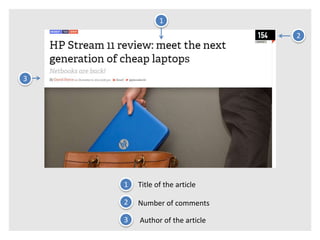
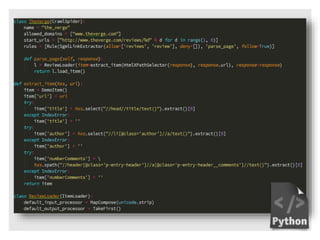
This document introduces Scrapy, an open source and collaborative framework for extracting data from websites. It discusses what Scrapy is used for, its advantages over alternatives like Beautiful Soup, and provides steps to install Scrapy and create a sample scraping project. The sample project scrapes review data from The Verge website, including the title, number of comments, and author for the first 5 review pages. The document concludes by explaining how to run the spider and store the extracted data in a file.