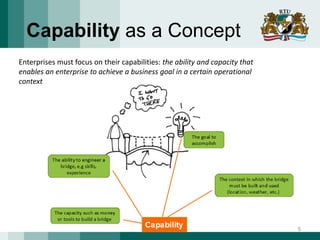
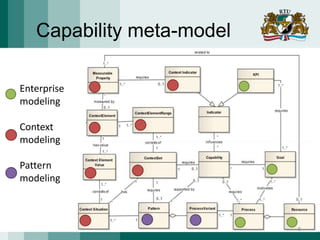
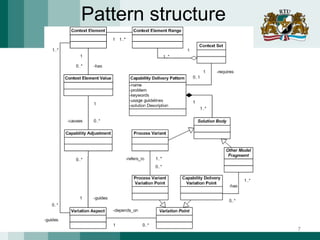
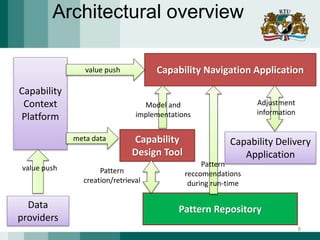
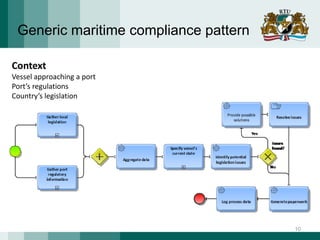
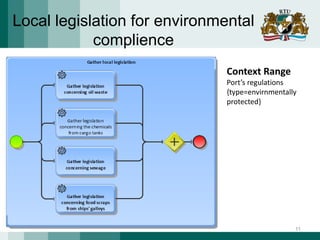
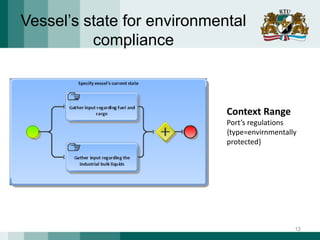
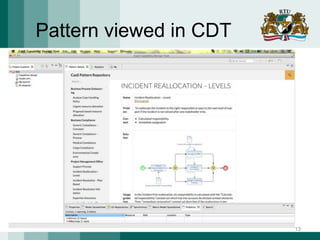
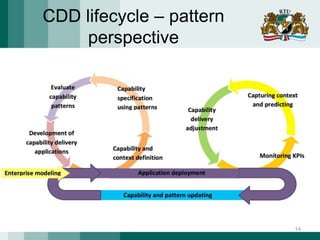
The document discusses the need for adaptive business applications and proposes the use of capability patterns to drive model-based development within a business context. It highlights the importance of integrating reusable software and organizational patterns to meet specific situational goals. The conclusions outline future work, including the development of a pattern repository for improved integration and support in capability-driven development.