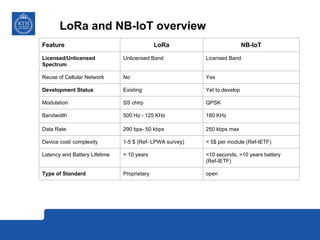
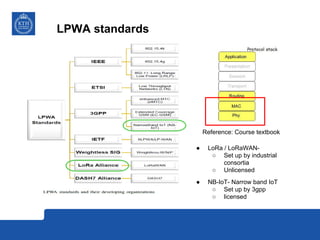
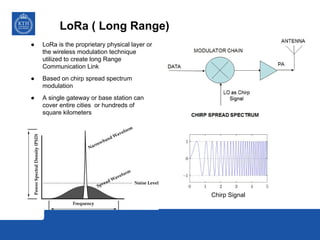
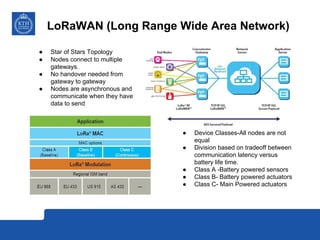
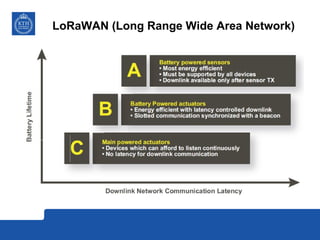
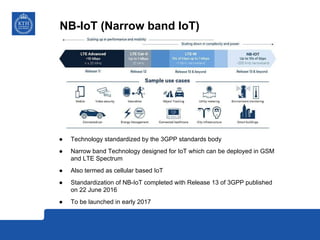
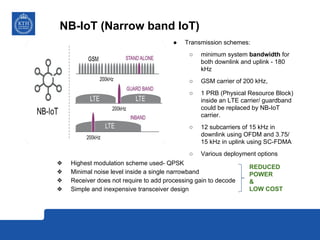
This document provides an overview and comparison of LoRa and NB-IoT low-power wide area network (LPWA) technologies. It discusses that both technologies were developed for applications requiring long battery life and low data rates. LoRa is an unlicensed standard based on chirp spread spectrum modulation, while NB-IoT is a licensed narrowband cellular standard developed by 3GPP. Key differences are that LoRa has lower device costs and supports higher latencies, while NB-IoT can leverage existing cellular networks and has higher data rates. In conclusion, LoRa is a new dedicated technology for IoT platforms, while NB-IoT uses existing cellular infrastructure.

![NB-IoT (Narrow band IoT)
● To enable low-complexity UE implementation, NB-IoT allows only one HARQ
process in both downlink and uplink, and allows longer UE decoding time
● Asynchronous, adaptive HARQ procedure is adopted to support scheduling
flexibility.
● Physical Channel/ Resource mapping
○ Extensive reuse of current LTE
(Long Term Evolution)
specifications
○ Few changes to physical channels
used in LTE (detailed review)
● Random Access :
○ *Contention based algorithm
similar to LTE [*Source- A Primer
on 3GPP Narrowband Internet of
Things (NB-IoT)]
UE
N/W
1
2
3
4
1. Preamble
2. Response containing advance
command and scheduling of the uplink
resources for the UE to use
3. Identity to the network
4. Contention resolution message](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/53283c72-7434-48a3-b4cc-41bb09879568-161031230026/85/LoRa-and-NB-IoT-11-320.jpg)