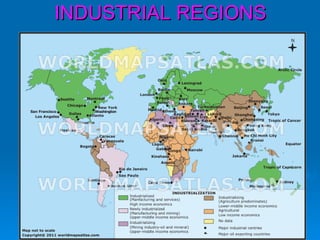
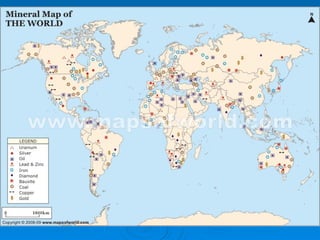
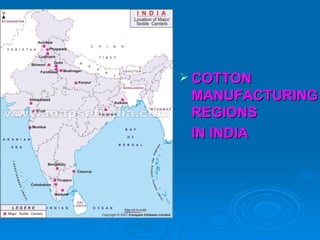
The document discusses different types of industries. It describes agro-based, mineral-based, marine-based and forest-based industries which use plant/animal, mineral ores, sea products, and forest produce as raw materials respectively. It also discusses factors affecting industry location and different sectors (private, public, joint, cooperative). Major global industries mentioned are iron/steel, textile, and information technology concentrated in countries like Germany, USA, China, India. Pittsburgh is highlighted as an important steel city in the US.