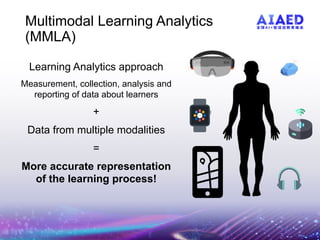
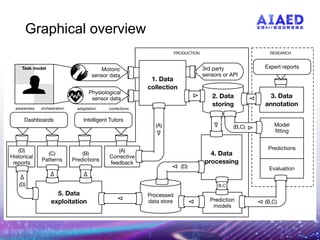
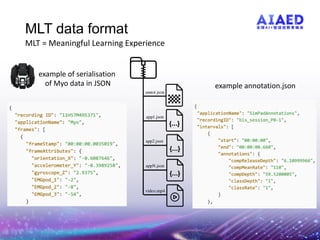
The document presents the multimodal learning analytics (MMLA) pipeline, a comprehensive framework designed to collect and analyze multimodal data to enhance learning experiences. It addresses challenges associated with complex multimodal data, offering solutions for quicker experiment setups, standard tools, and reduced data manipulation overhead. Current prototypes and applications demonstrate its utility in intelligent tutoring systems, with future directions including real-time feedback and collaborative learning capabilities.