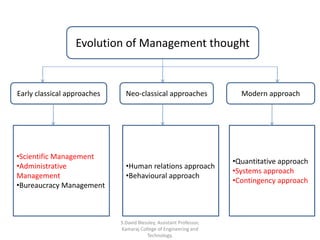
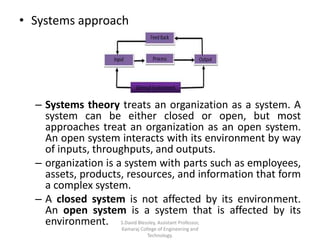
This document discusses the evolution of management theories including scientific management, administrative management, systems approach, and contingency approach. It provides details on scientific management pioneers like Taylor and the Gilbreths and their contributions like time and motion studies. It also summarizes Taylor's 14 principles of management and administrative theory. Finally, it describes key concepts of the systems approach in viewing an organization as an open system that interacts with its external environment.