1. AVAudioEngine is a framework that simplifies building real-time audio apps on iOS and macOS. It allows playing, recording, and processing audio using a node-based graph architecture.
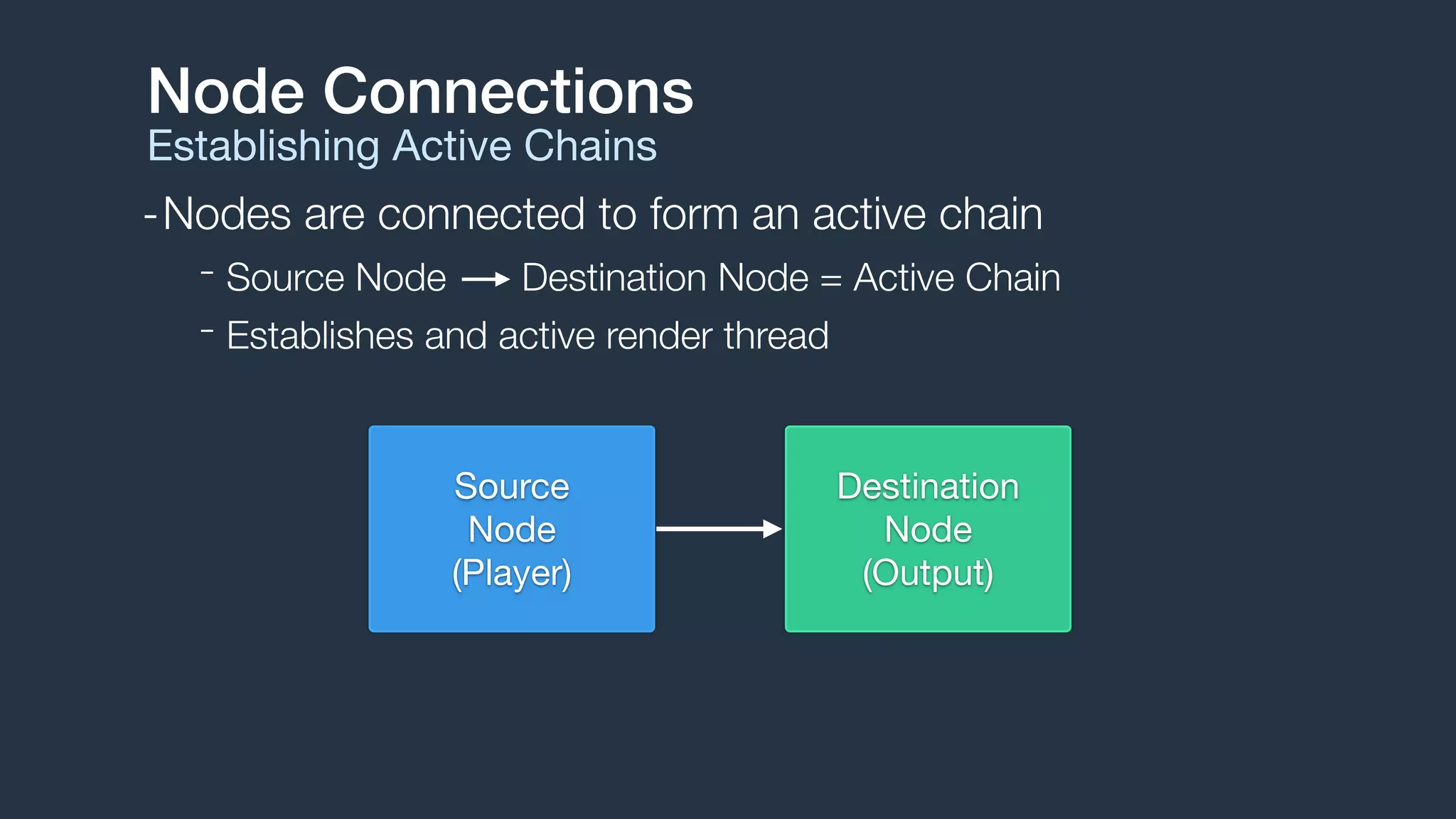
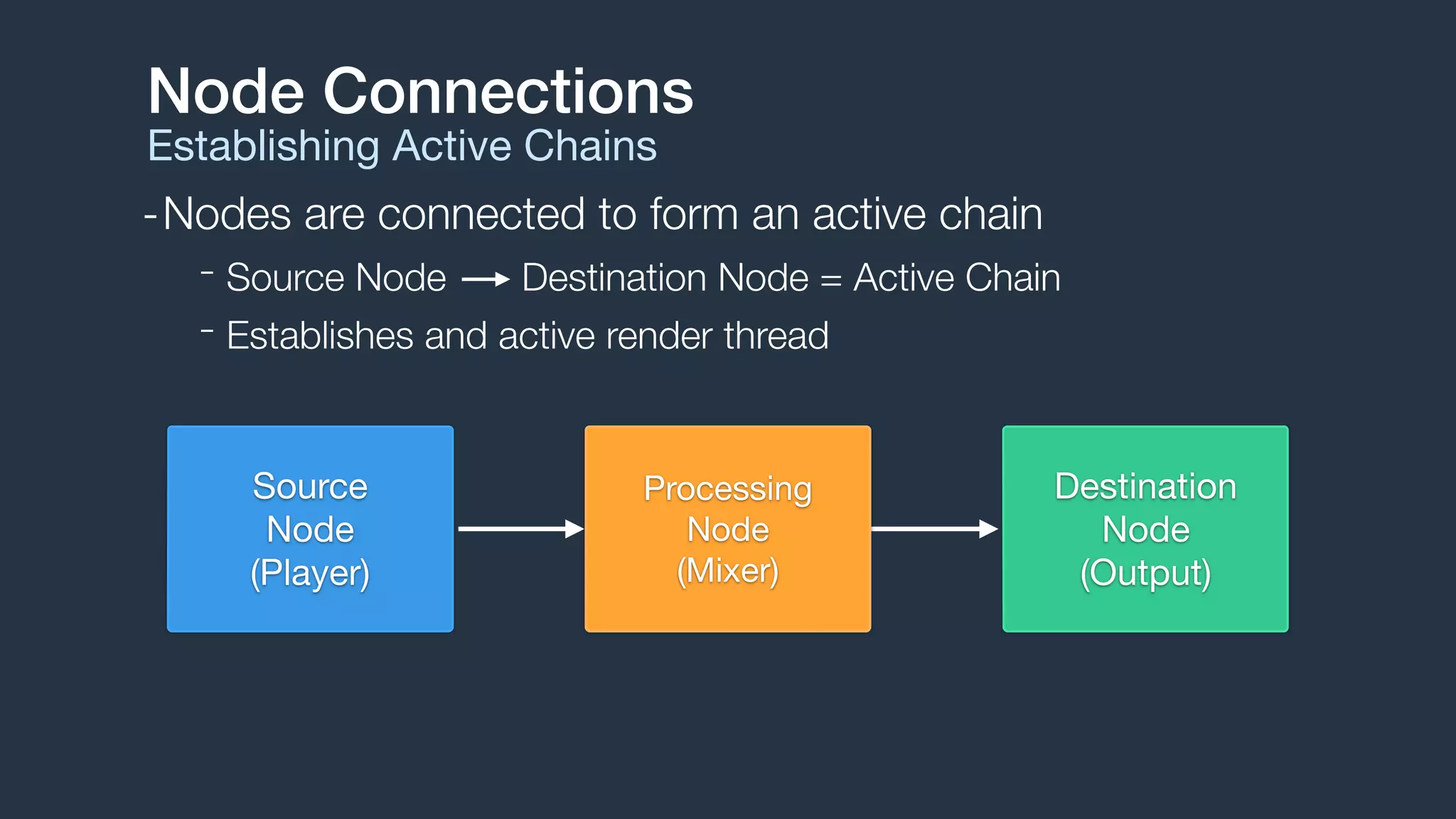
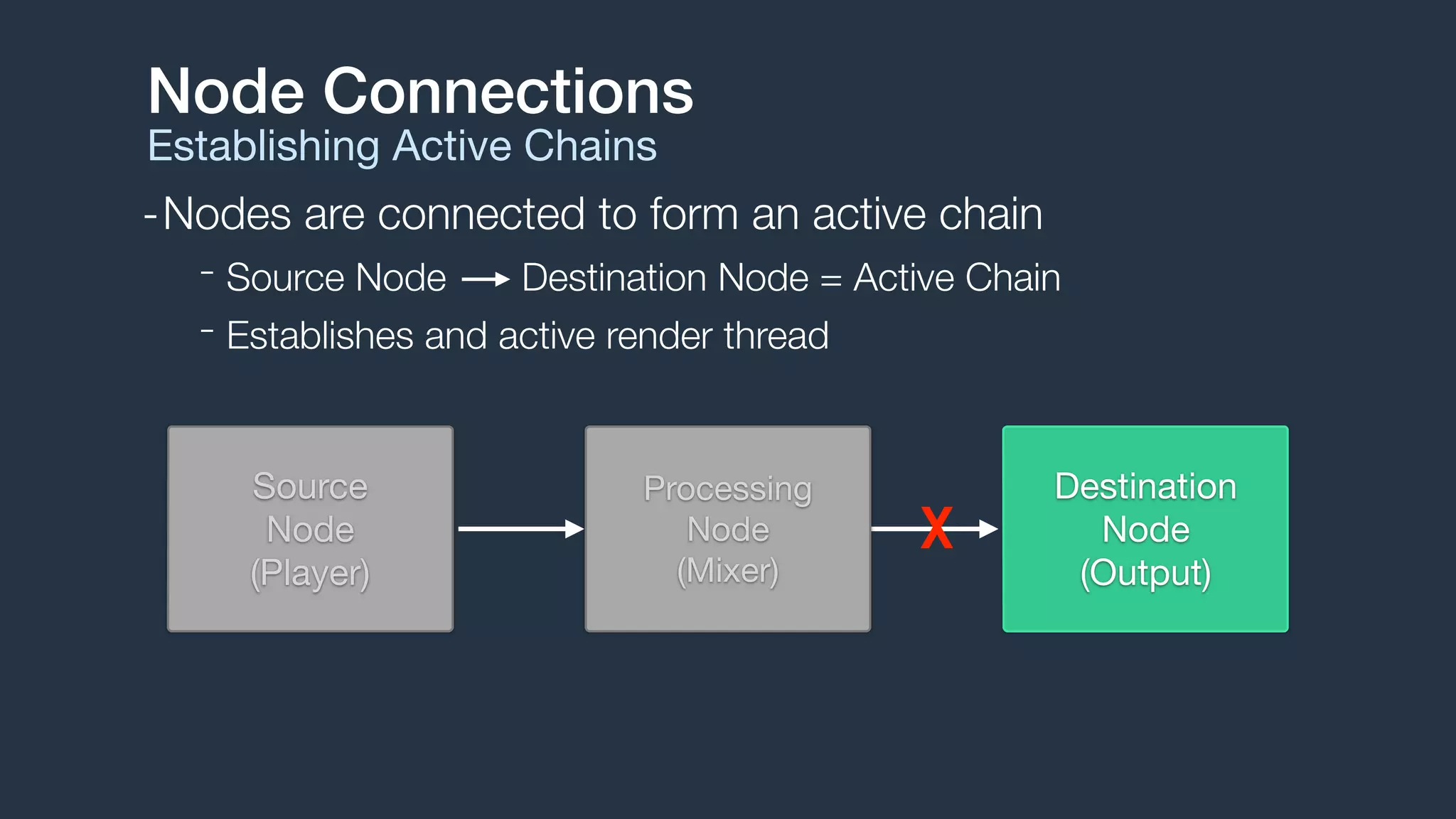
2. Audio flows through a graph of connected audio nodes, forming active chains that establish audio processing threads. Common node types include sources, processors, and destinations.
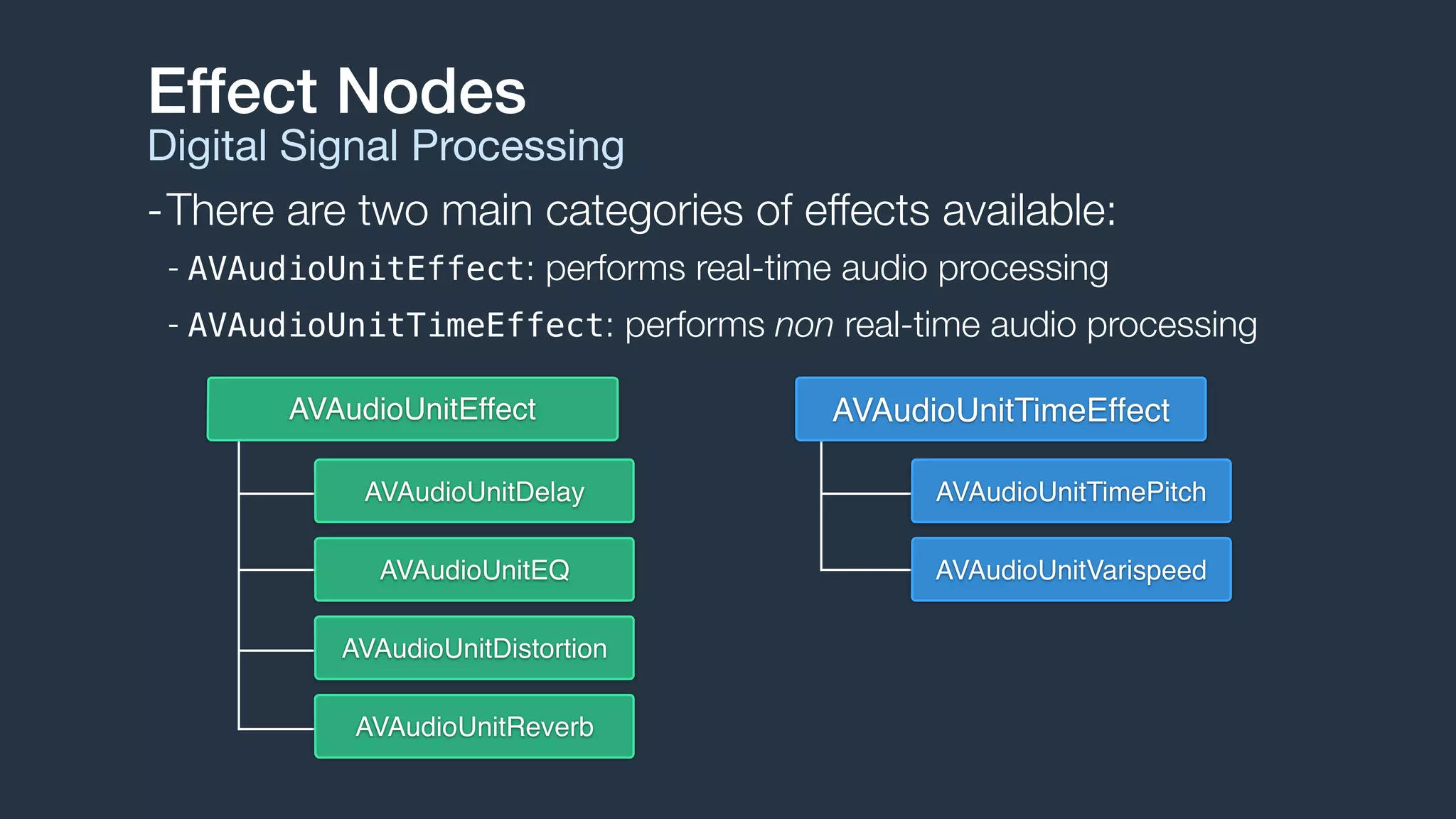
3. The engine handles audio format management, buffer scheduling, and thread synchronization. It supports audio file and buffer playback, recording, effects processing, audio mixing, and MIDI playback through sampler instruments.










![Engine Setup
Basic Recipe
// 1. Create engine (example only, needs to be strong reference)
AVAudioEngine *engine = [[AVAudioEngine alloc] init];
// 2. Create a player node
AVAudioPlayerNode *player = [[AVAudioPlayerNode alloc] init];
// 3. Attach node to the engine
[engine attachNode:player];
// 4. Connect player node to engine's main mixer
AVAudioMixerNode *mixer = engine.mainMixerNode;
[engine connect:player to:mixer format:[mixer outputFormatForBus:0]];
// 5. Start engine
NSError *error;
if (![engine startAndReturnError:&error]) {
// handle error
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-16-2048.jpg)

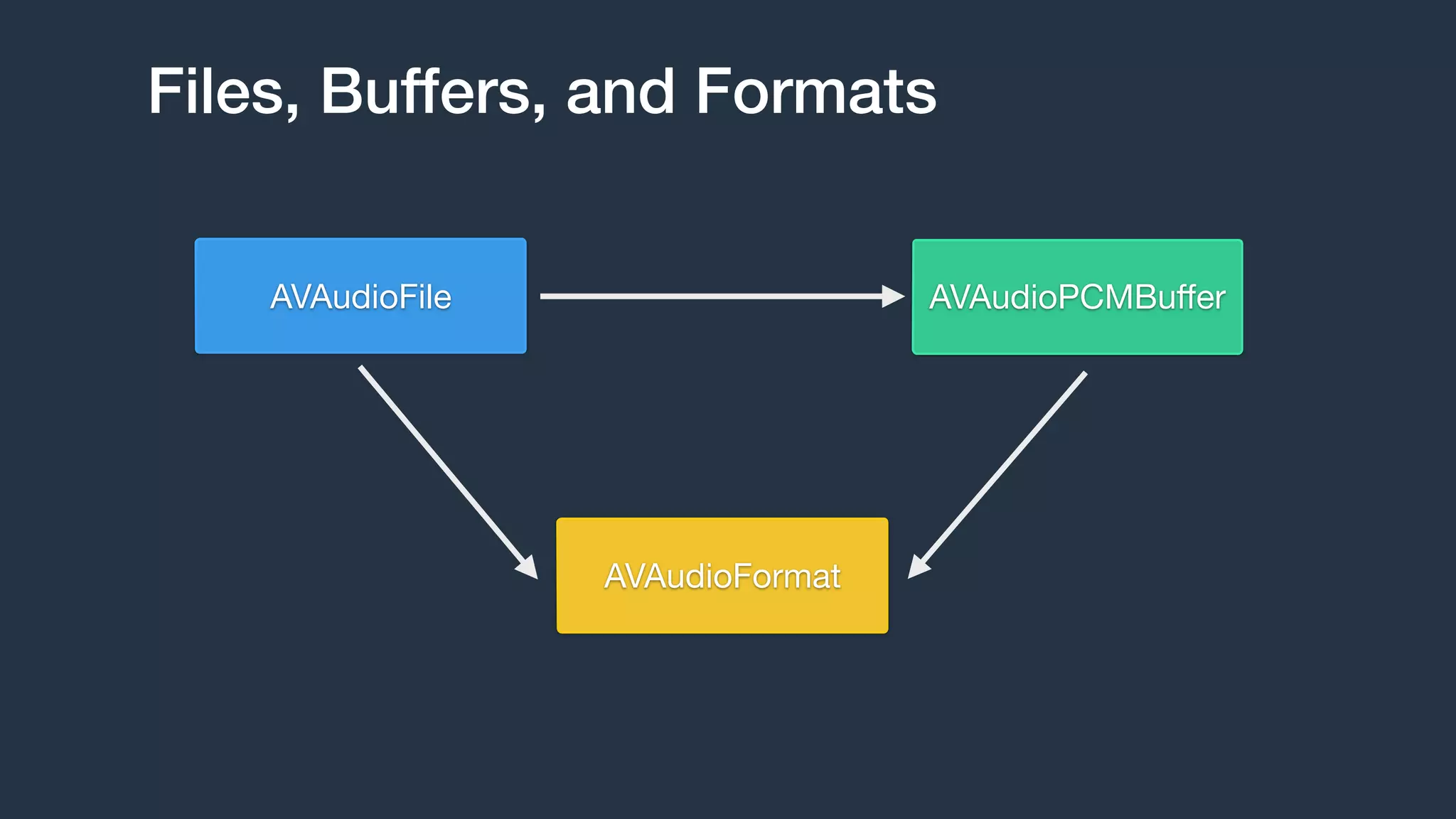



![Creating Files and Buffers
AVAudioFile and AVAudioPCMBuffer
NSURL *url = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"groove"
withExtension:@"m4a"];
// Create AVAudioFile
AVAudioFile *file = [[AVAudioFile alloc] initForReading:url
error:nil];
// Create AVAudioPCMBuffer
AVAudioFormat *format = file.processingFormat;
AVAudioFrameCount capacity = (AVAudioFrameCount)file.length;
AVAudioPCMBuffer *buffer =
[[AVAudioPCMBuffer alloc] initWithPCMFormat:format
frameCapacity:capacity];
// Read AVAudioFile -> AVAudioPCMBuffer
[file readIntoBuffer:buffer error:nil];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-23-2048.jpg)
![AVPlayerNode
Scheduling Files and Buffers
Immediate File Playback
[playerNode scheduleFile:audioFile atTime:nil completionHandler:nil];
[playerNode play];
Future Buffer Playback
// Play audio file 5 seconds from now
double sampleRate = buffer.format.sampleRate;
double sampleTime = sampleRate * 5.0;
AVAudioTime *futureTime = [AVAudioTime timeWithSampleTime:sampleTime
atRate:sampleRate];
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:audioBuffer atTime:futureTime options:0 completionHandler:nil];
[playerNode play];
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:audioBuffer completionHandler:nil];
[playerNode play];
Immediate Buffer Playback](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-24-2048.jpg)
![-Scheduling multiple buffers queues them serially
Scheduling Options
AVAudioPlayerNodeBufferOptions
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:buffer1 atTime:nil options:0 completionHandler:nil];
[playerNode play];
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:buffer2 atTime:nil options:0 completionHandler:nil];
buffer1 buffer2
time
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:buffer2
atTime:nil
options:AVAudioPlayerNodeBufferInterrupts completionHandler:nil];
-Schedule with interruption option to change this behavior
buffer1 buffer2
time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-25-2048.jpg)
![-Schedule a single looping buffer
Scheduling Options
AVAudioPlayerNodeBufferOptions
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:buffer1
atTime:nil
options:AVAudioPlayerNodeBufferLoops completionHandler:nil];
buffer1
[playerNode scheduleBuffer:buffer2
atTime:nil
options:AVAudioPlayerNodeBufferInterruptsAtLoop completionHandler:nil];
-Schedule with interruption or interruption at loop
buffer1 buffer2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-26-2048.jpg)



![Node Taps
Installing a tap
AVAudioMixerNode *mixer = self.engine.mainMixerNode;
AVAudioFrameCount bufferSize = 4096;
AVAudioFormat *format = [mixer outputFormatForBus:0];
[mixer installTapOnBus:0
bufferSize:bufferSize
format:format
block:^(AVAudioPCMBuffer *buffer, AVAudioTime *when) {
// Process AVAudioPCMBuffer
}];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/avaudioengine-141116185315-conversion-gate01/75/Building-Modern-Audio-Apps-with-AVAudioEngine-33-2048.jpg)