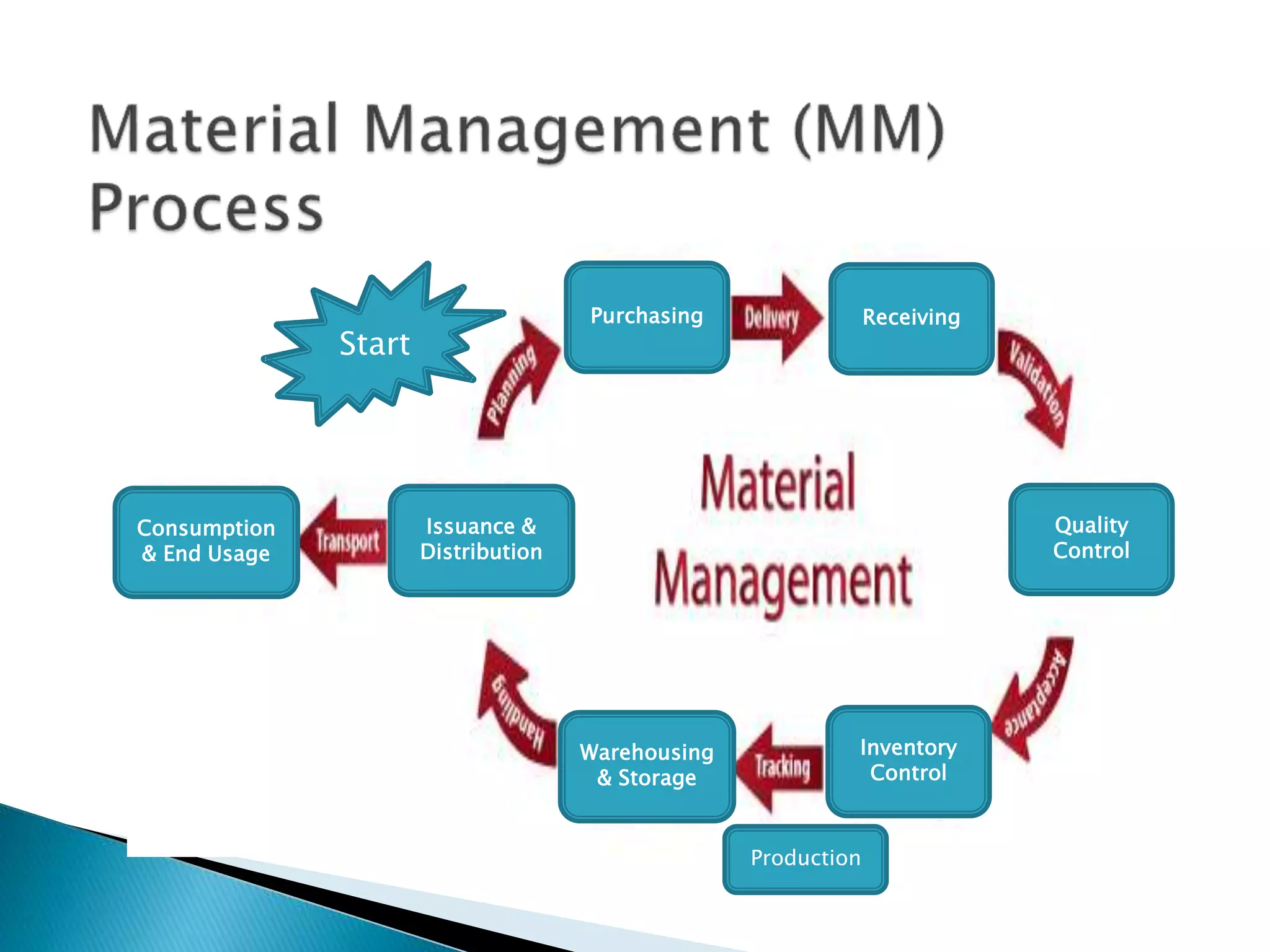
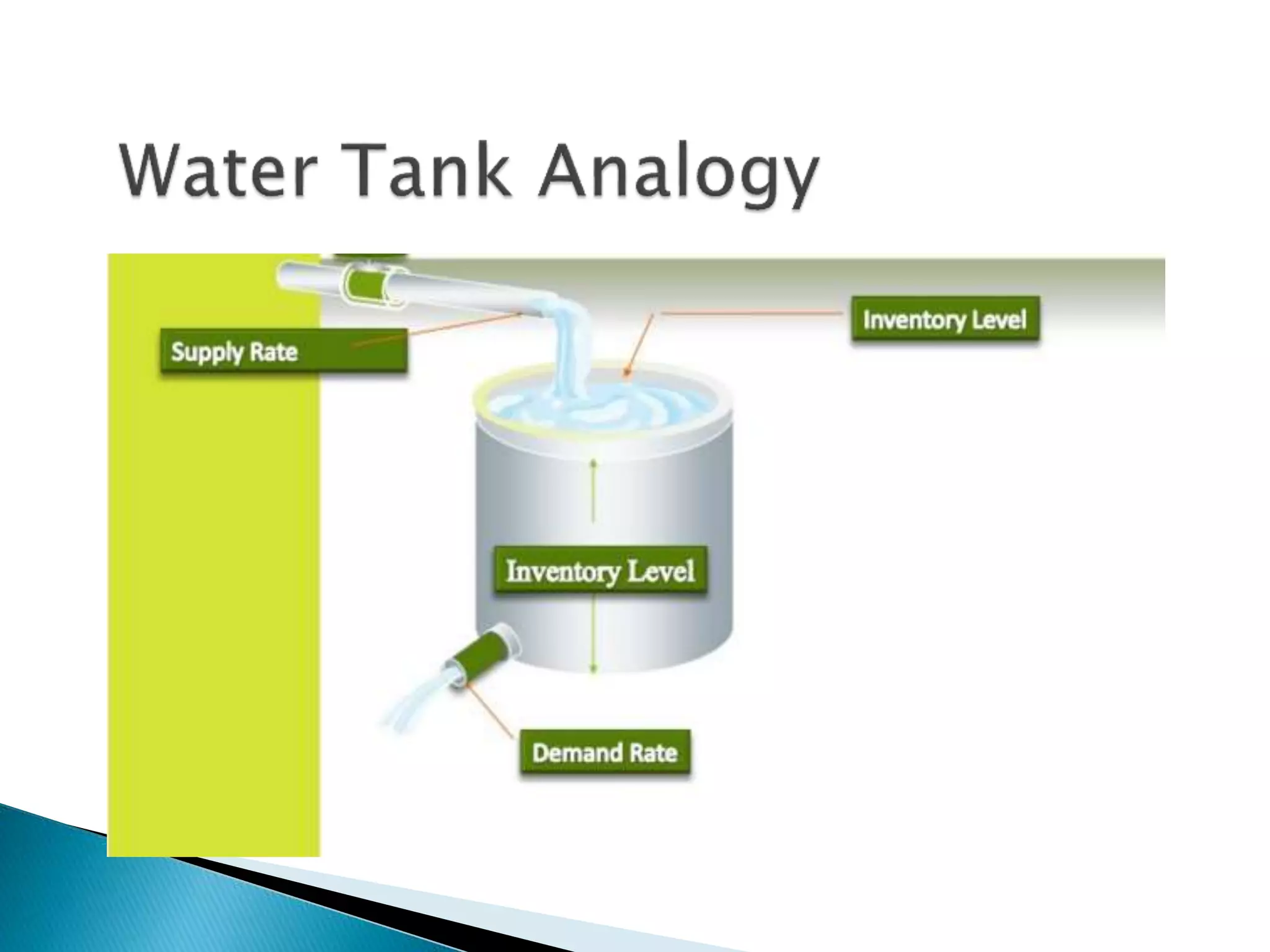
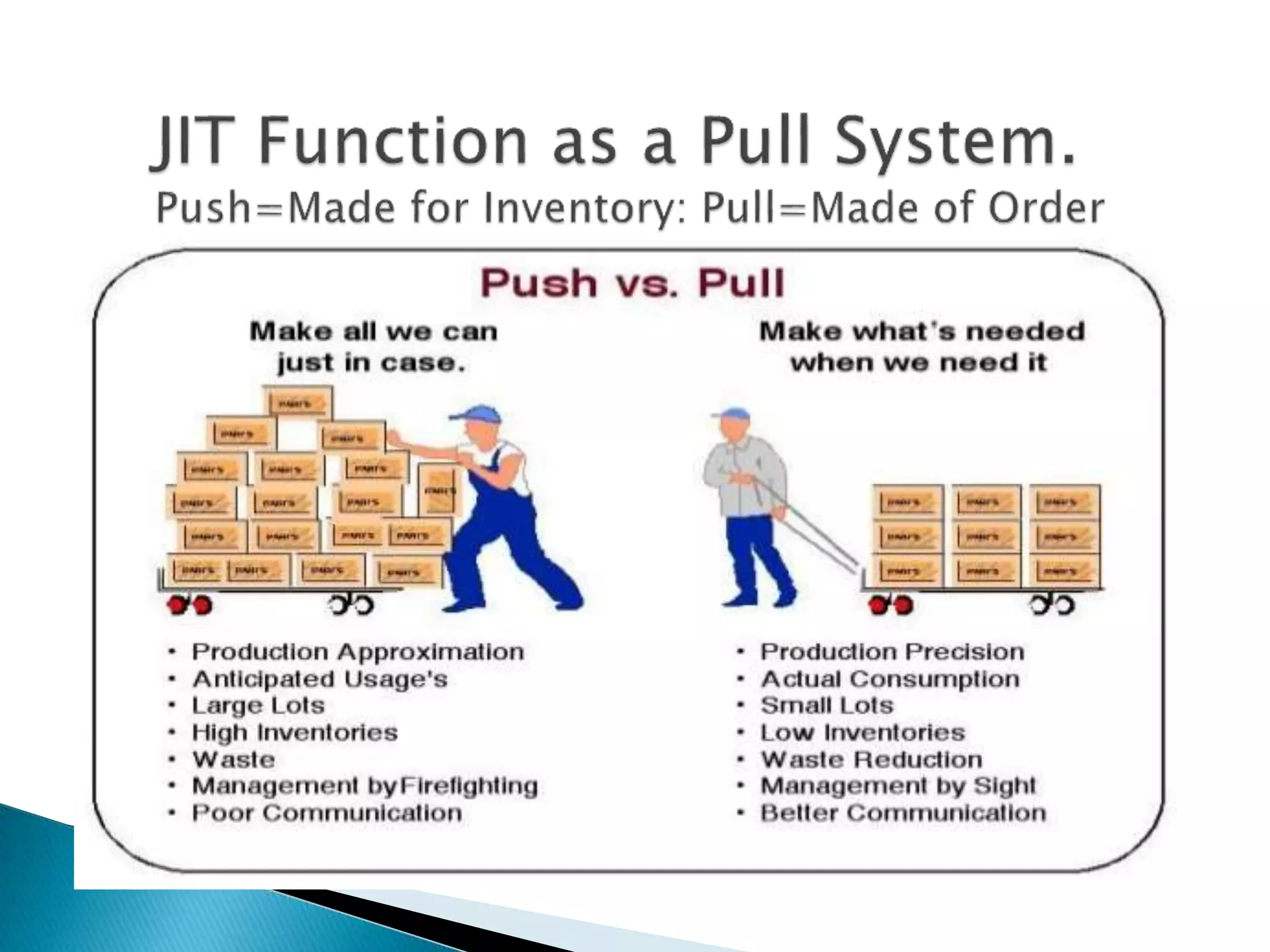
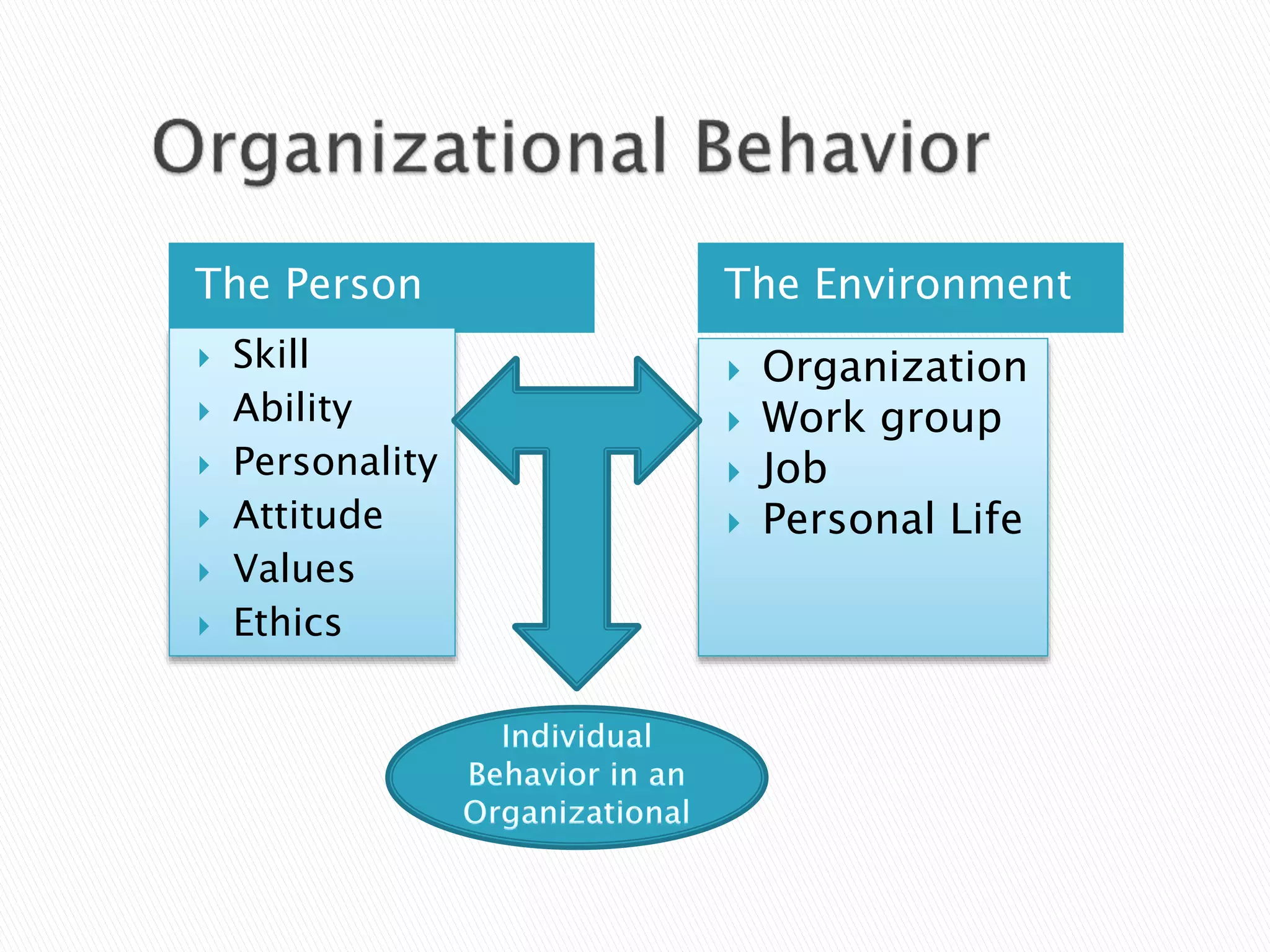
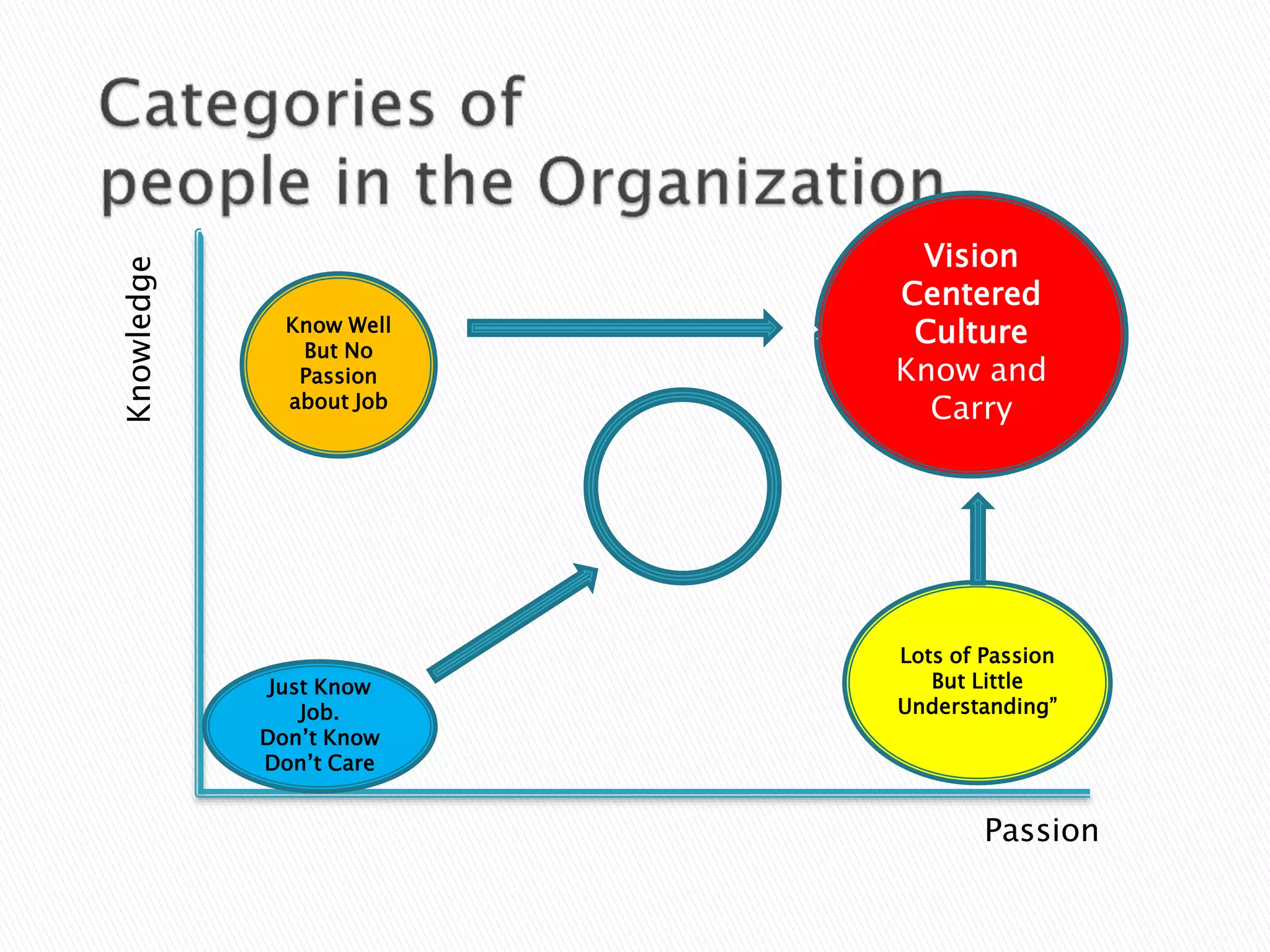
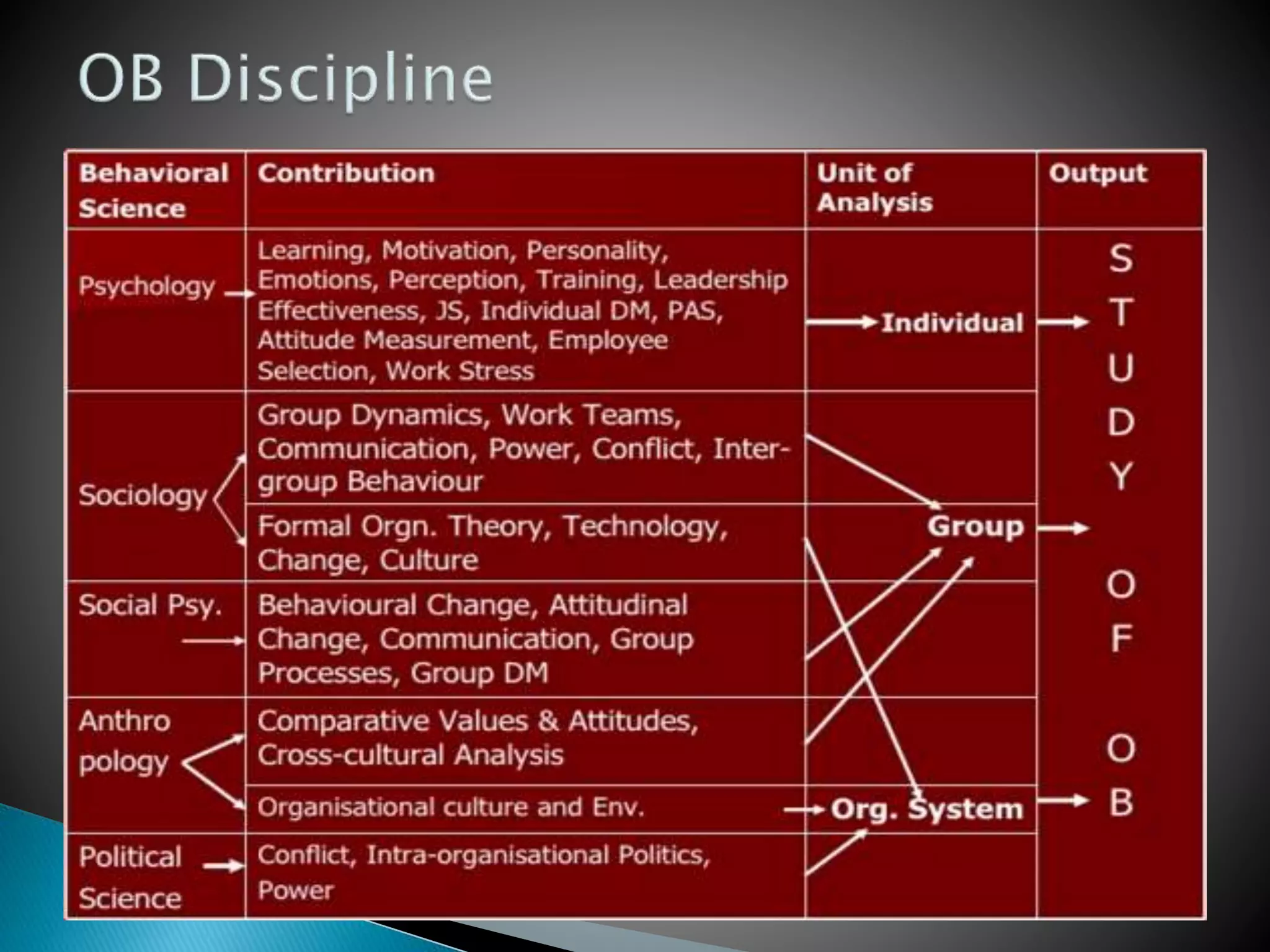
The document discusses material management in three parts. It first outlines the scope, objectives, departments, and functions of material management. This includes material planning, purchasing, inventory control, and warehousing. It then explains why material management is necessary, such as stabilizing production and meeting demand. Finally, it discusses the systems used in material management and challenges in implementing material management, such as forecasting demand accurately and managing information.