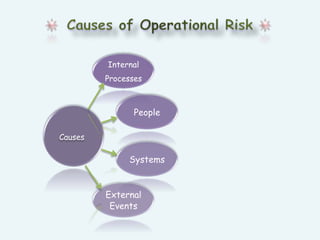
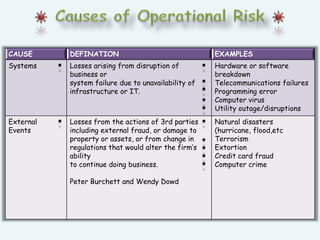
Operational risk refers to the risk of losses resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or people, or from external events. It is the risk remaining after accounting for market, credit, and other risks. Some key causes of operational risk include internal and external fraud, workplace issues, problems with clients, damage to physical assets, and business disruptions. Industries with lower human interaction tend to have lower operational risk. A case study describes how State Bank of India implemented straight-through processing to reduce operational risk from manual errors in transferring dealing data between its treasury and banking systems.