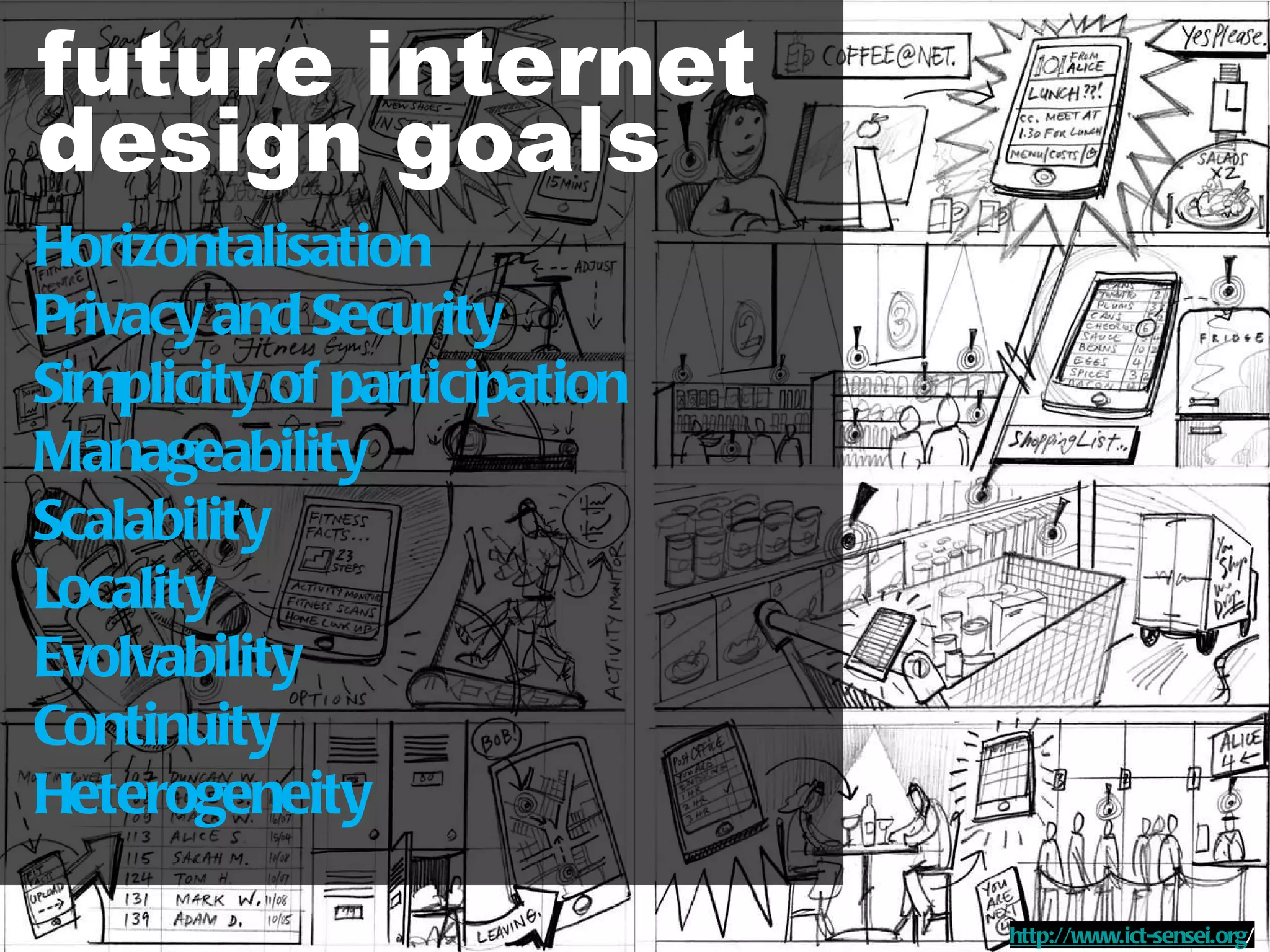
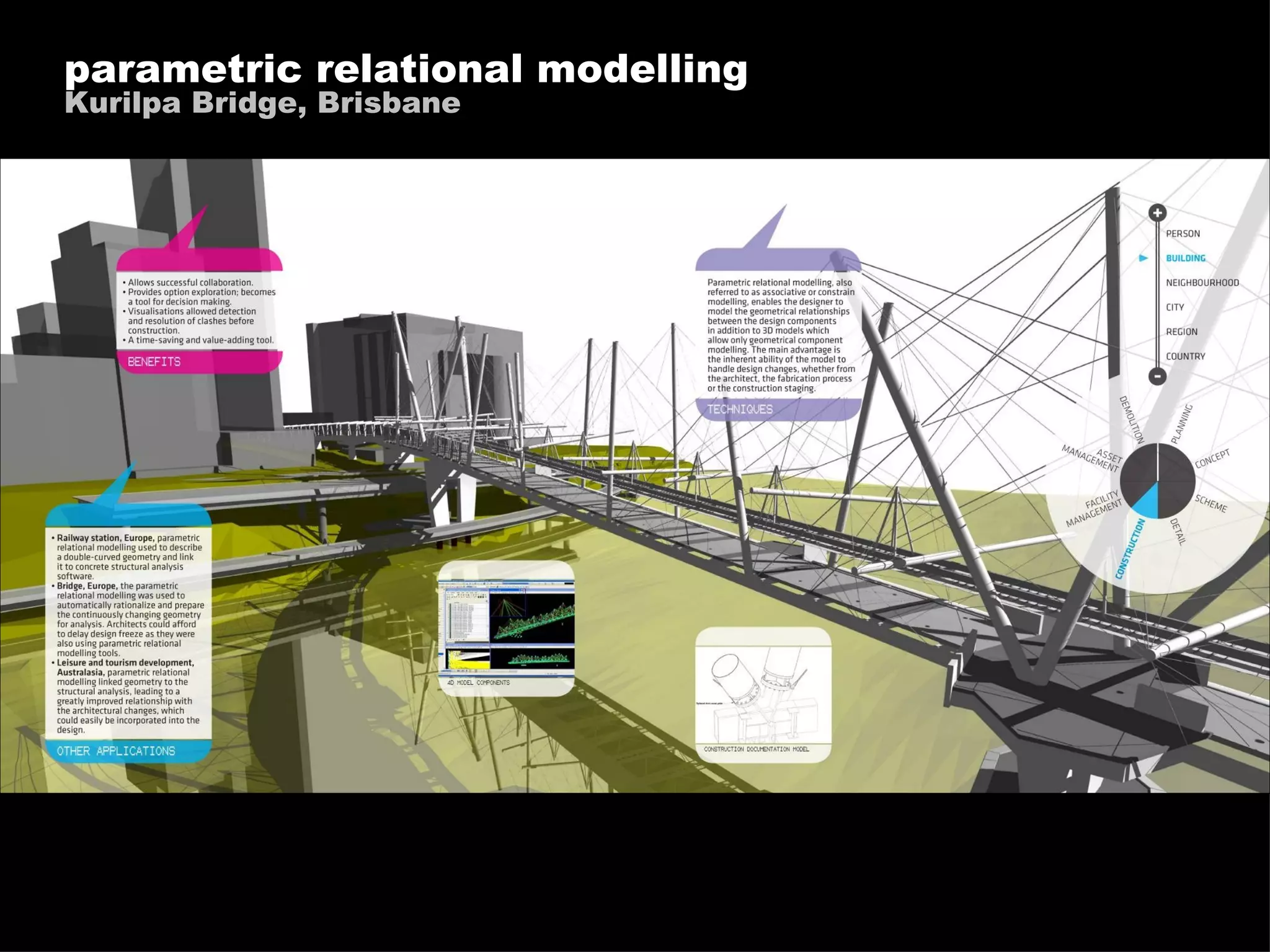
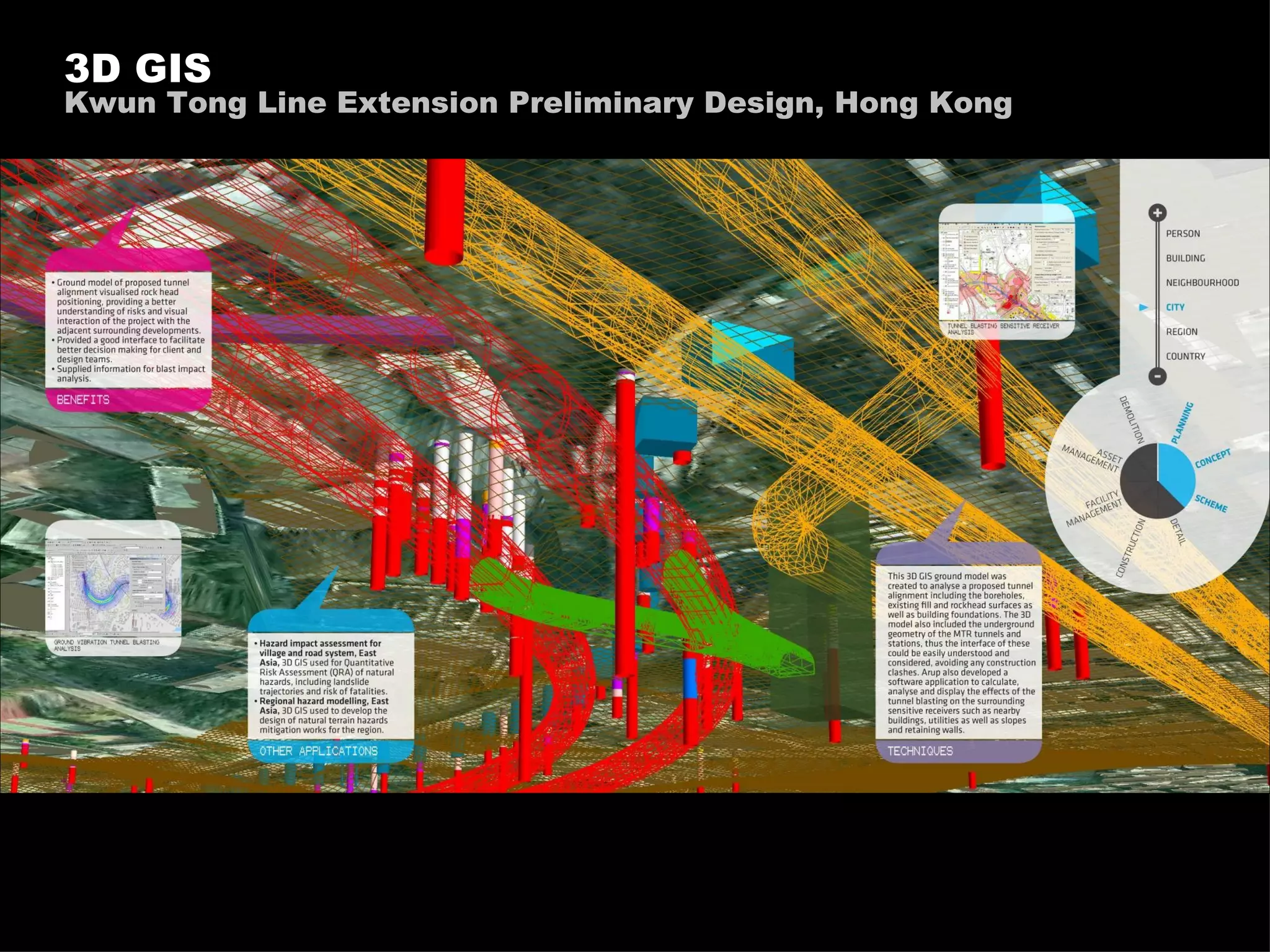
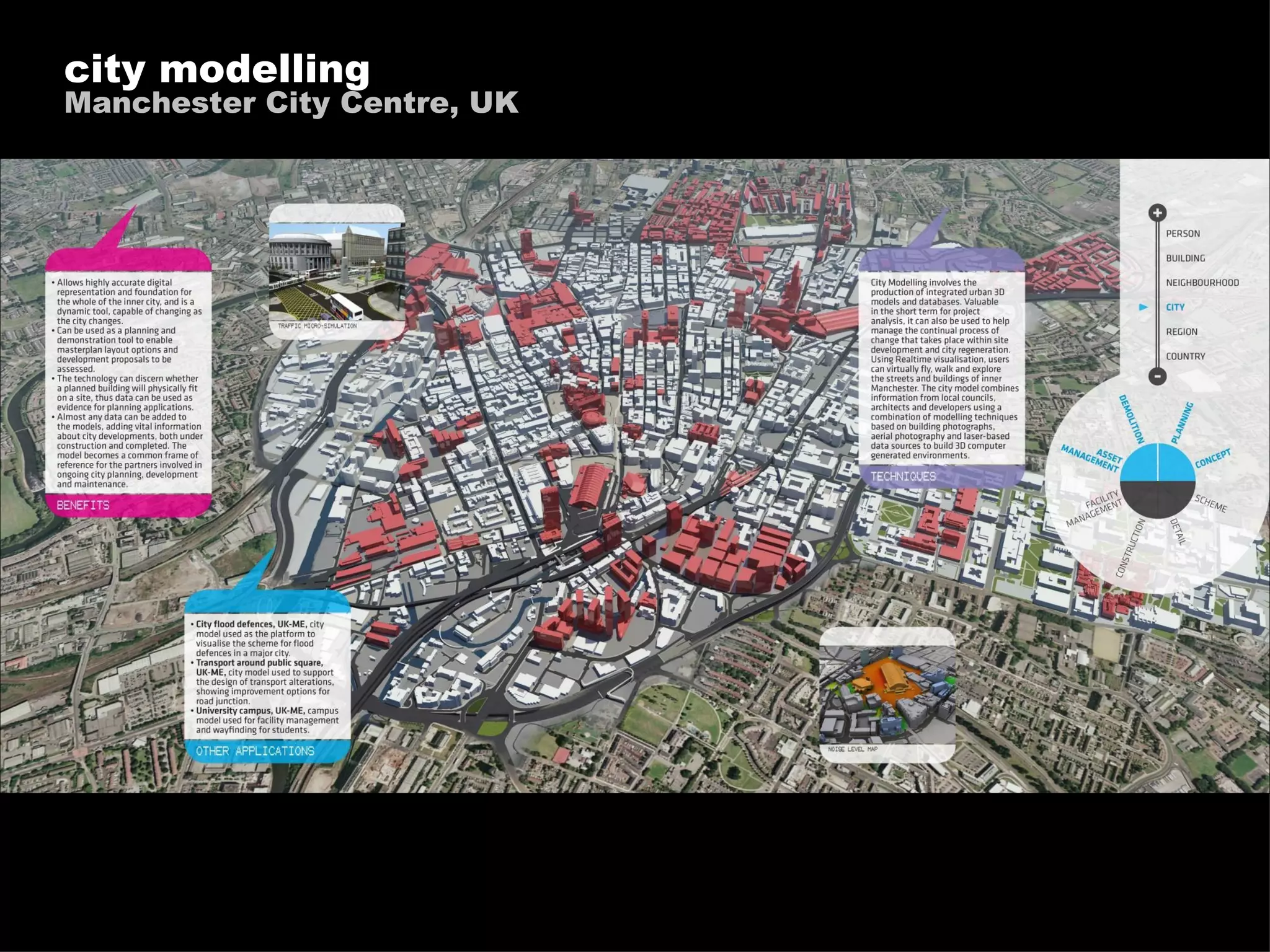
The document discusses how information technology is profoundly impacting how the built environment is planned, designed, constructed, and operated. It mentions examples of using multi-disciplinary simulation, visualization, parametric modeling, 3D GIS, and BIM technologies in major infrastructure and building projects. It also discusses using continuous post-occupancy feedback and data shadows to better understand resource use and adapt buildings over time. Finally, it explores the potential of urban informatics and ambient information displays to make cities more efficient, connected, and provide a high quality of life for citizens.










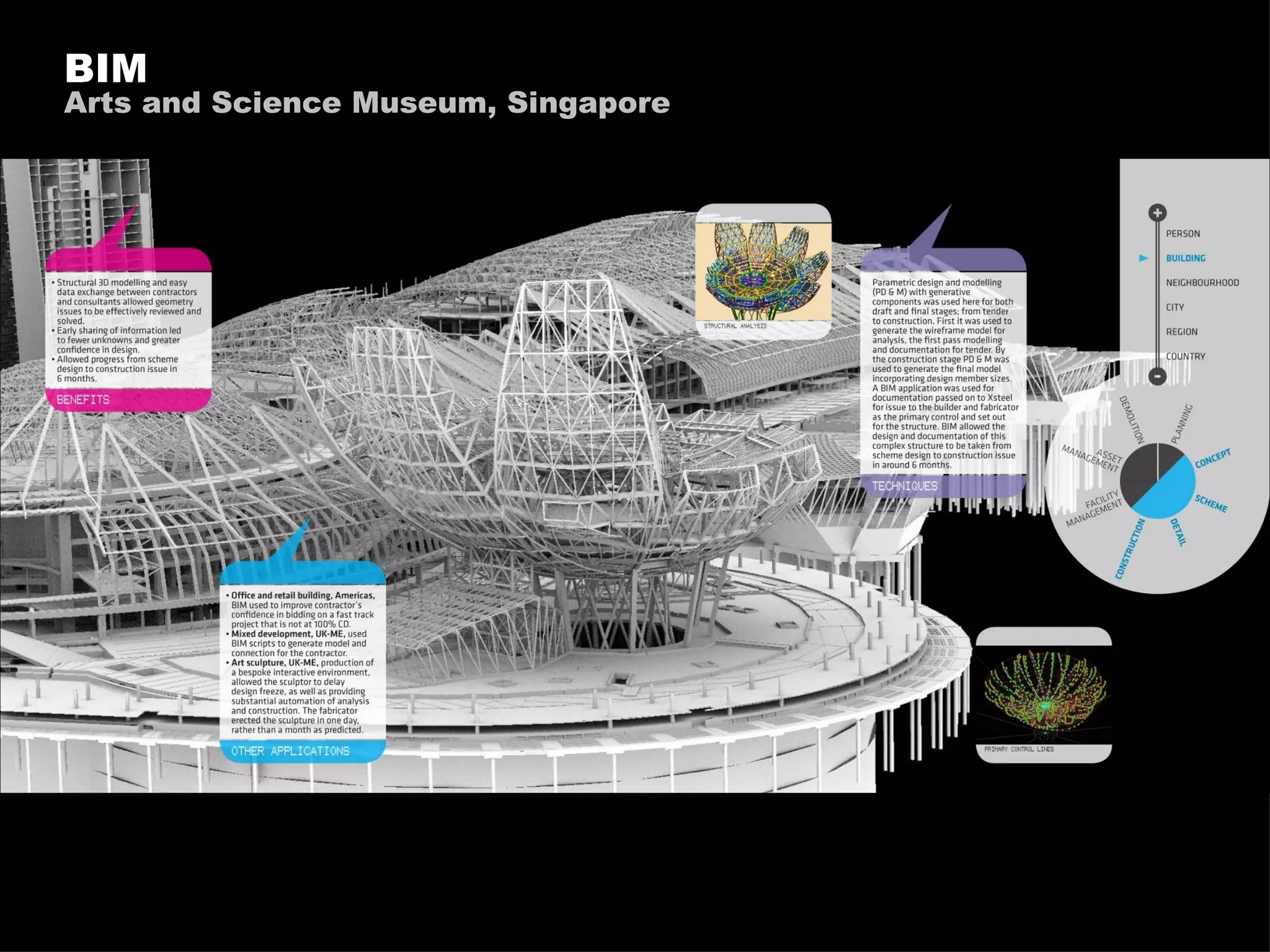

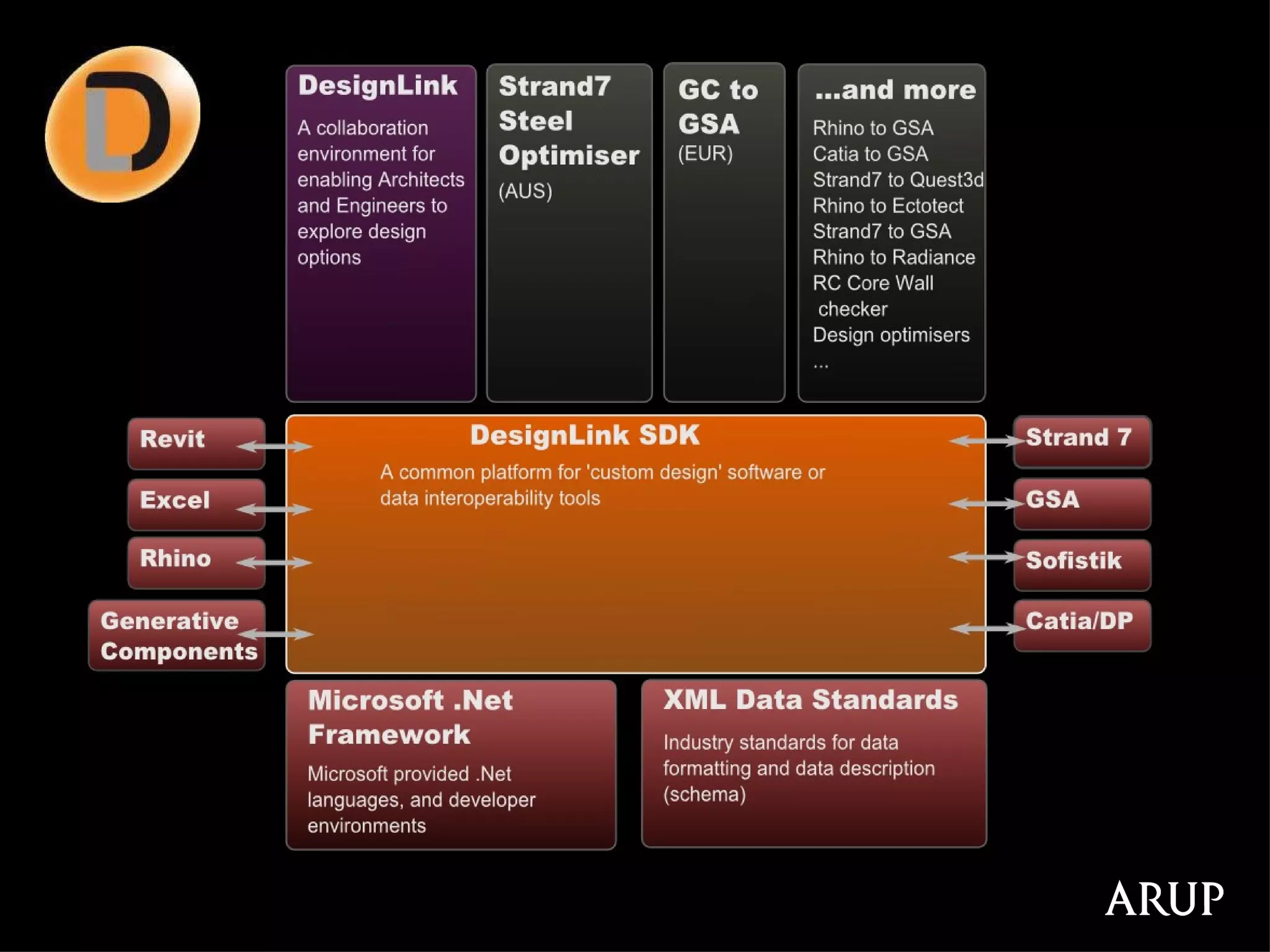




![[understanding resource use - regulation, publicity, cost saving]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-21-2048.jpg)
![[understanding resource use - regulation, publicity, cost saving]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-22-2048.jpg)
![[understanding resource use - regulation, publicity, cost saving]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-23-2048.jpg)
![[adaptive ambient information - making it playful]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-24-2048.jpg)

![urban informatics efficiency connectivity [cities to be better managed, more resource efficient and maintain a high quality of life]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-26-2048.jpg)
![[first really comprehensive review of informatics at a city level with a client]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-27-2048.jpg)
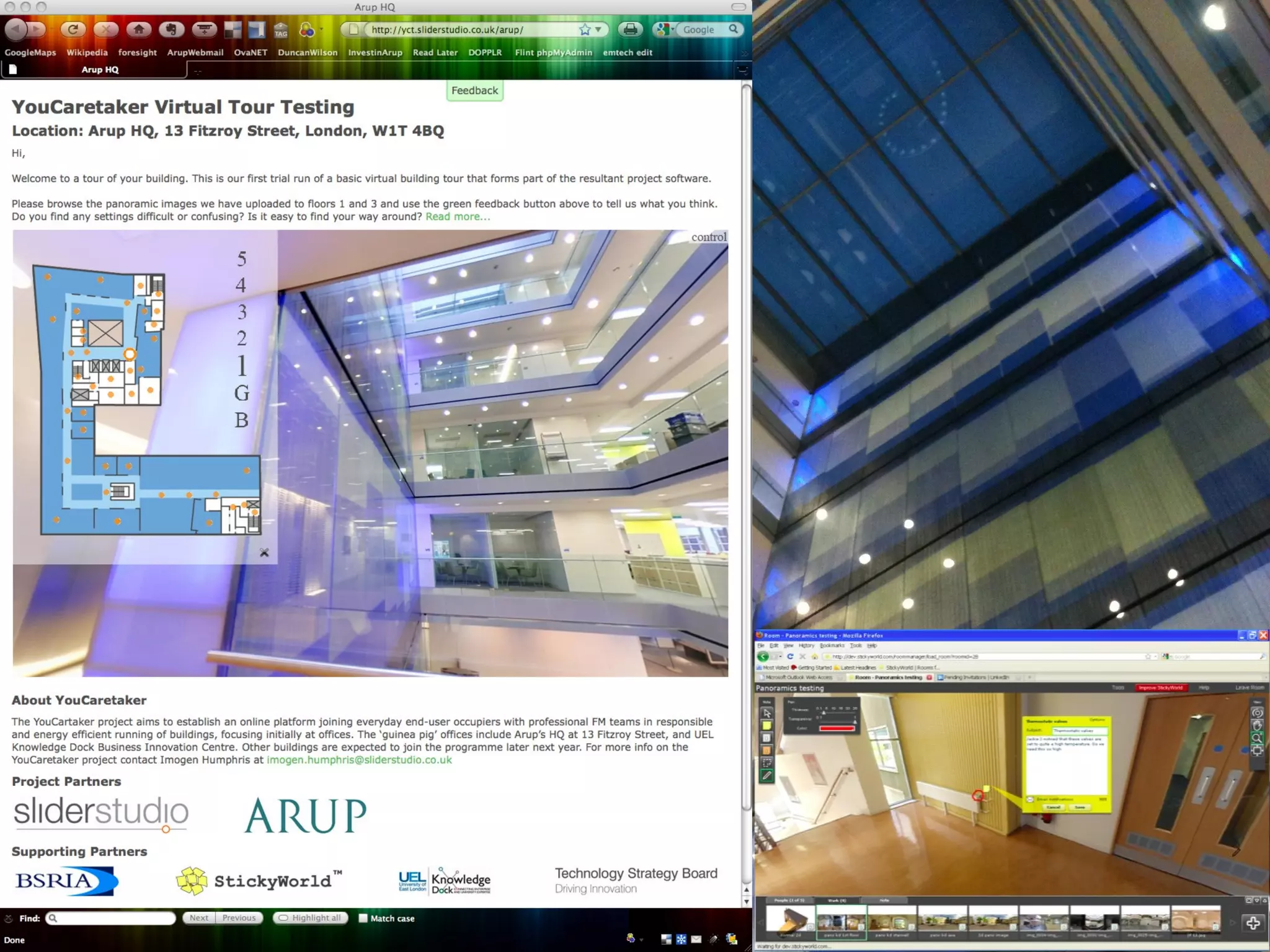

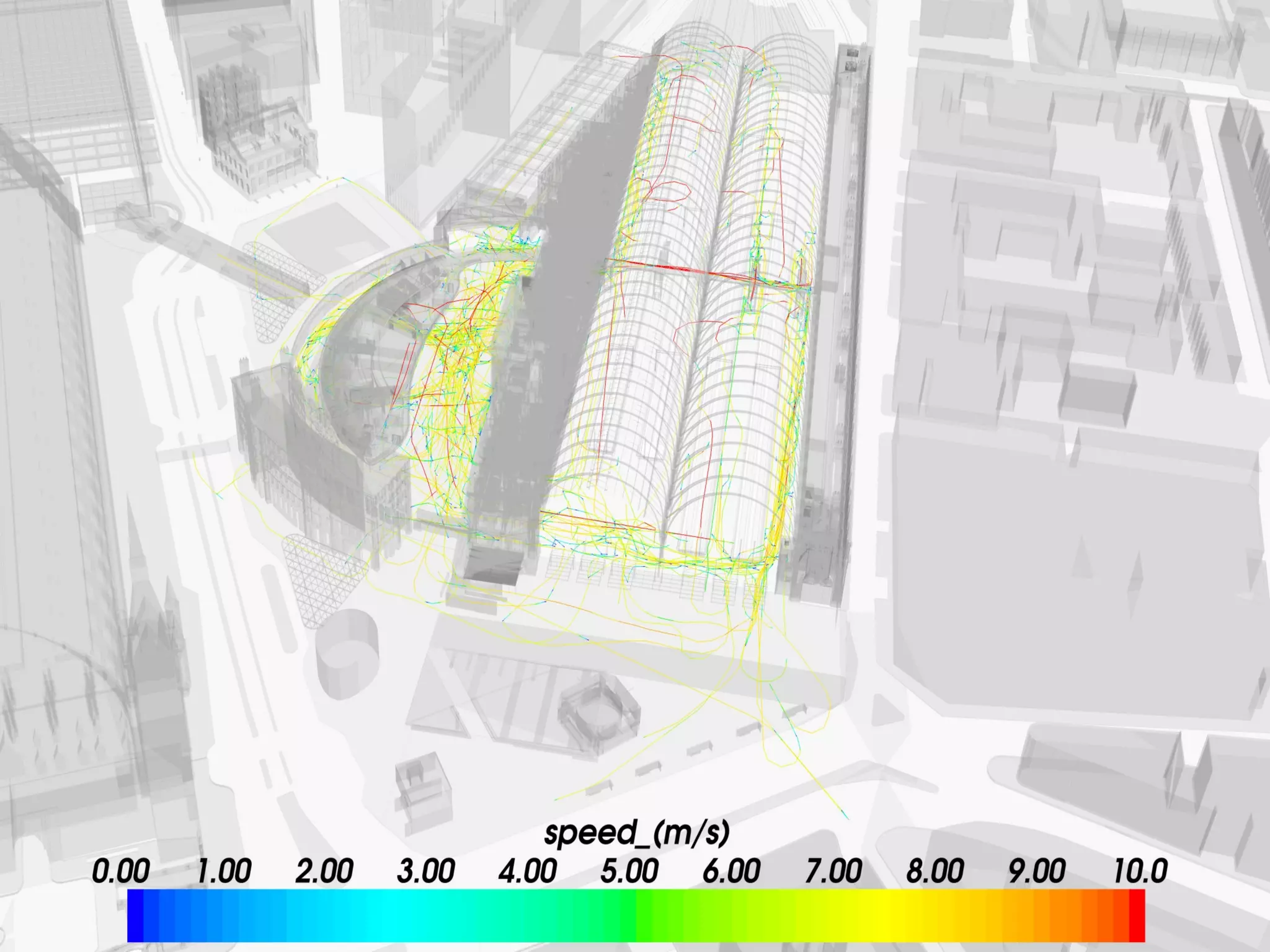
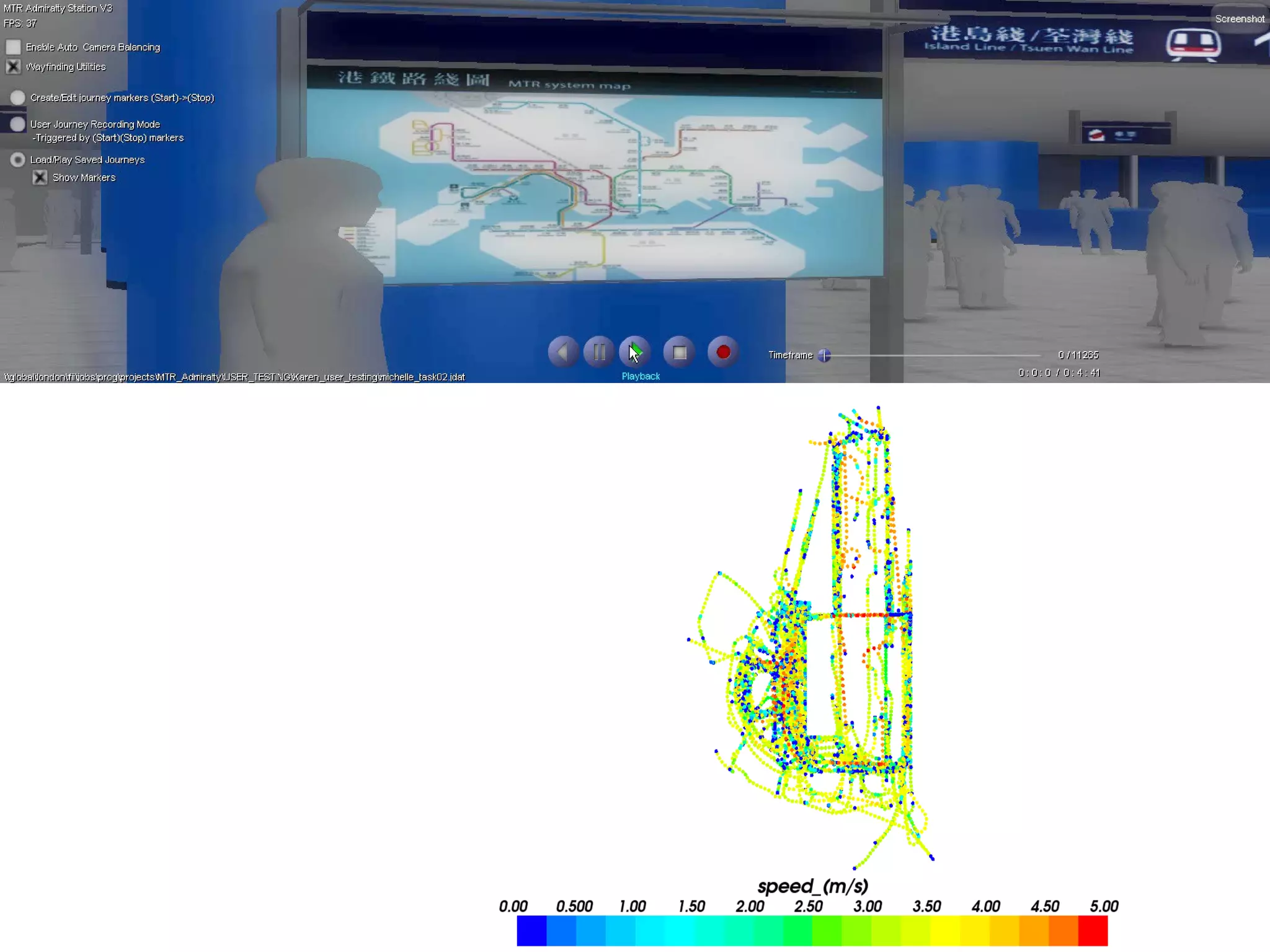


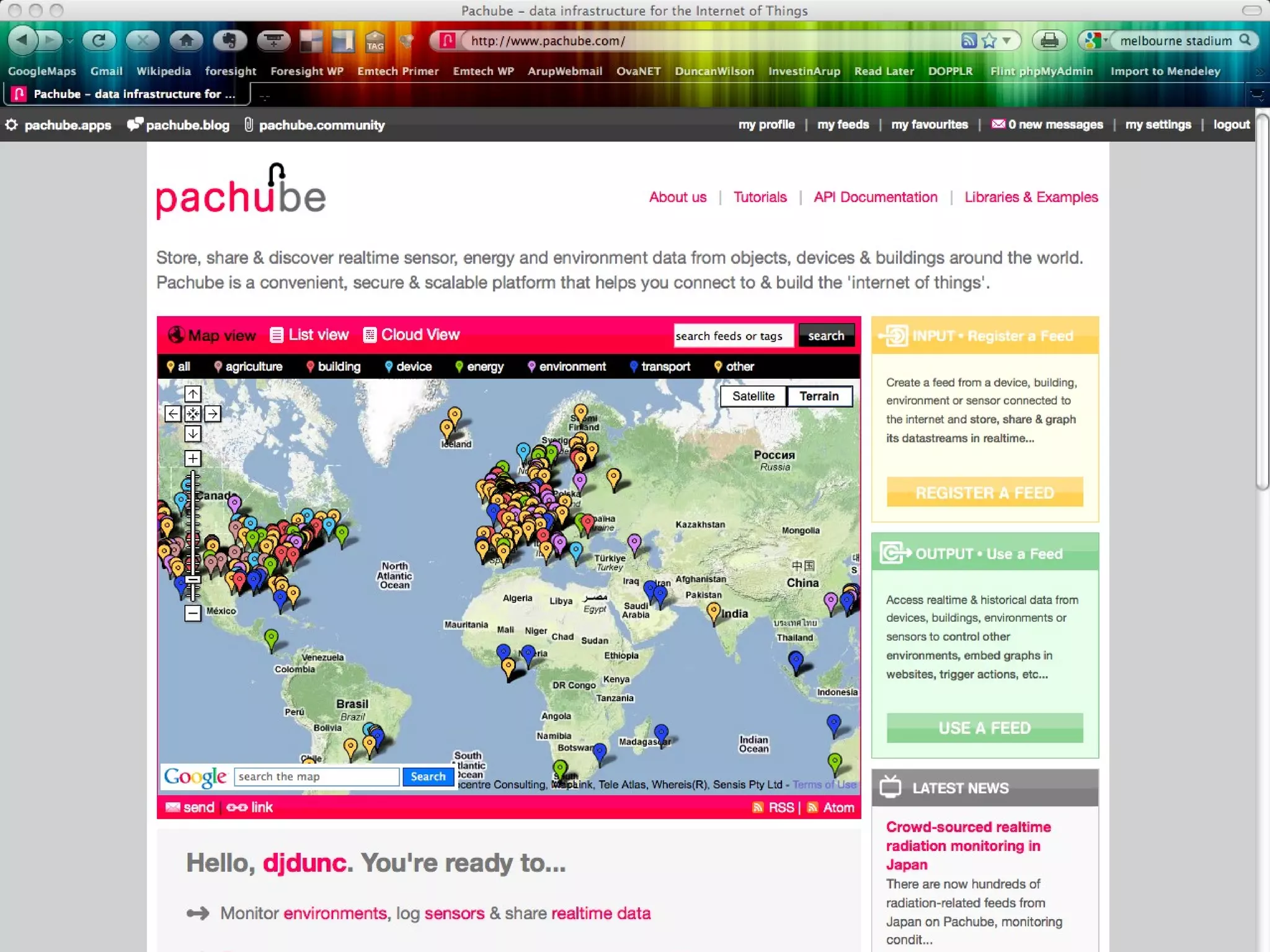
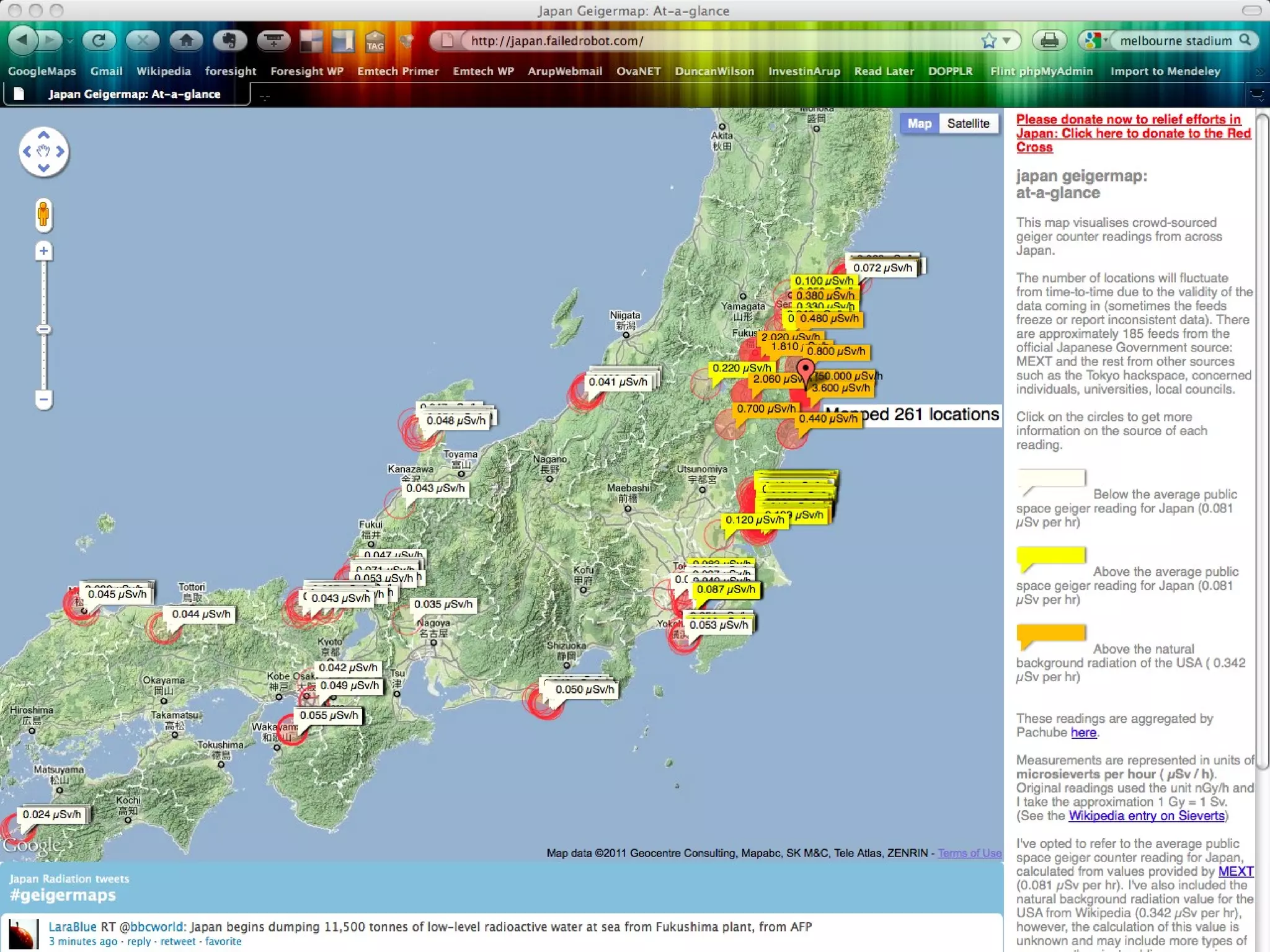

![Place-stat s Place-stat us Place-stat ements [understanding flow]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-37-2048.jpg)


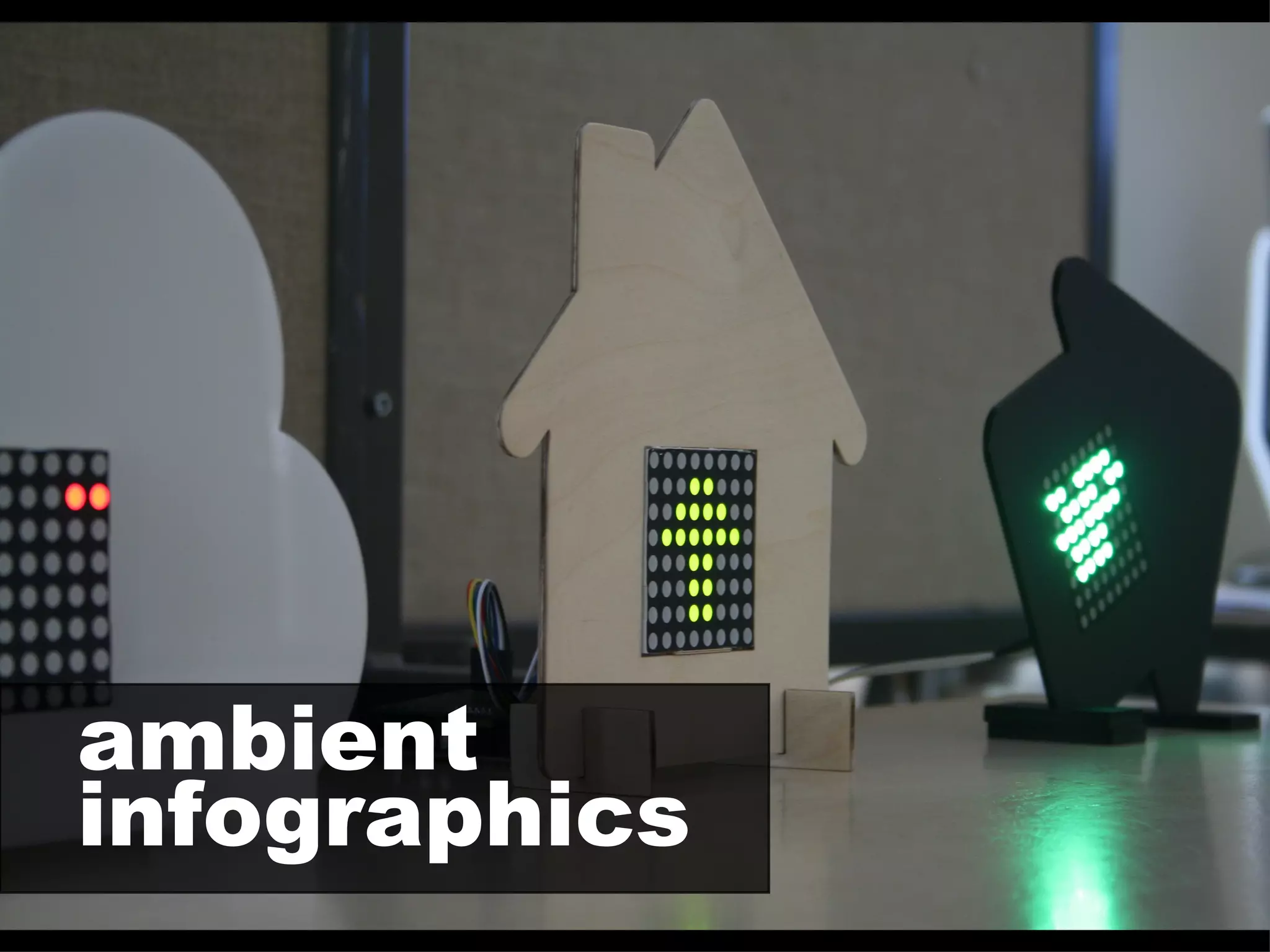

![[making explicit what is largely an invisible process of knowledge work – providing context around a space]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-42-2048.jpg)

![[the “hello world” of urban informatics]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011enrfuturetech-110520093744-phpapp02/75/2011-ENR-Future_Tech-44-2048.jpg)