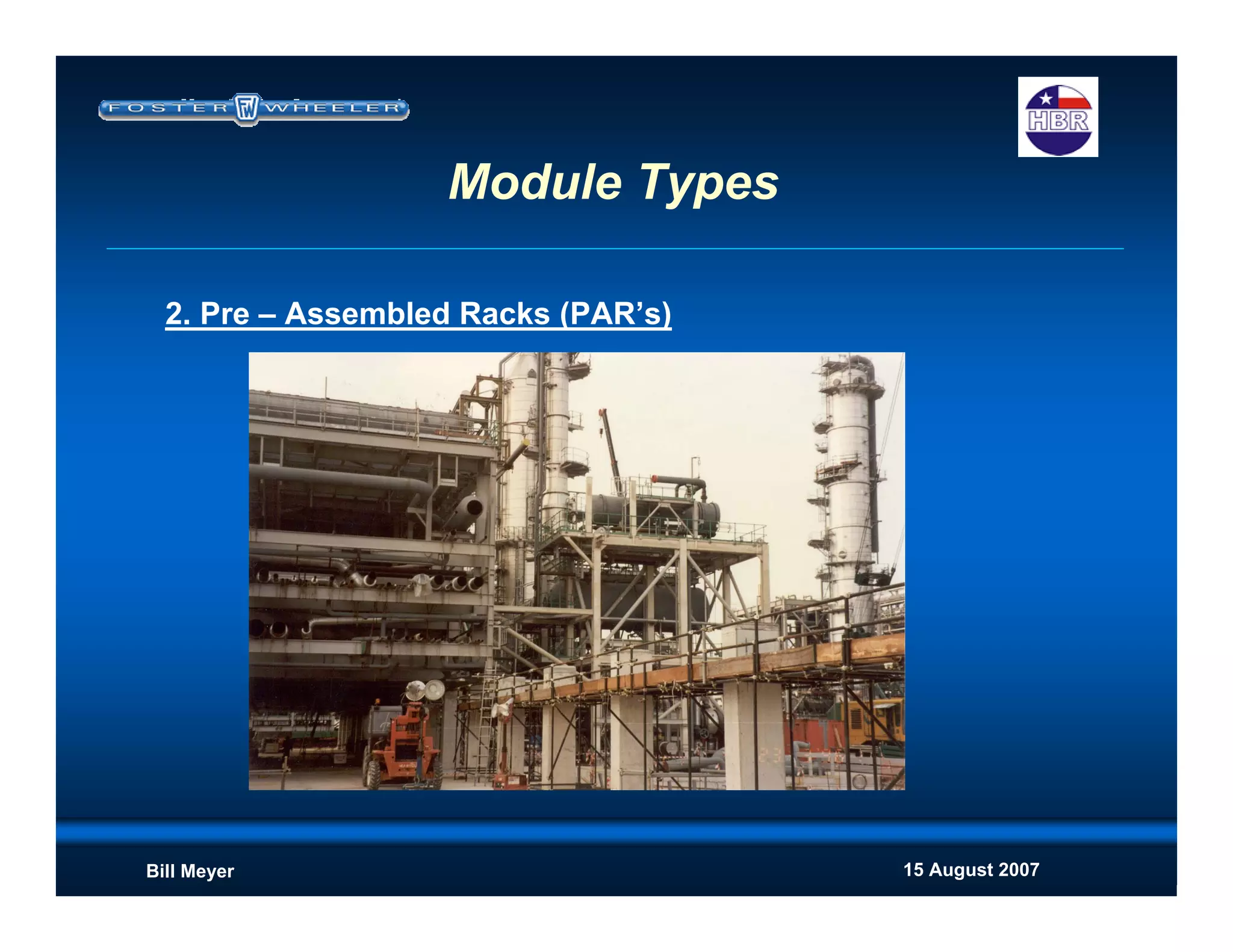
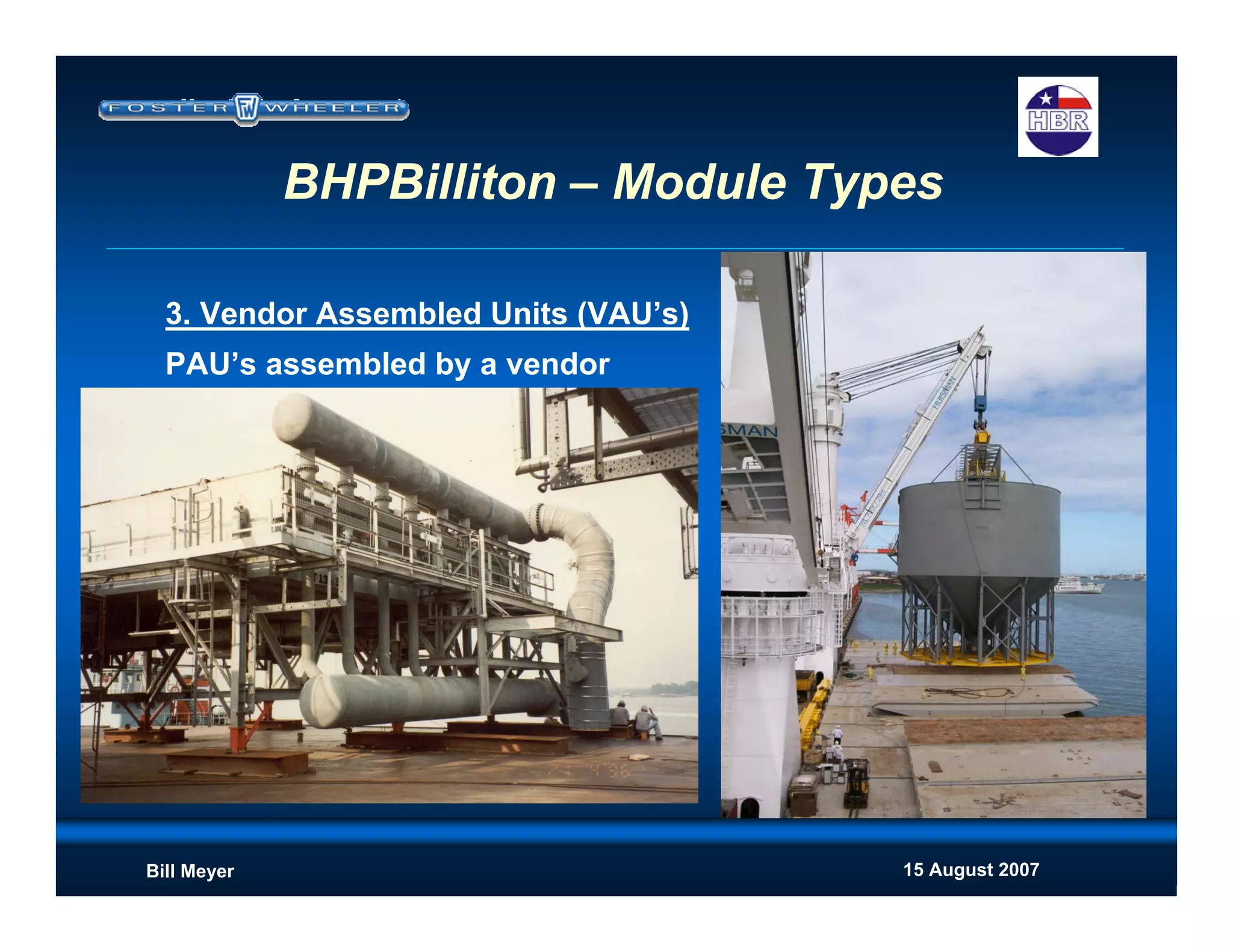
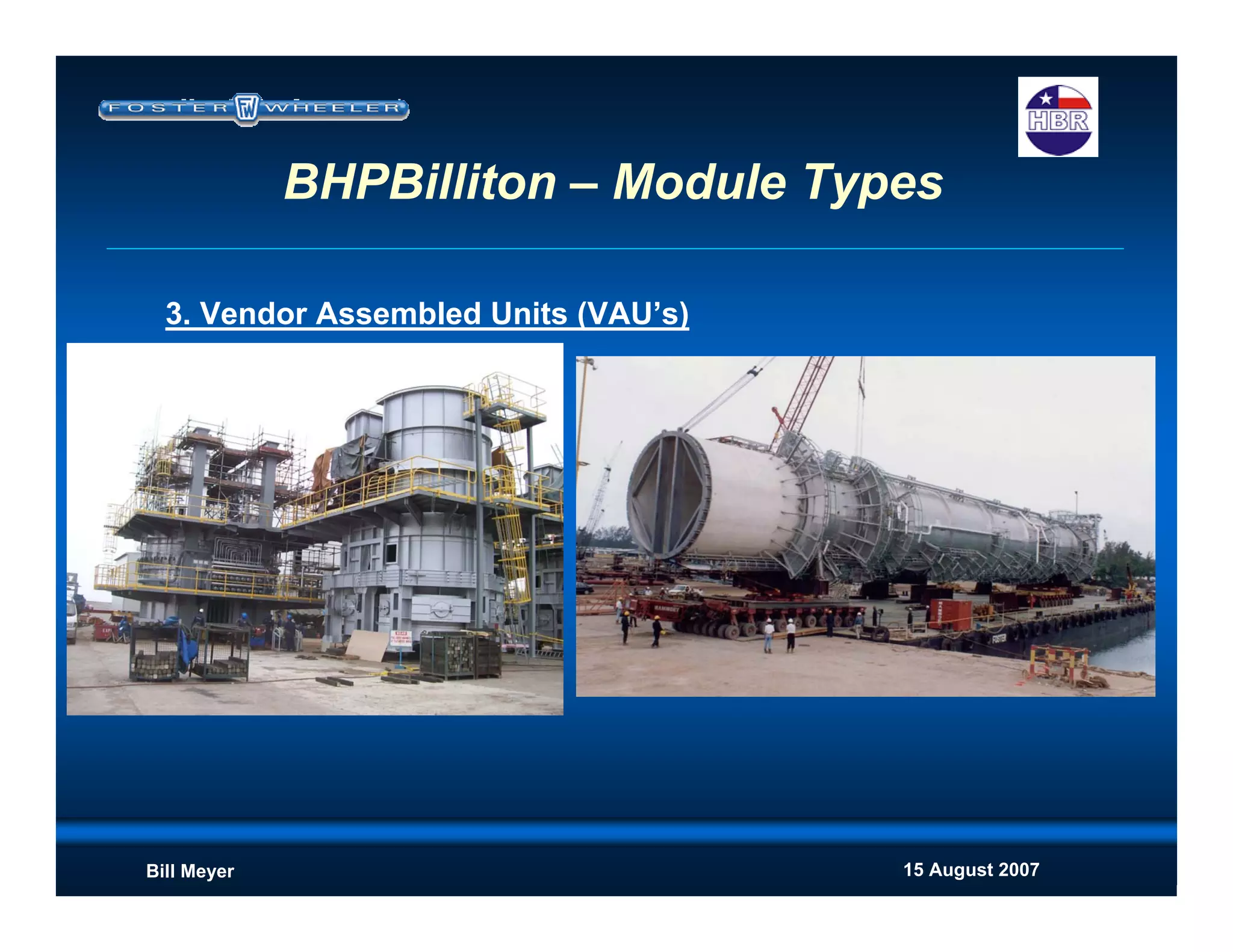
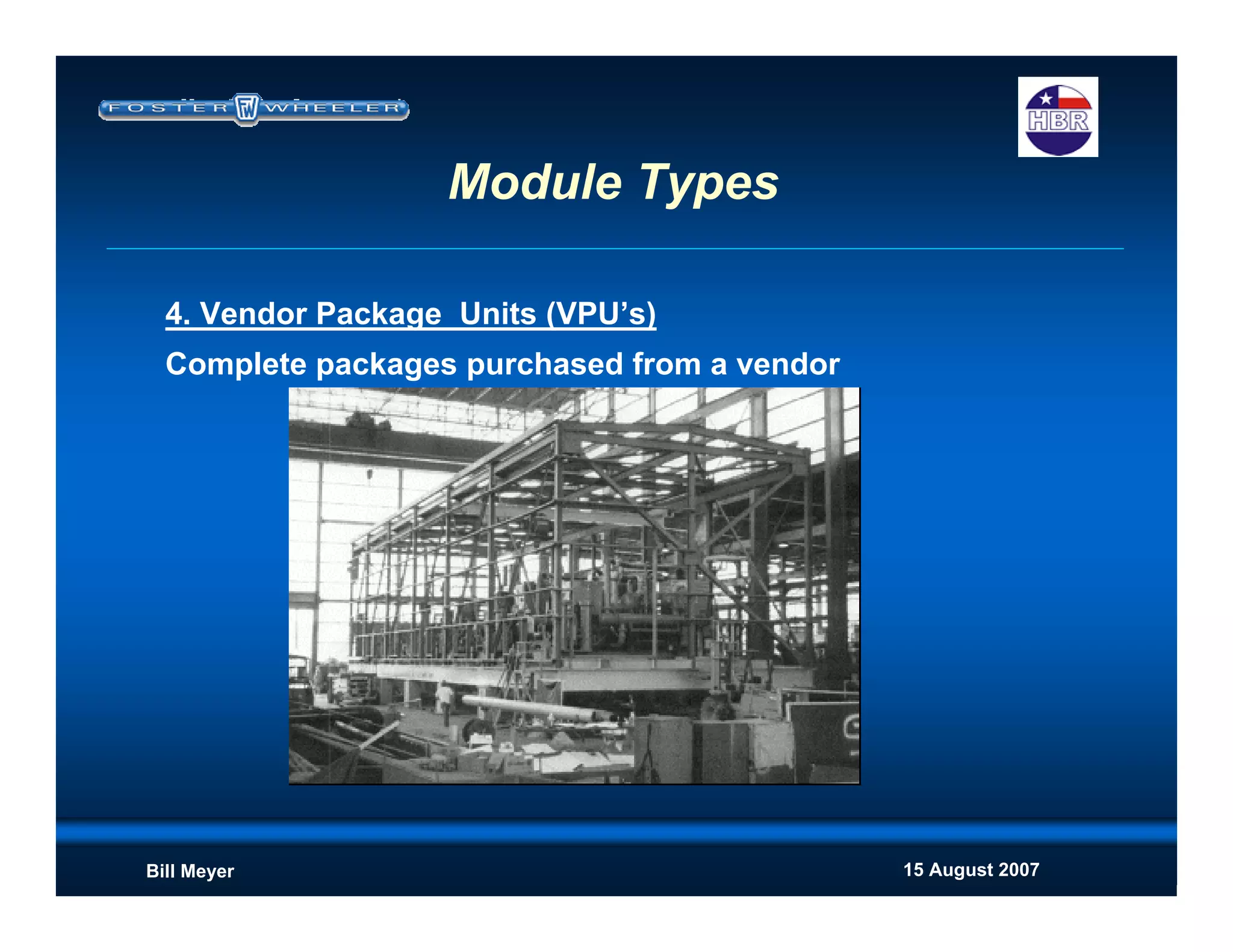
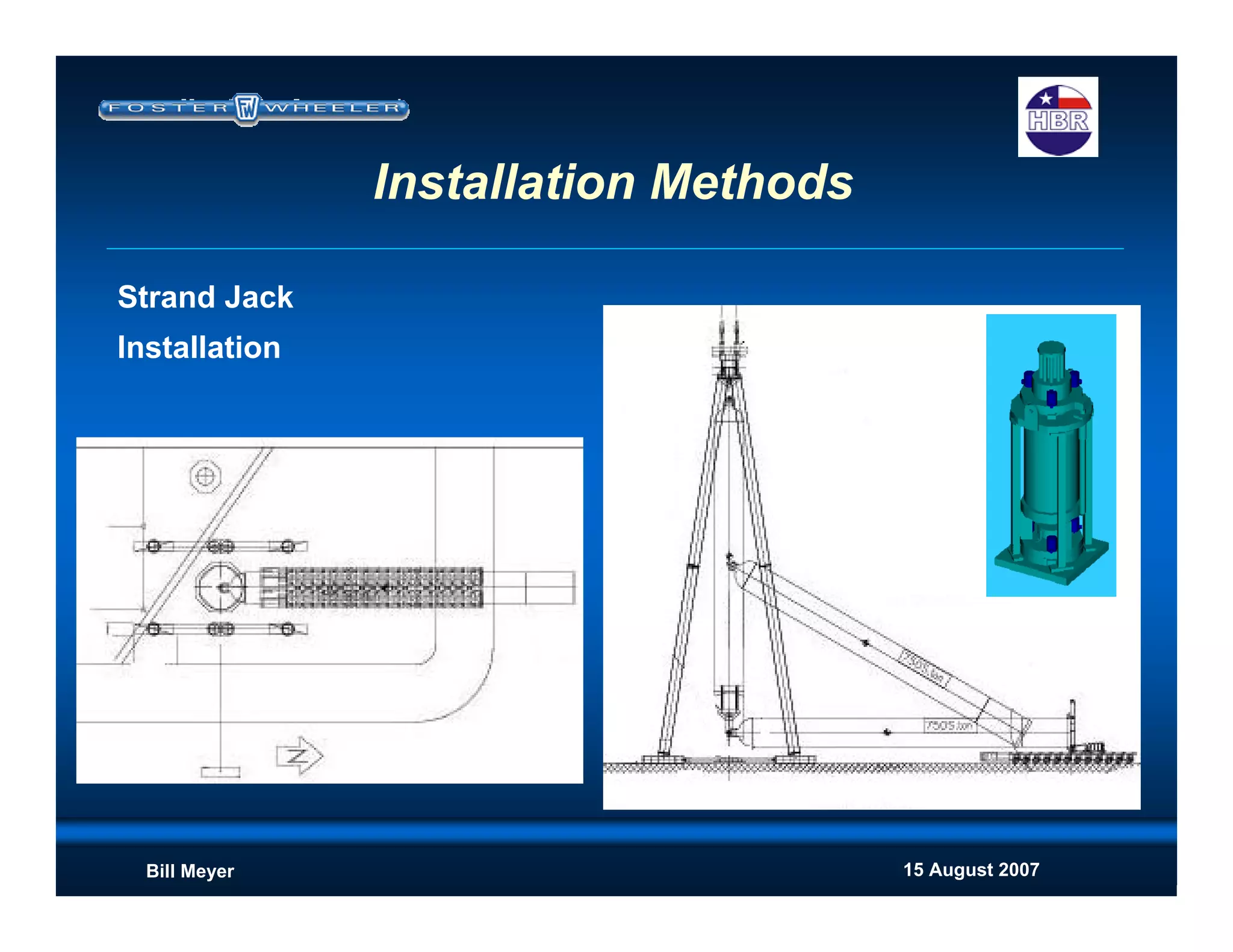
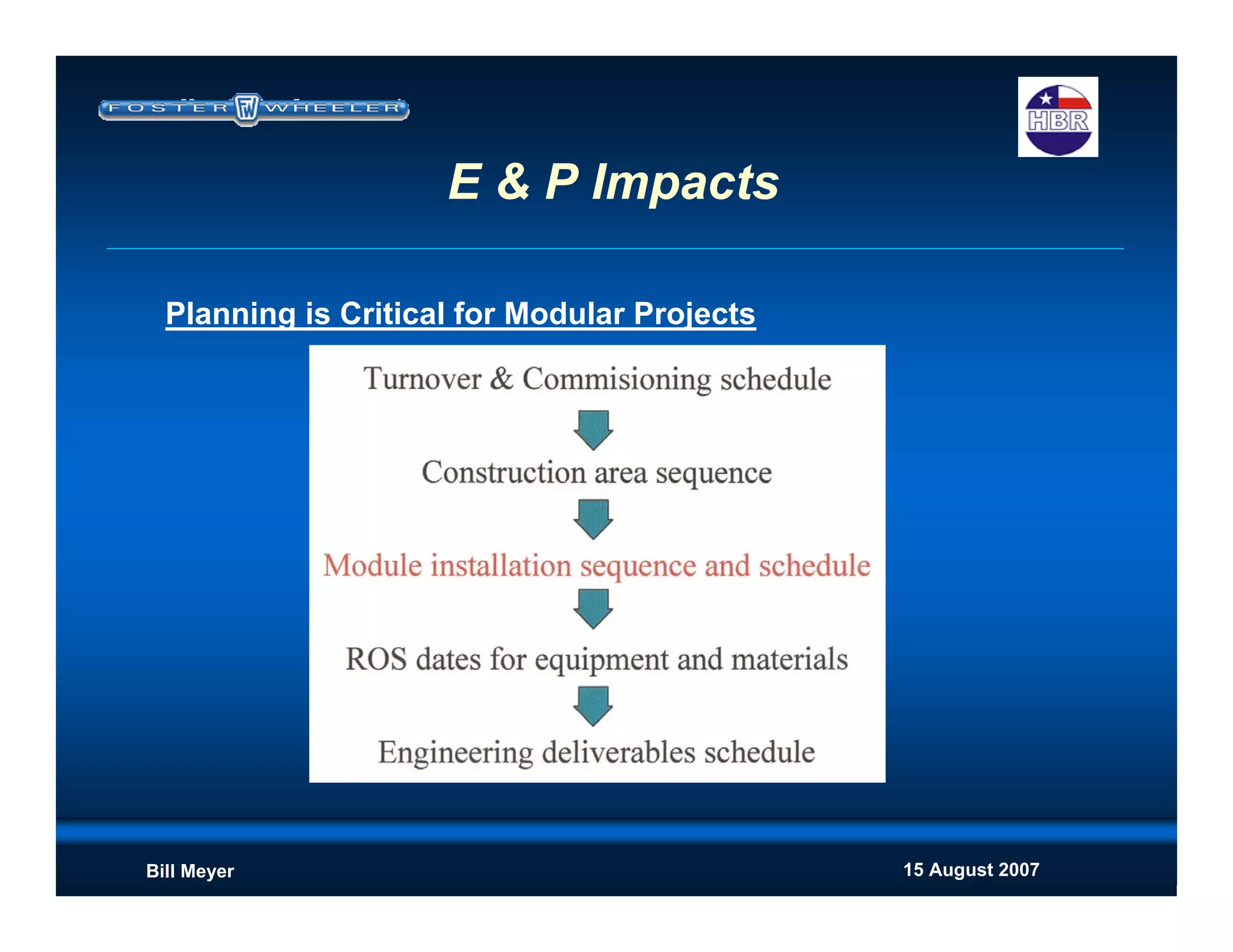
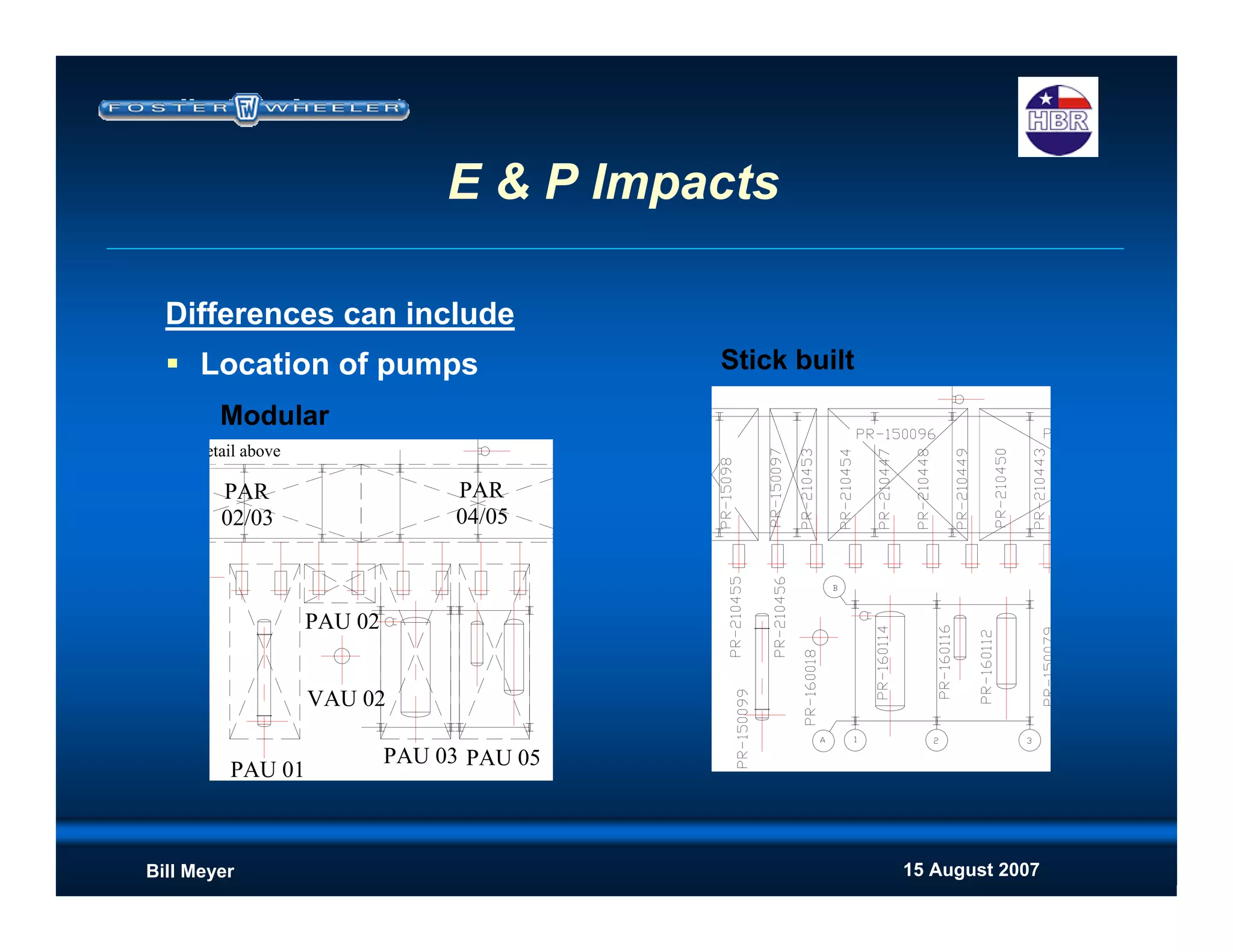
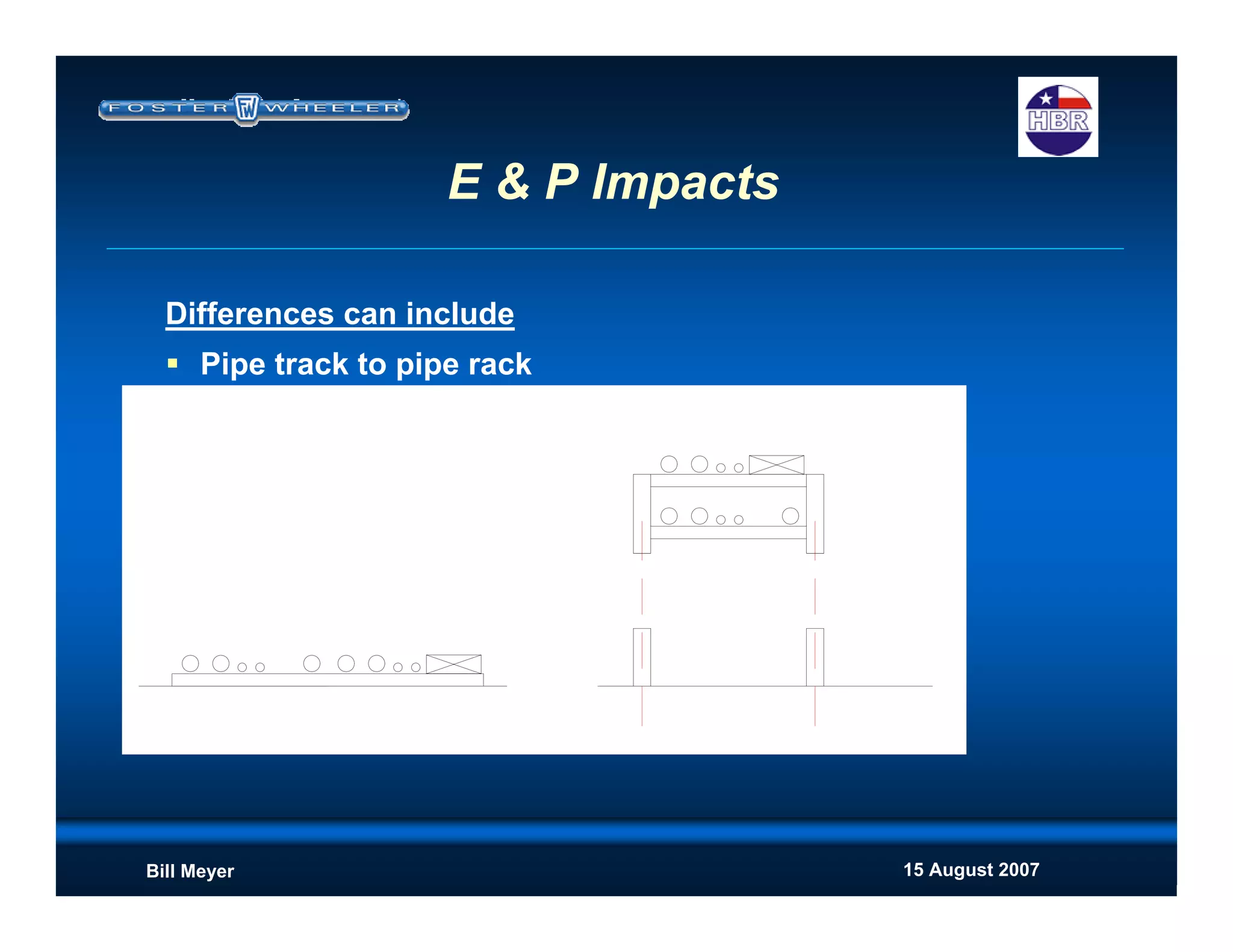
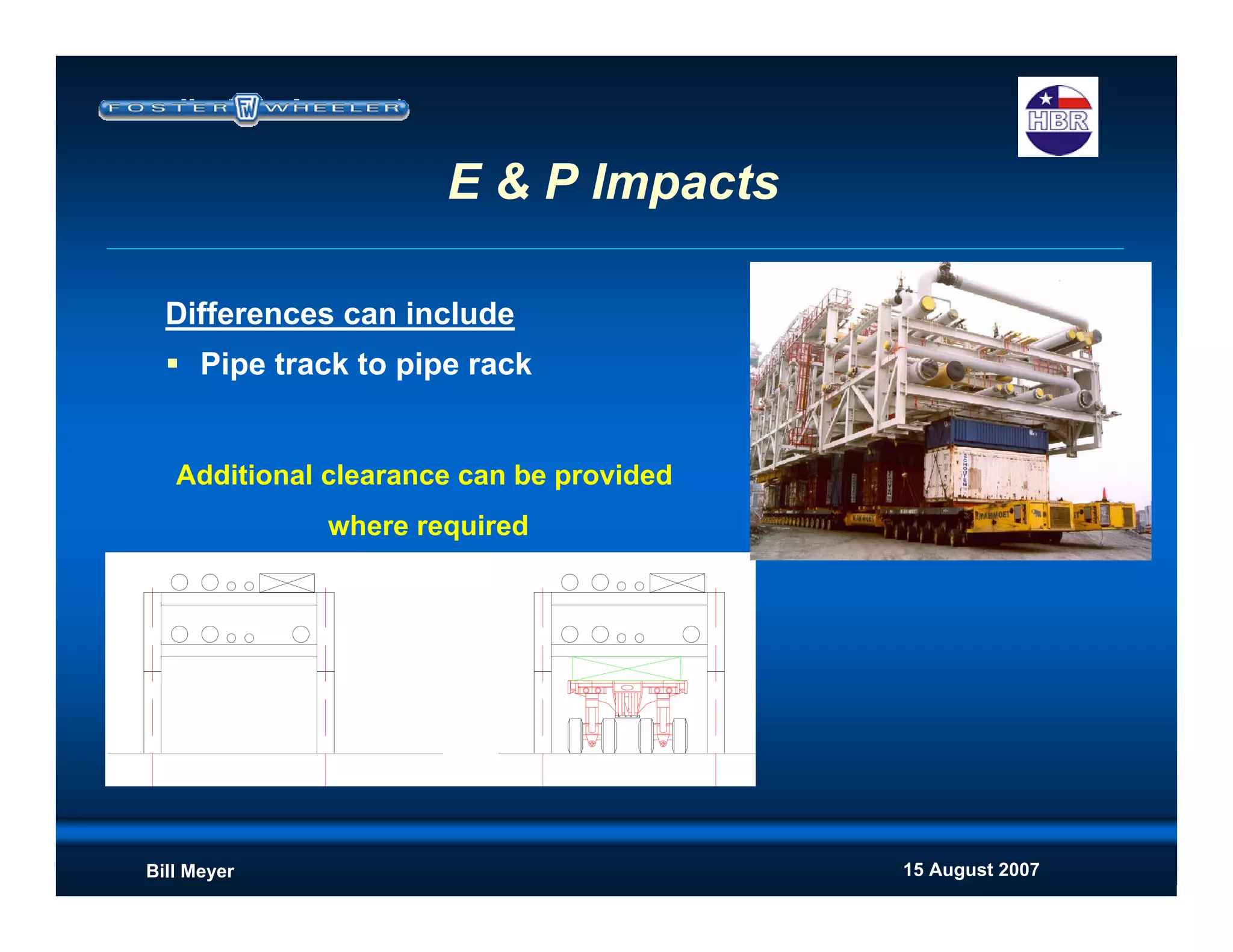
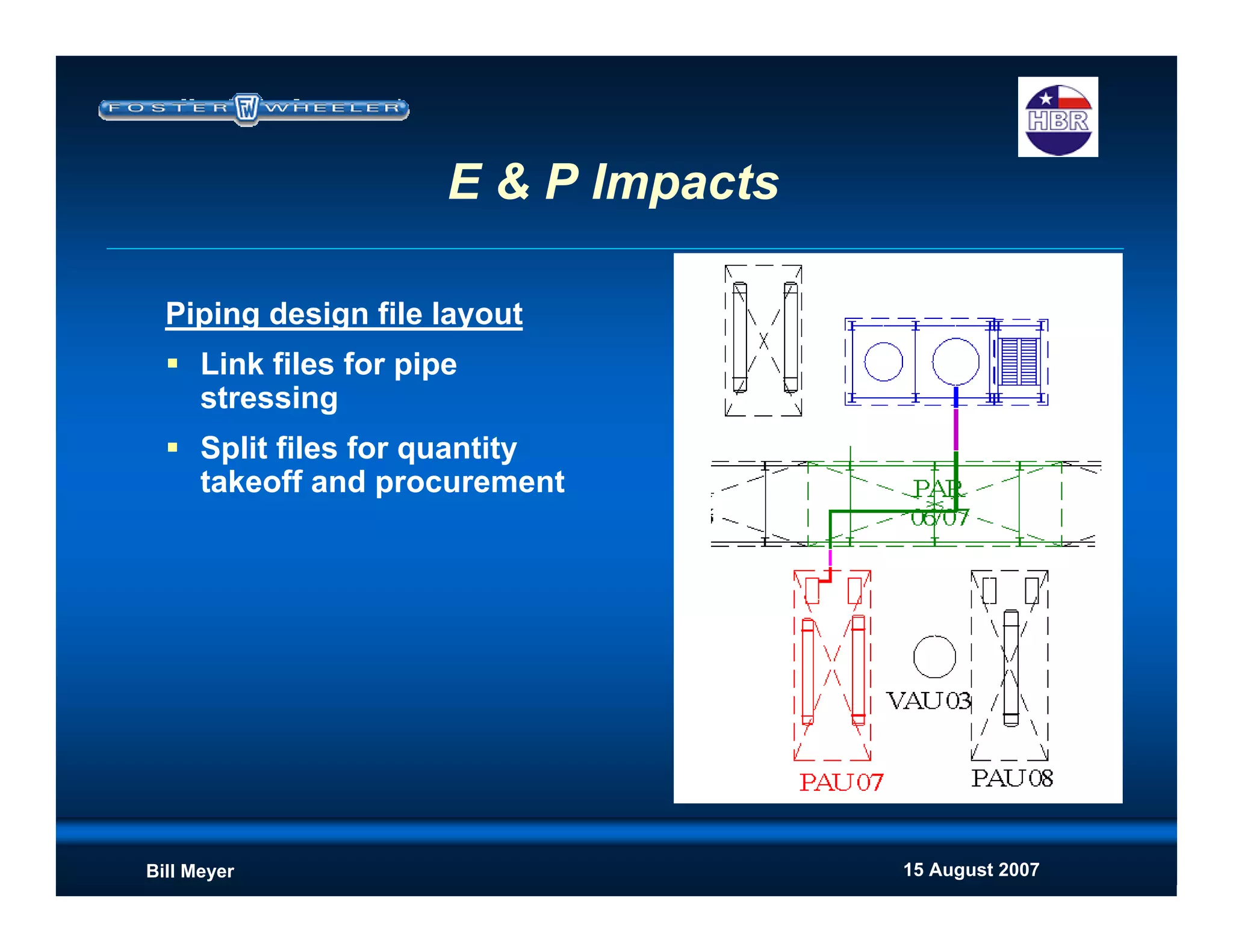
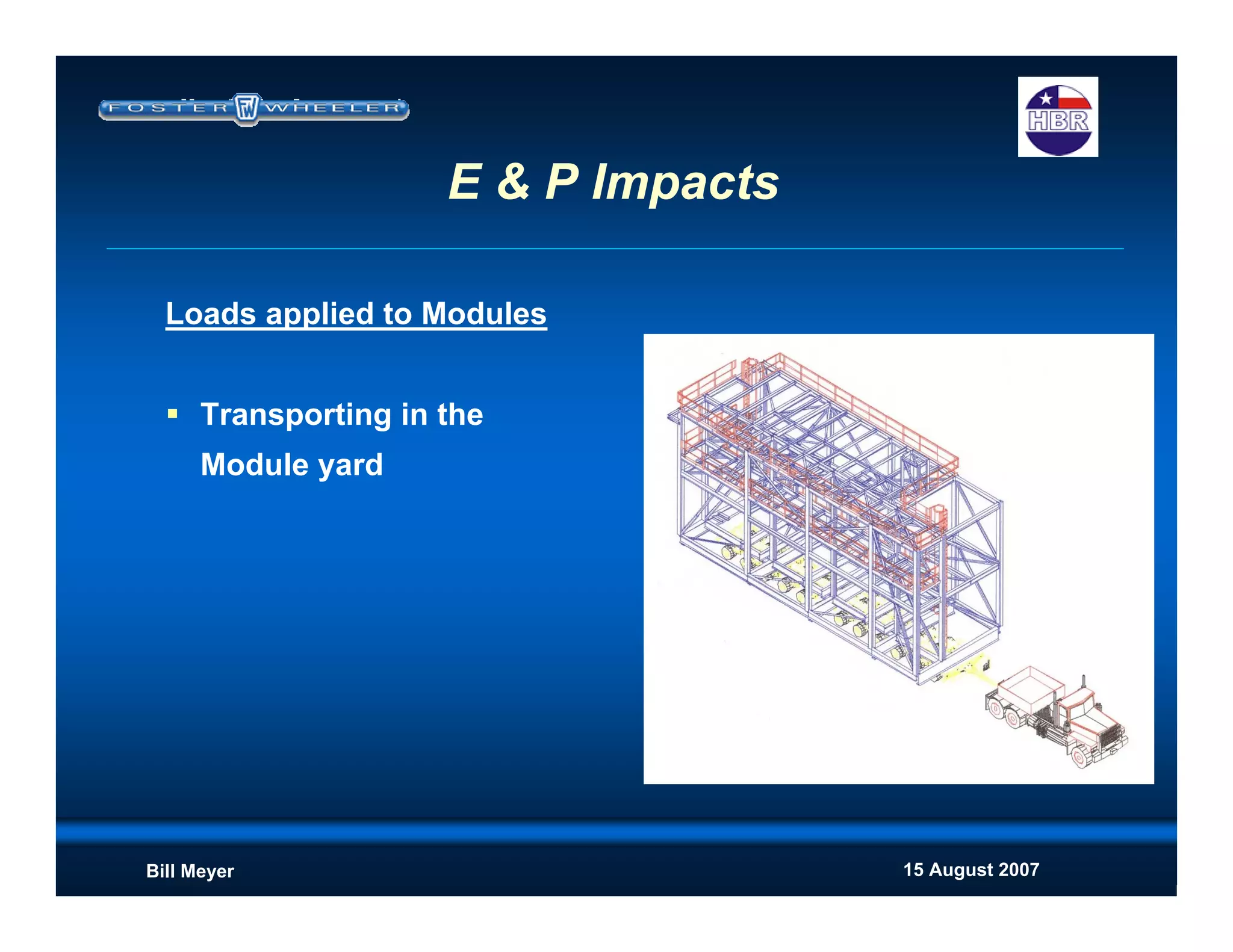
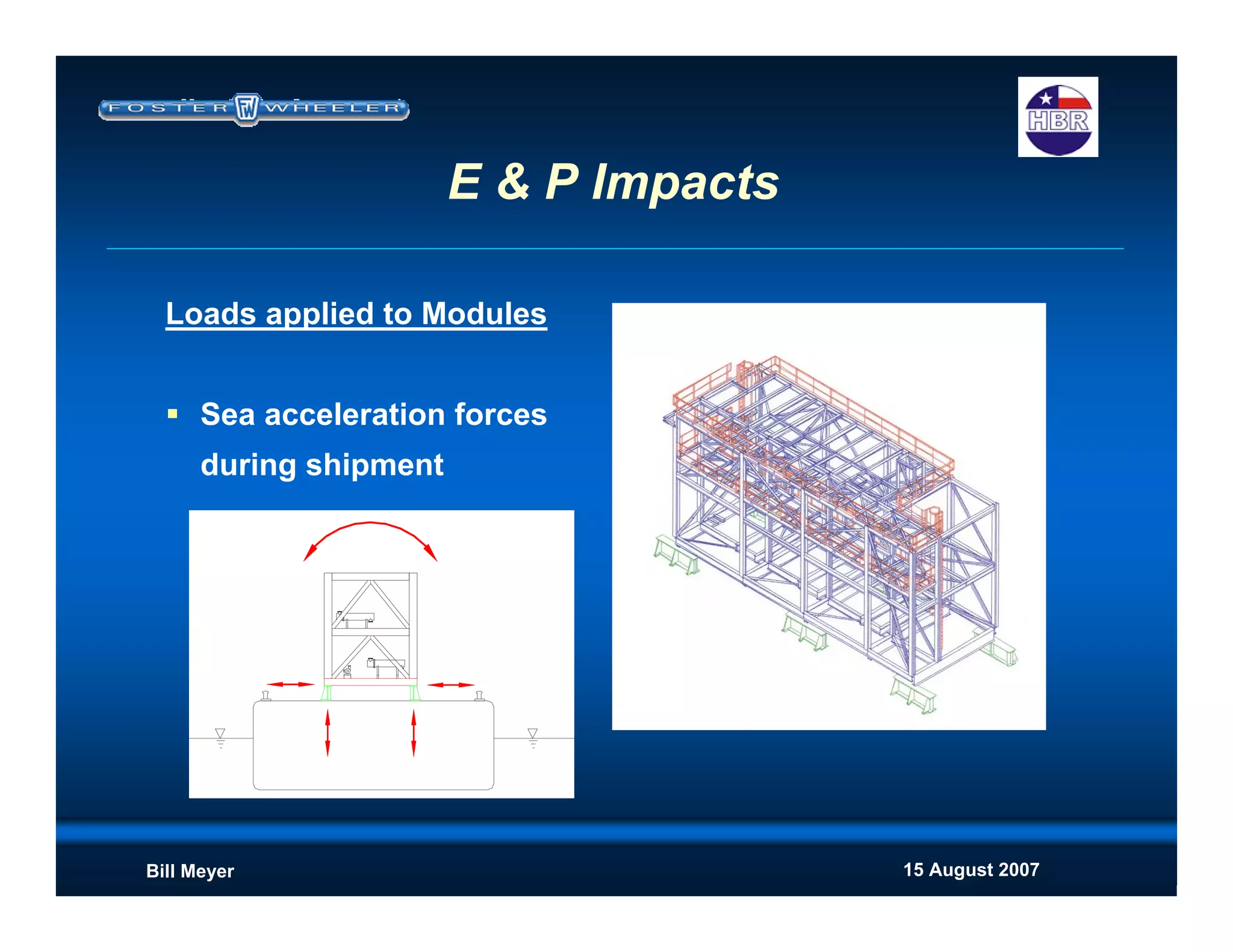
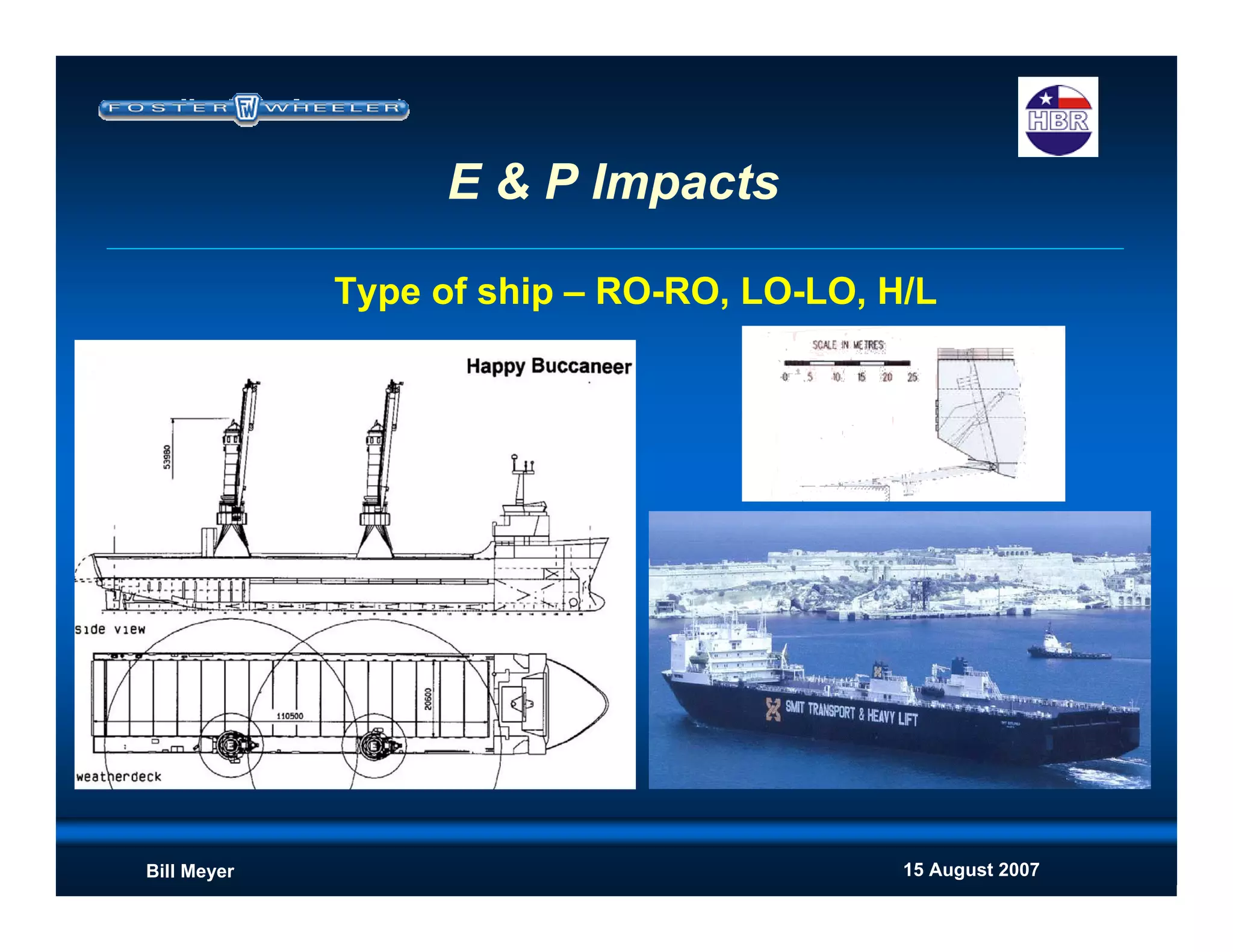
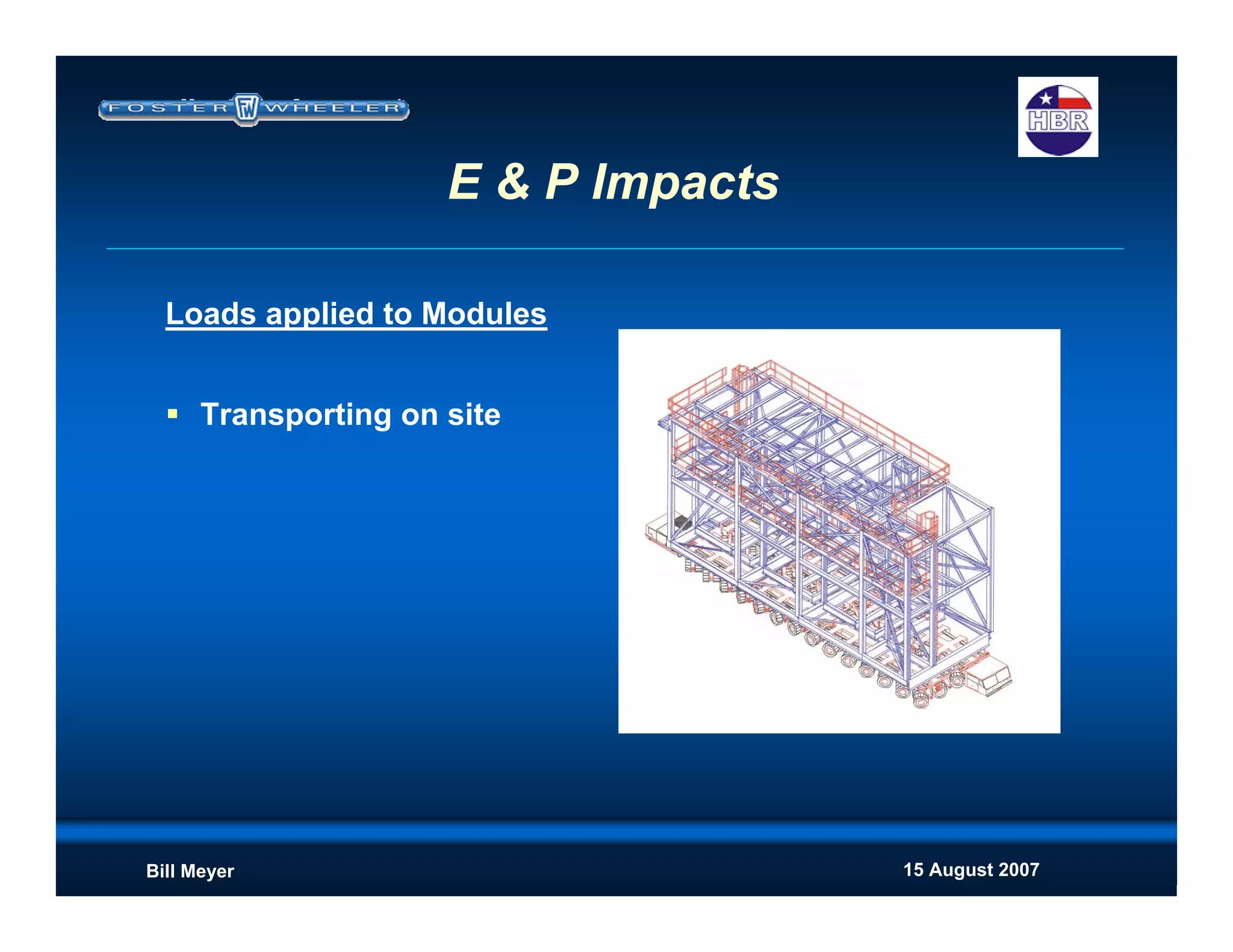
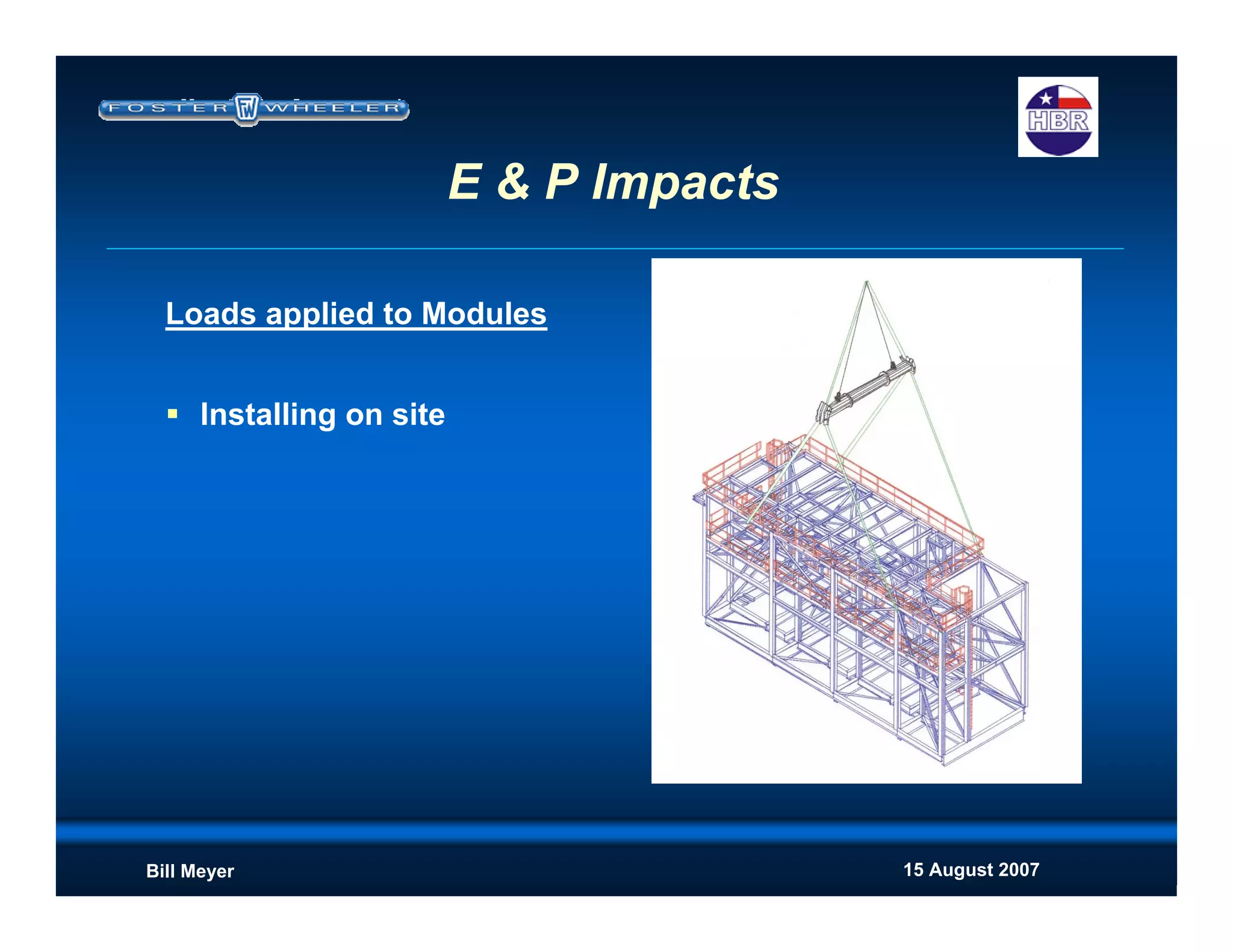
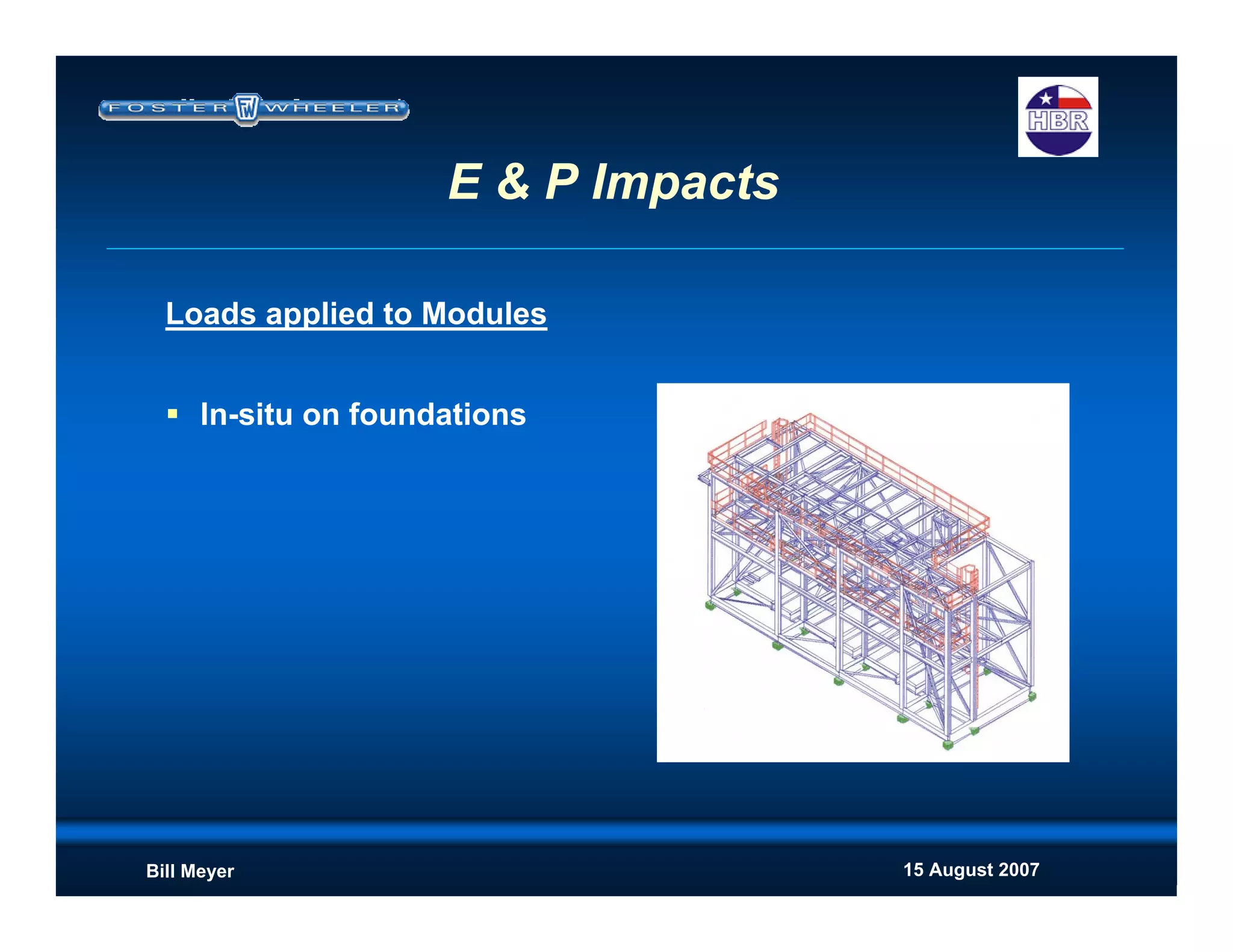
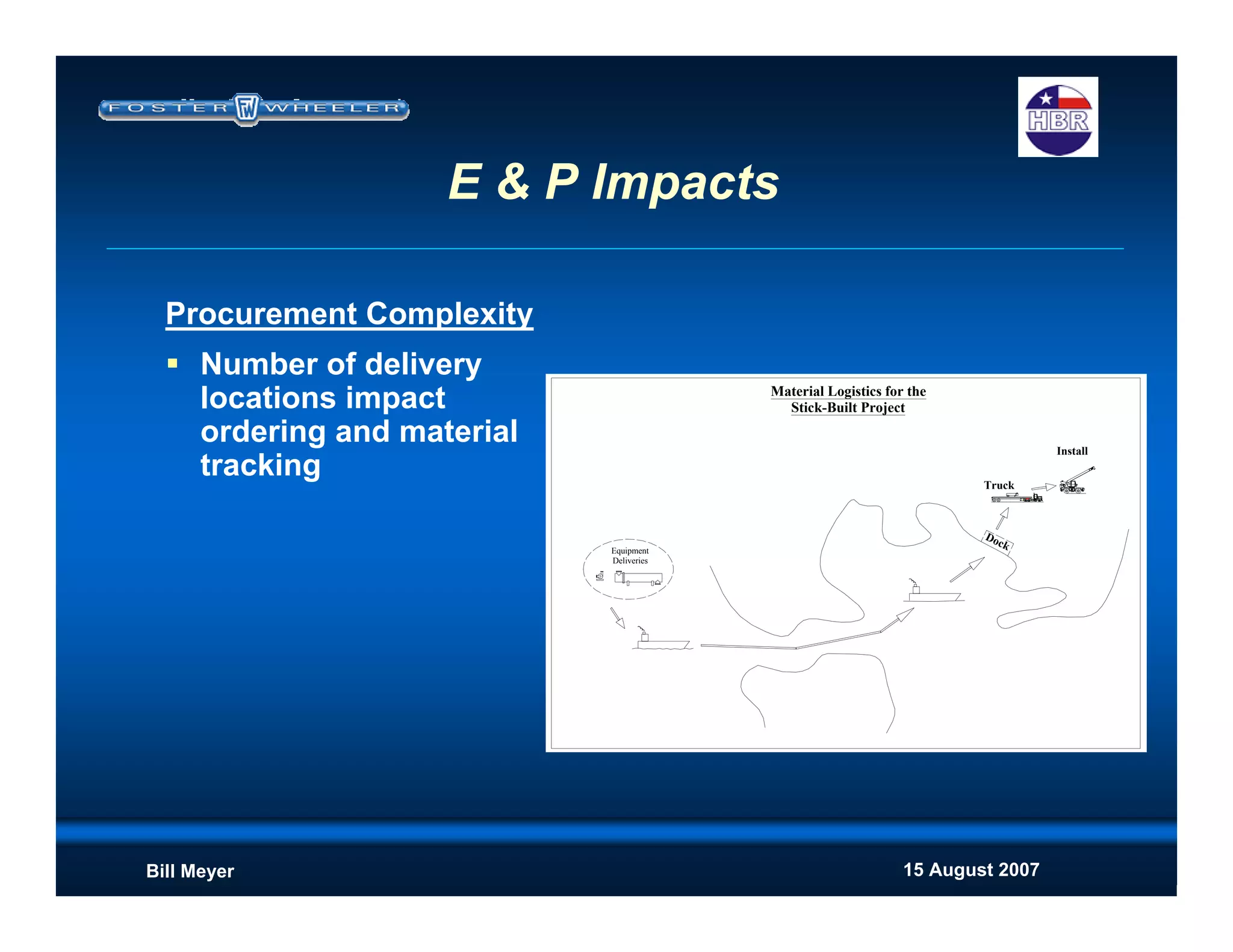
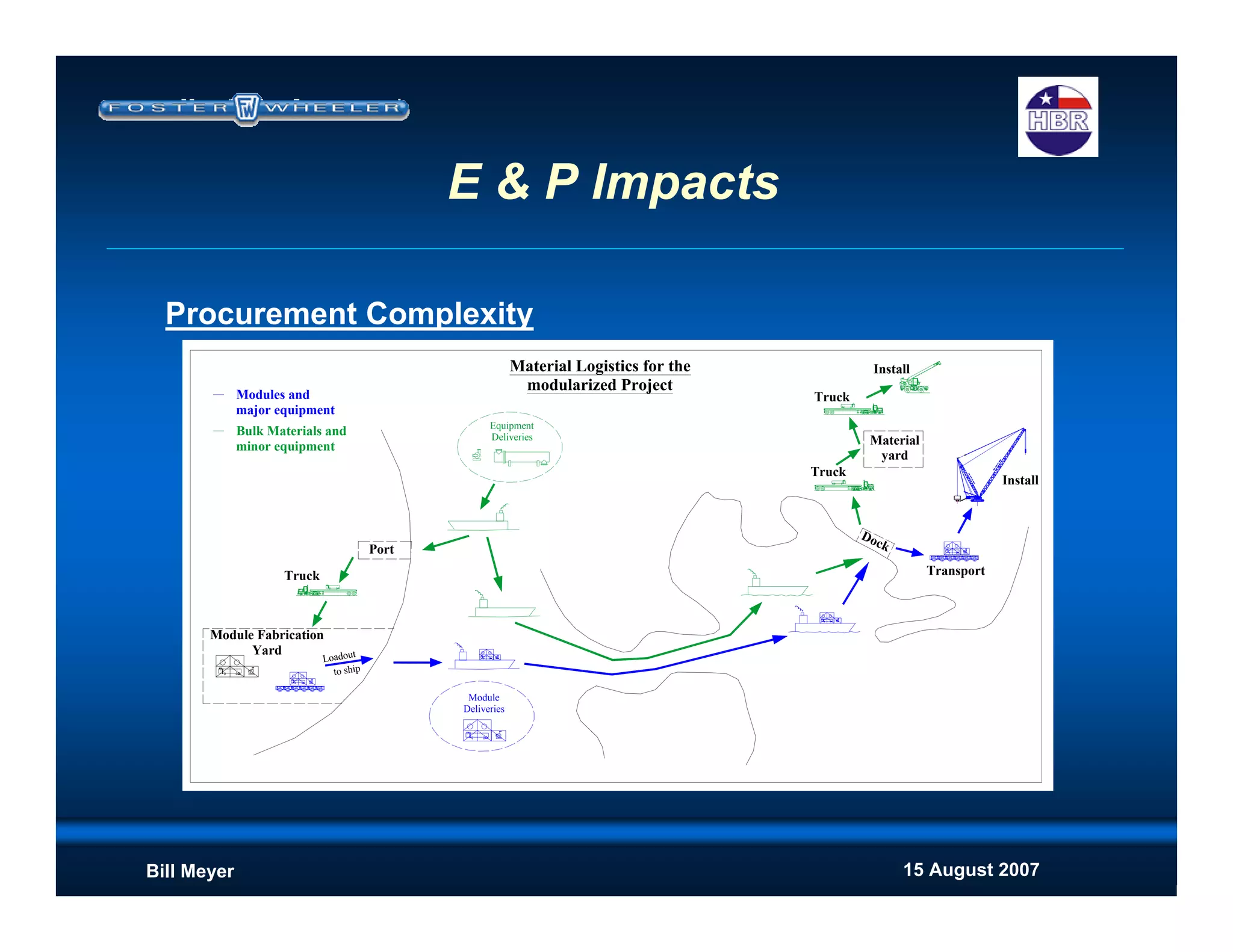
This document discusses modularization for engineering projects. It covers modularization drivers like cost and schedule reductions. It describes module types like pre-assembled units and racks. Installation methods like cranes and transporters are outlined. Engineering and procurement impacts for modular projects are also covered, such as additional planning needs for piping layout and load considerations.





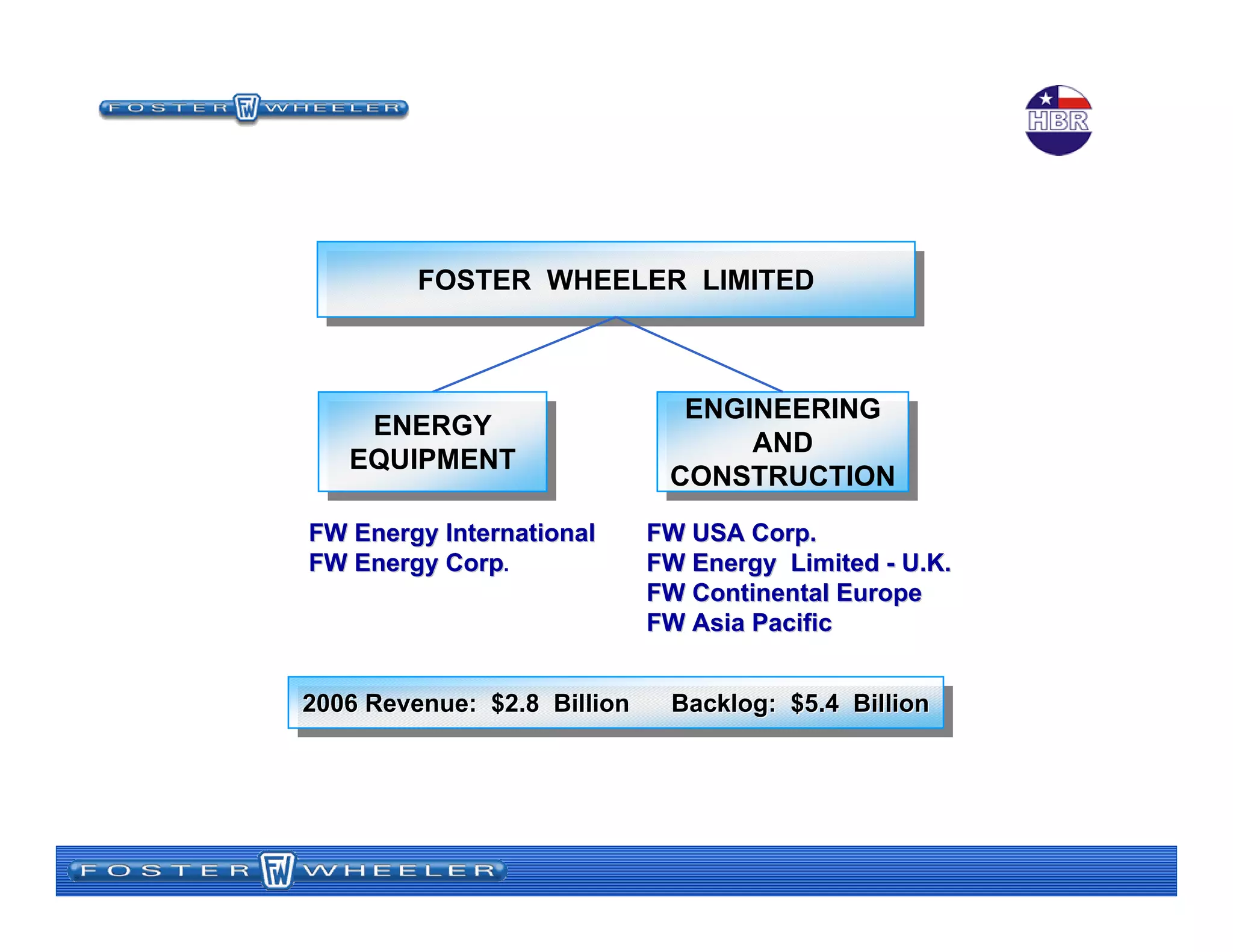
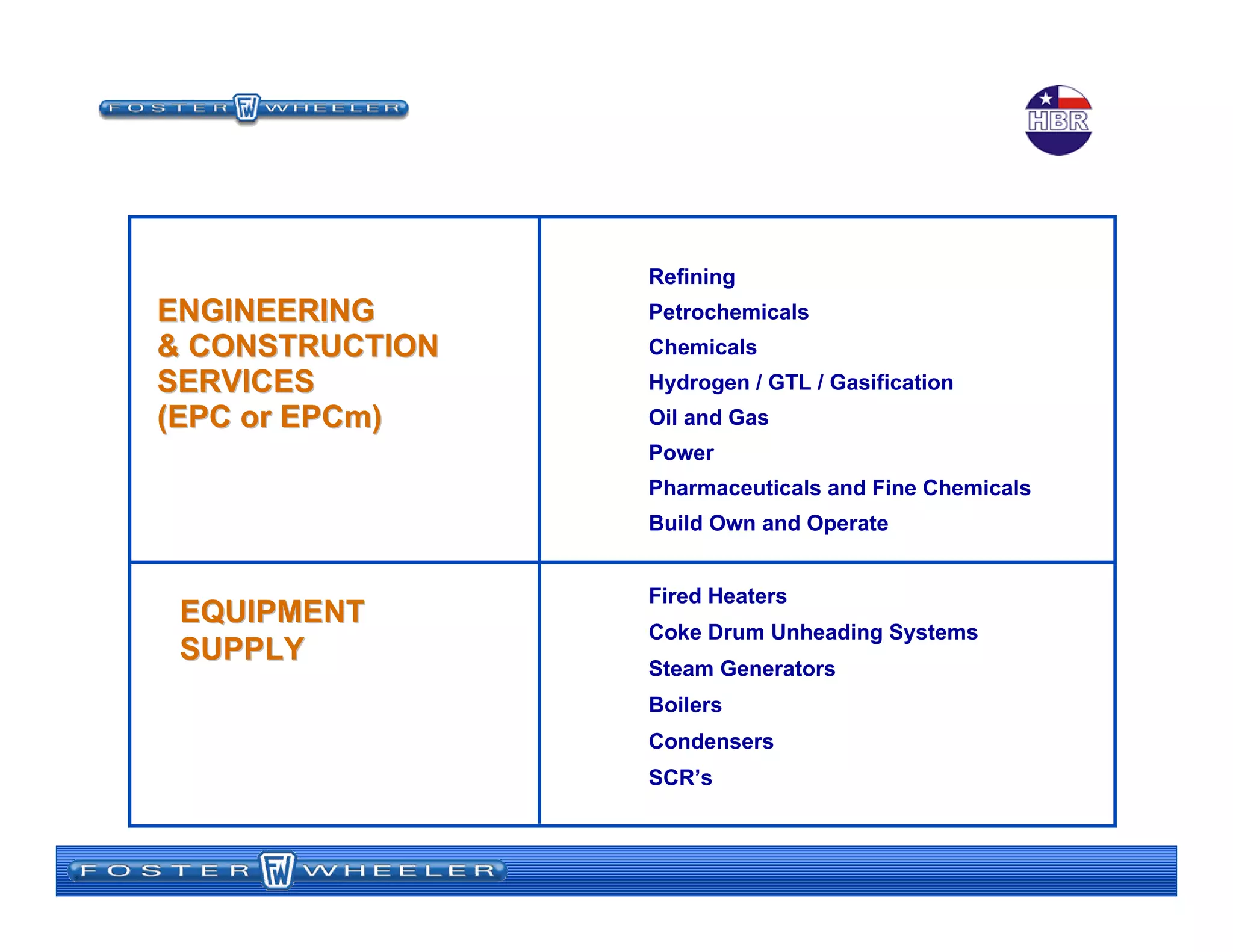







![15 August 2007Bill Meyer
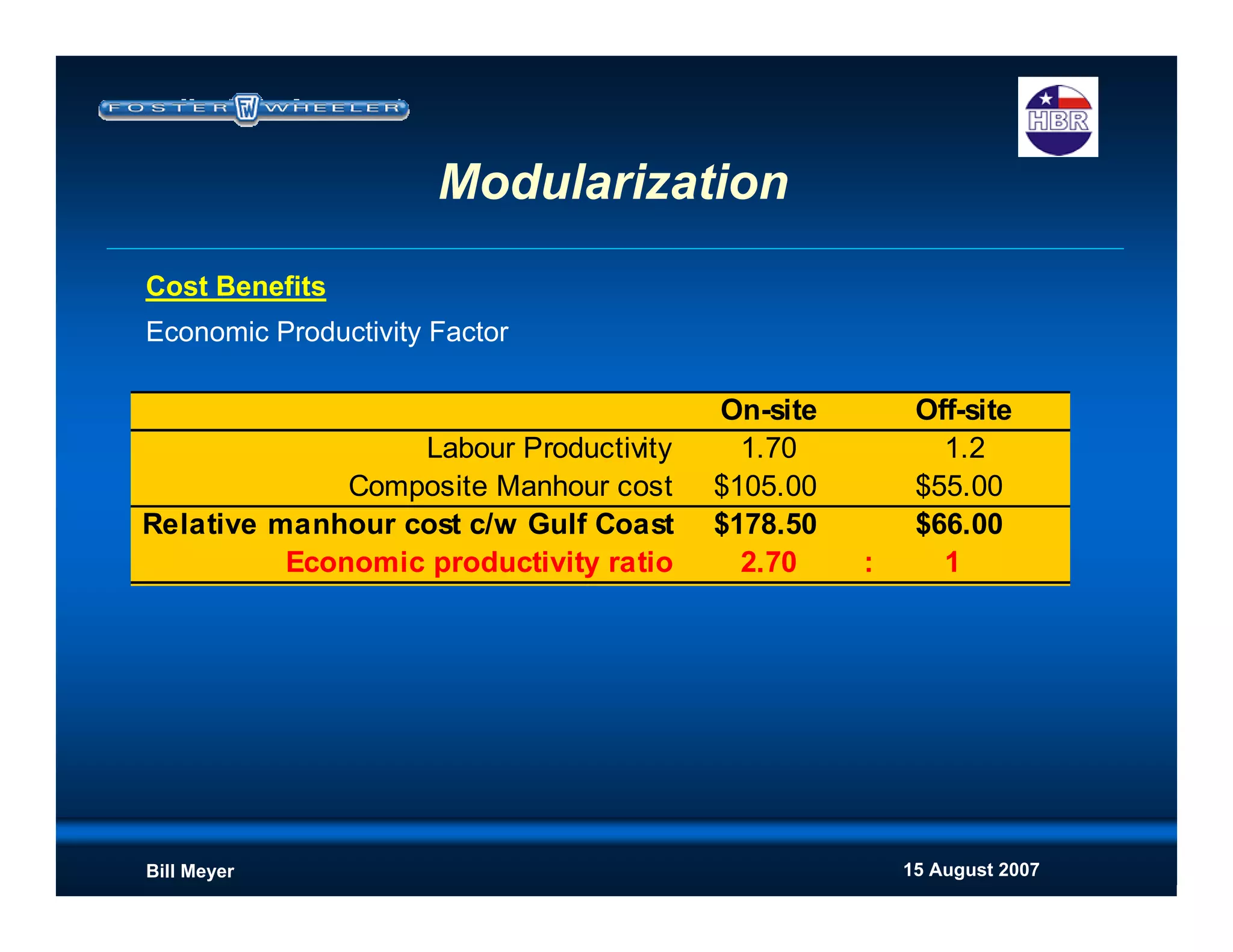
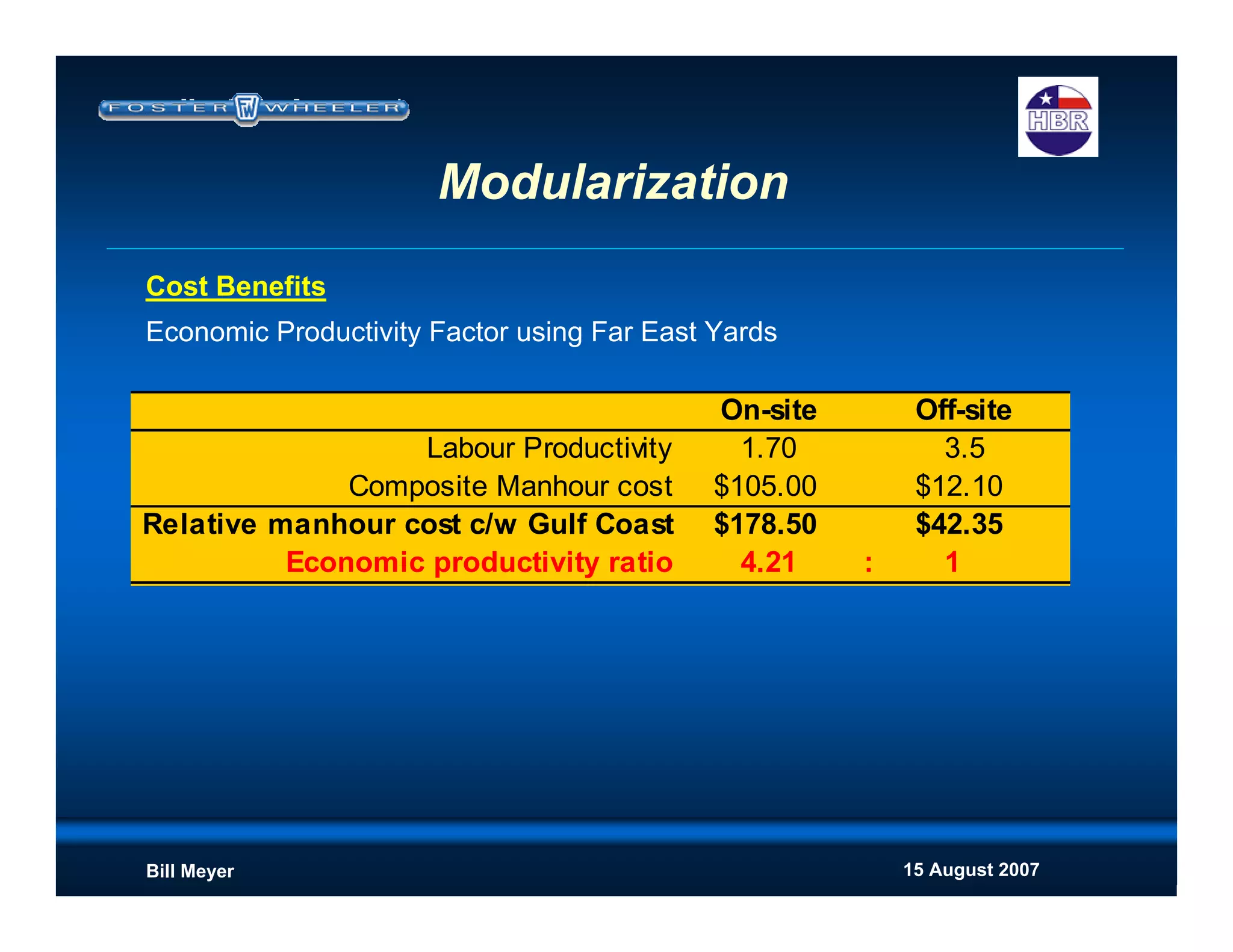
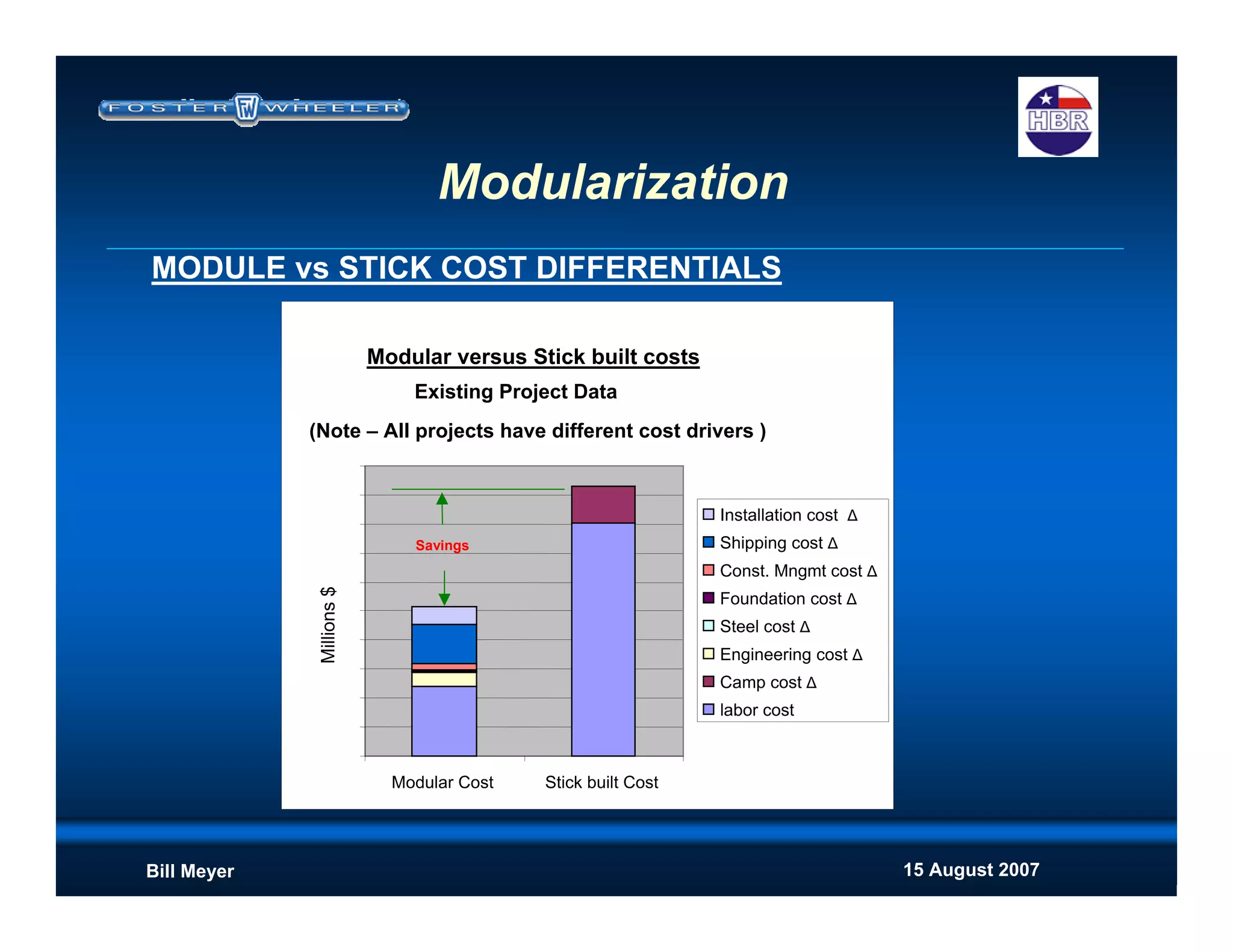
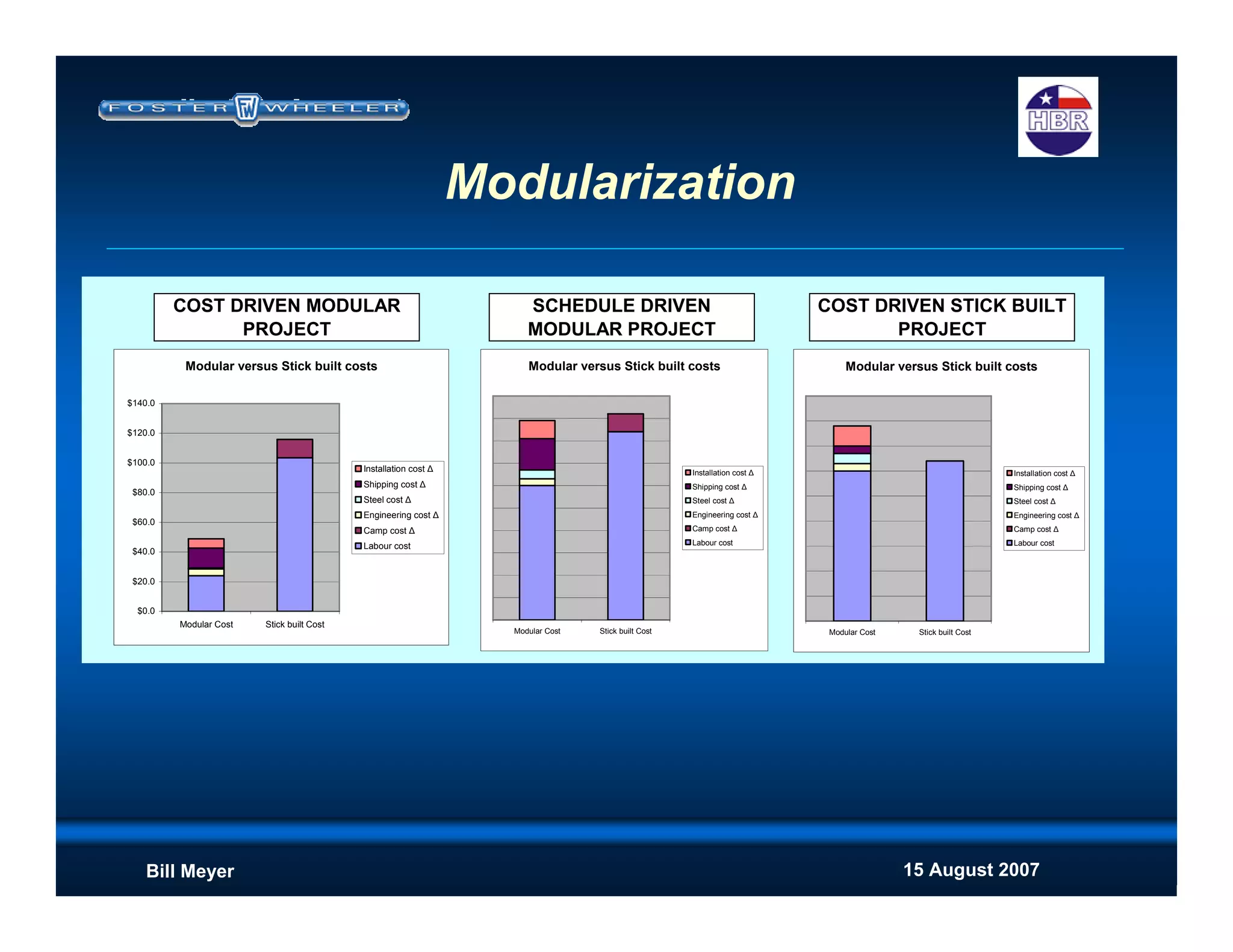
Cost Upside
Move labor cost offsite to cheaper labor supply
Reduce indirect costs (camp, construction supervision, consumables etc
at the site rates)
Improved productivity (weather, flexible workforce, site accessability etc)
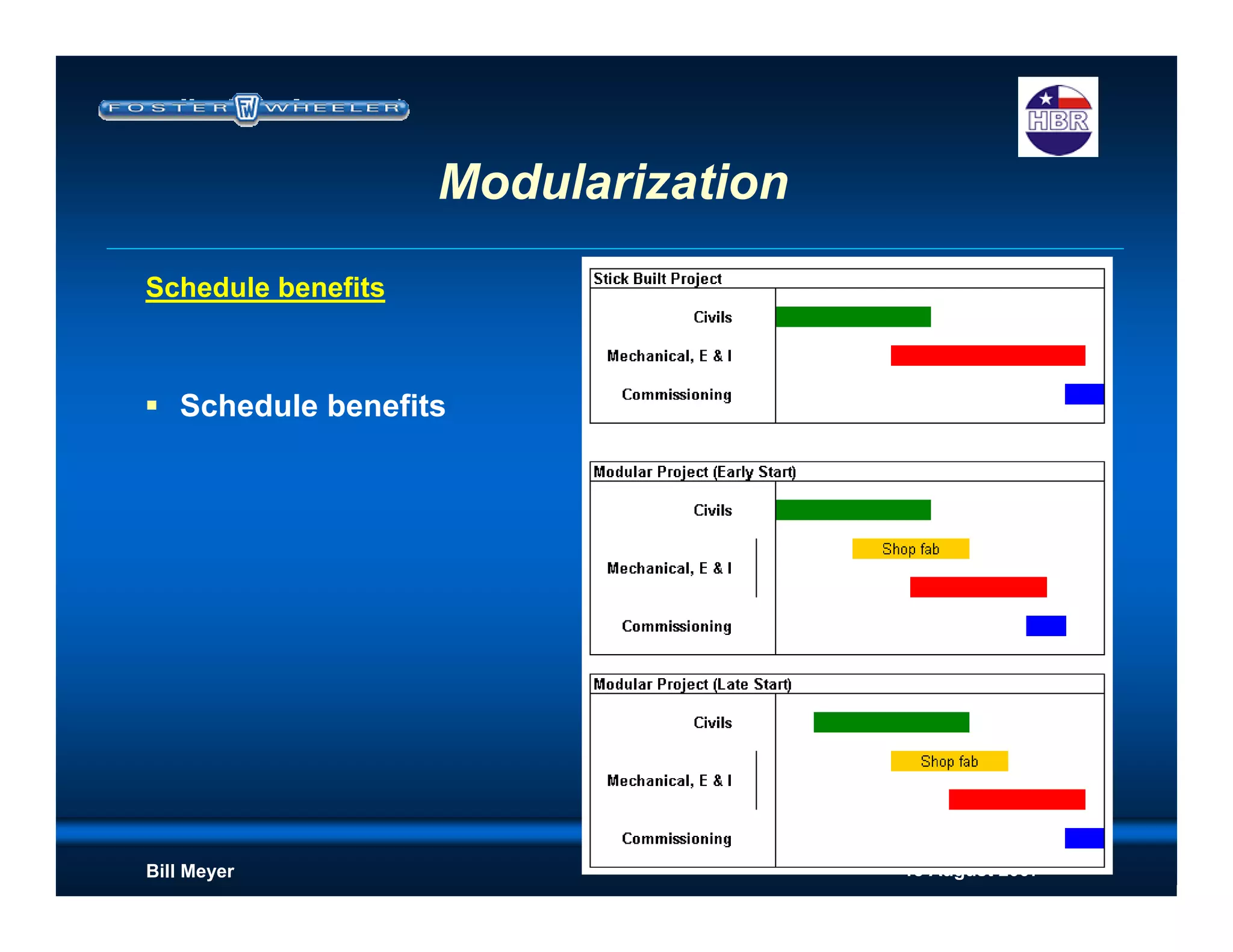
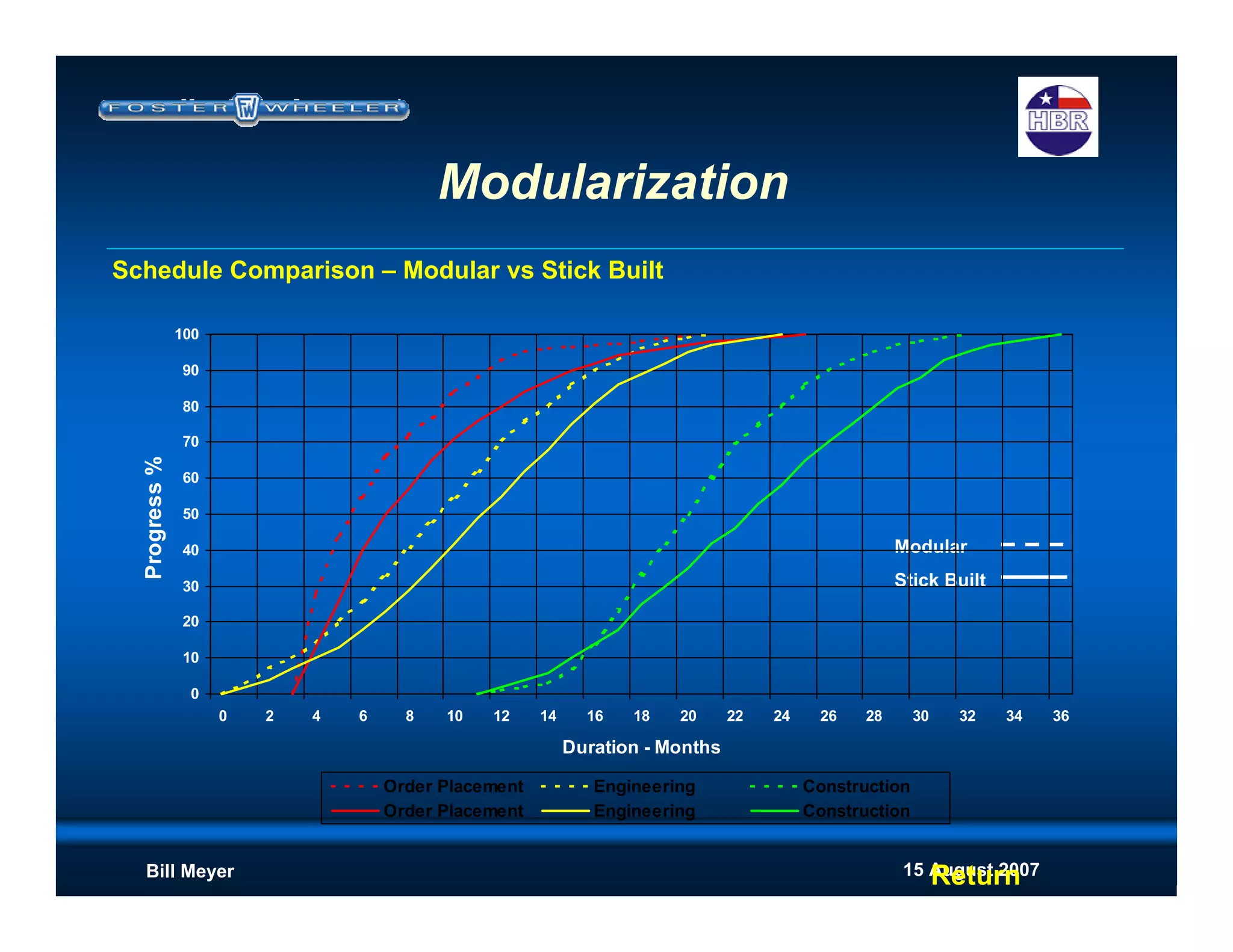
Reduced schedule - reduces construction indirects
[Positive impact to NPV if revenue stream begins earlier]
Modularization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modularizationpresentationforhbr-12905111549698-phpapp01/75/Modularizationpresentationfor-Hbr-16-2048.jpg)