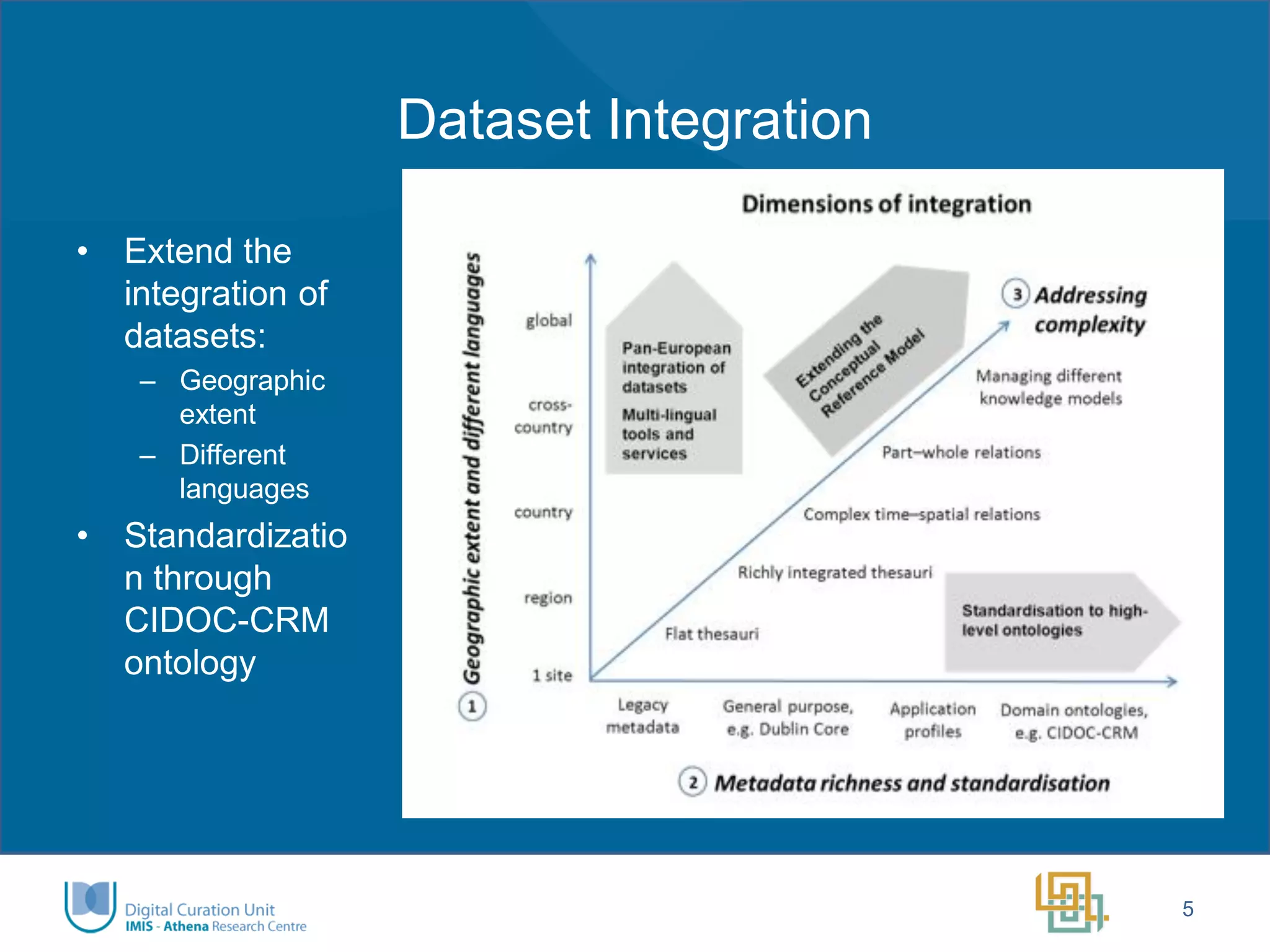
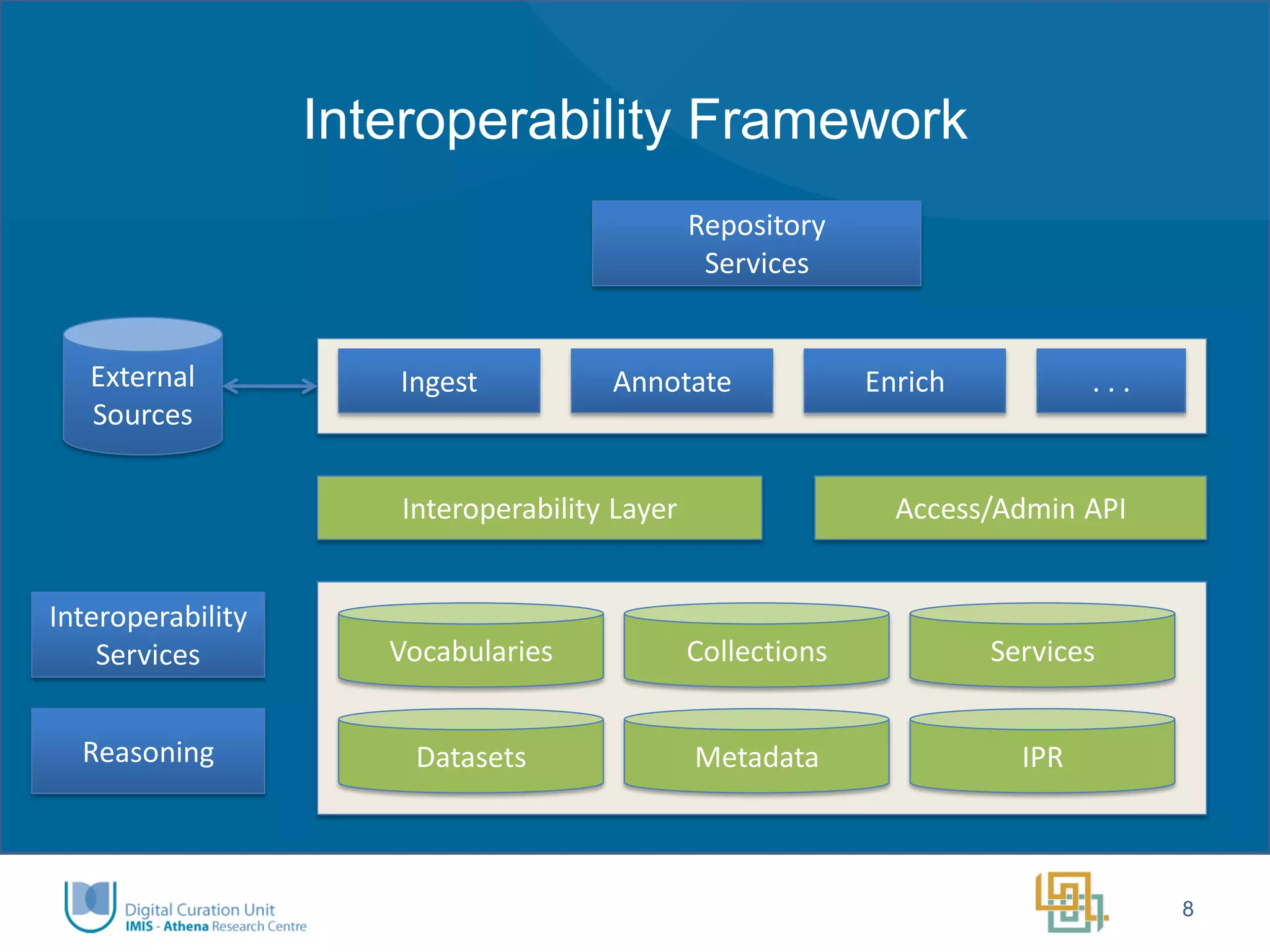
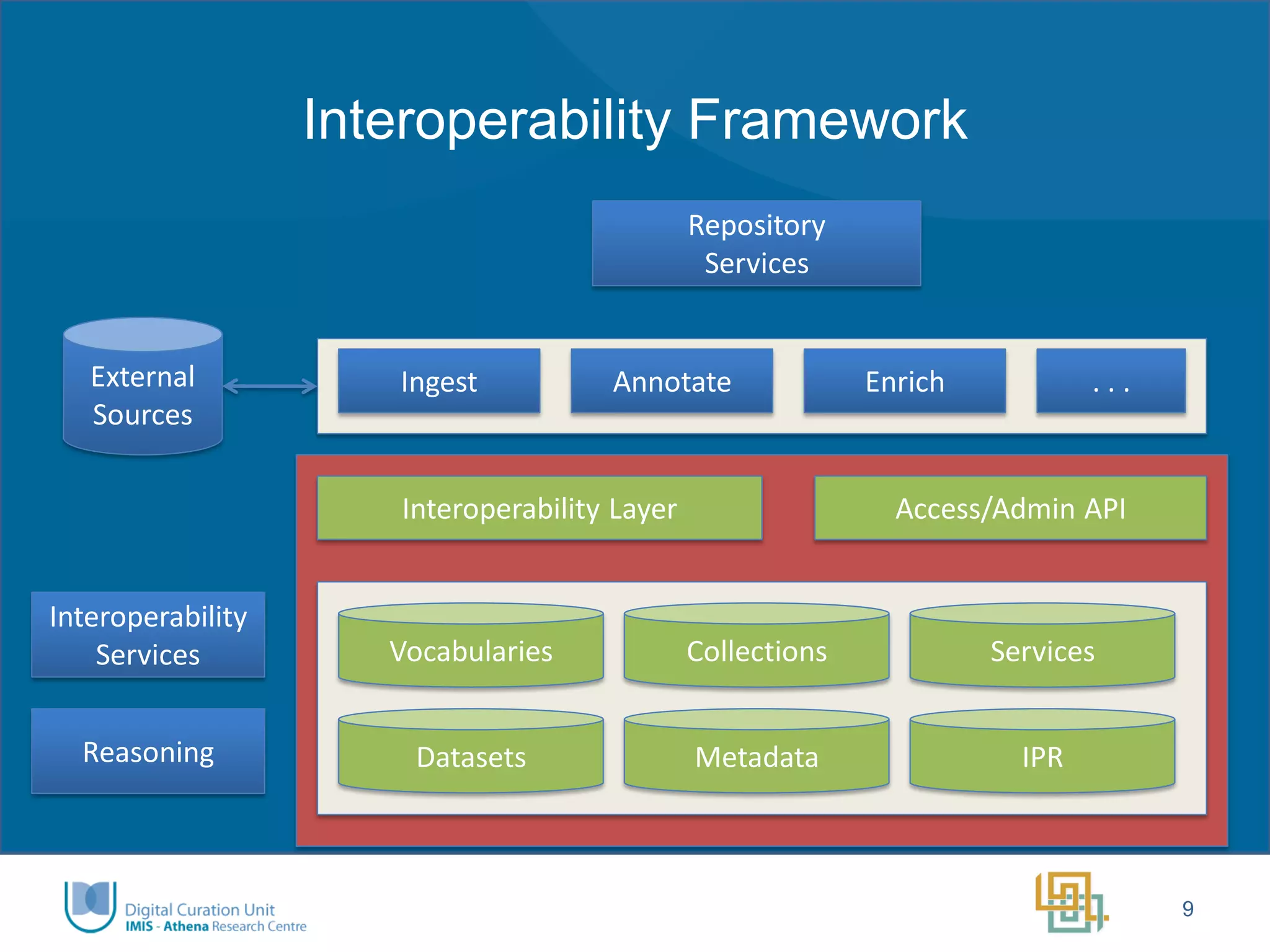
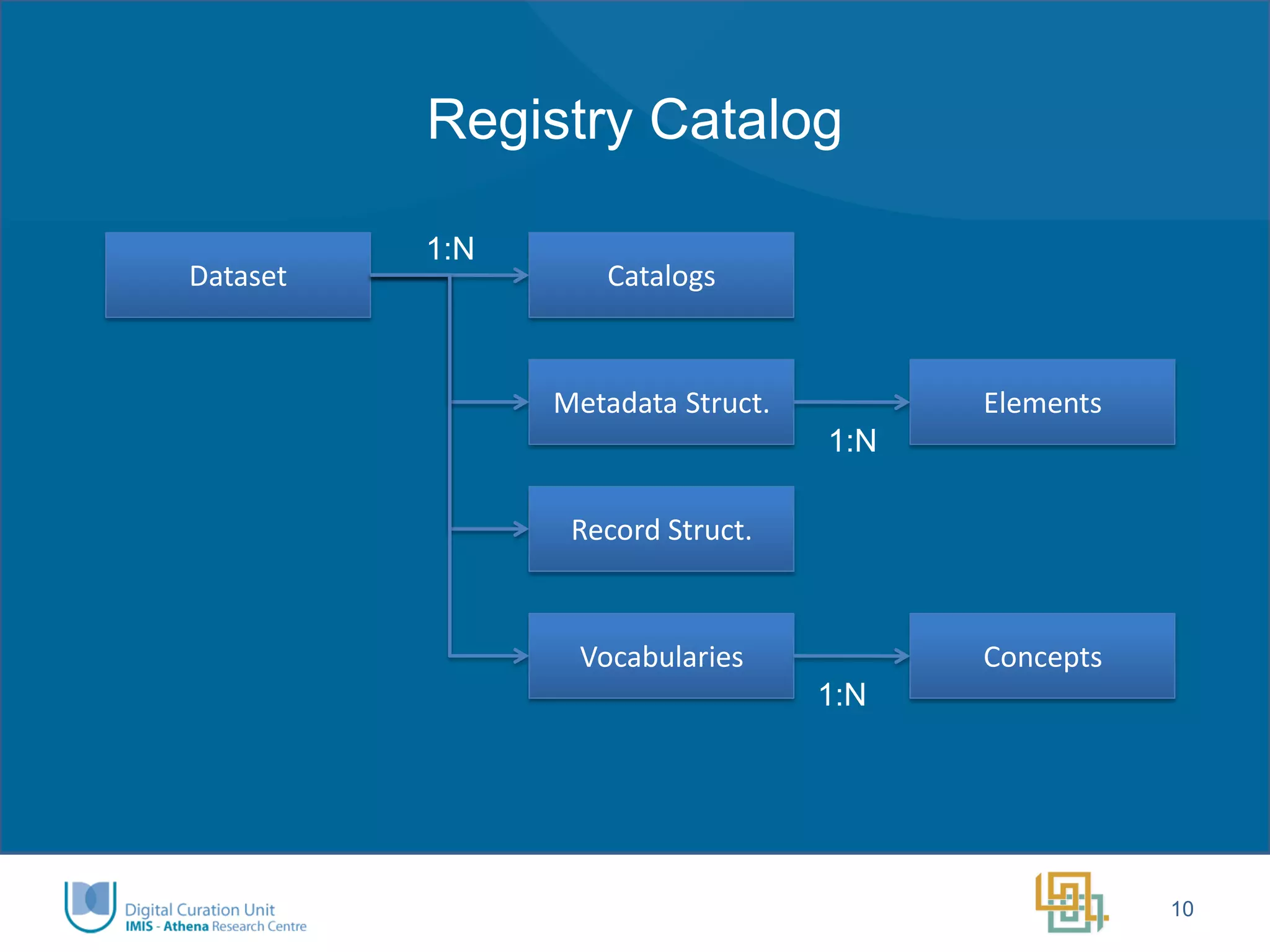
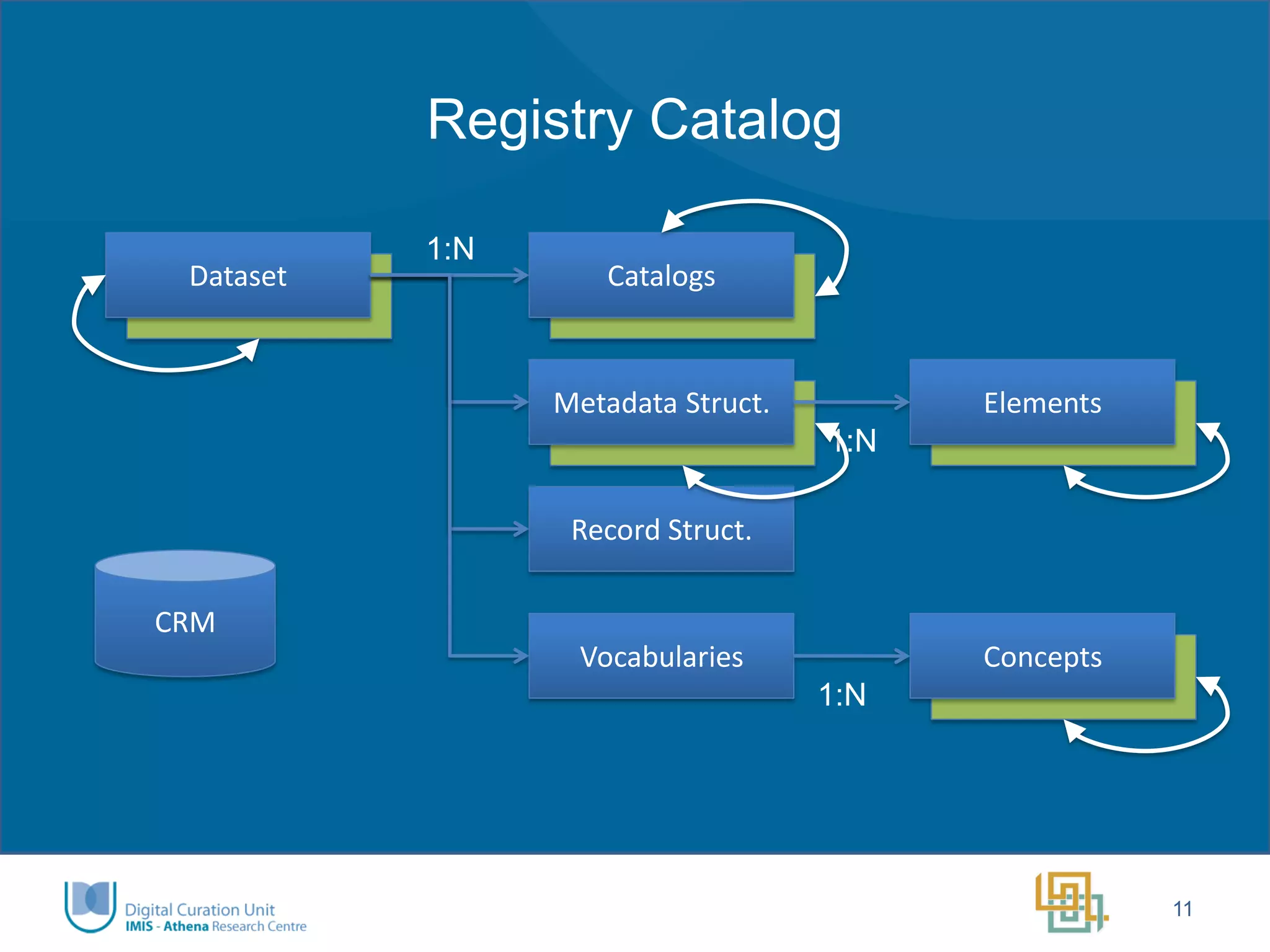
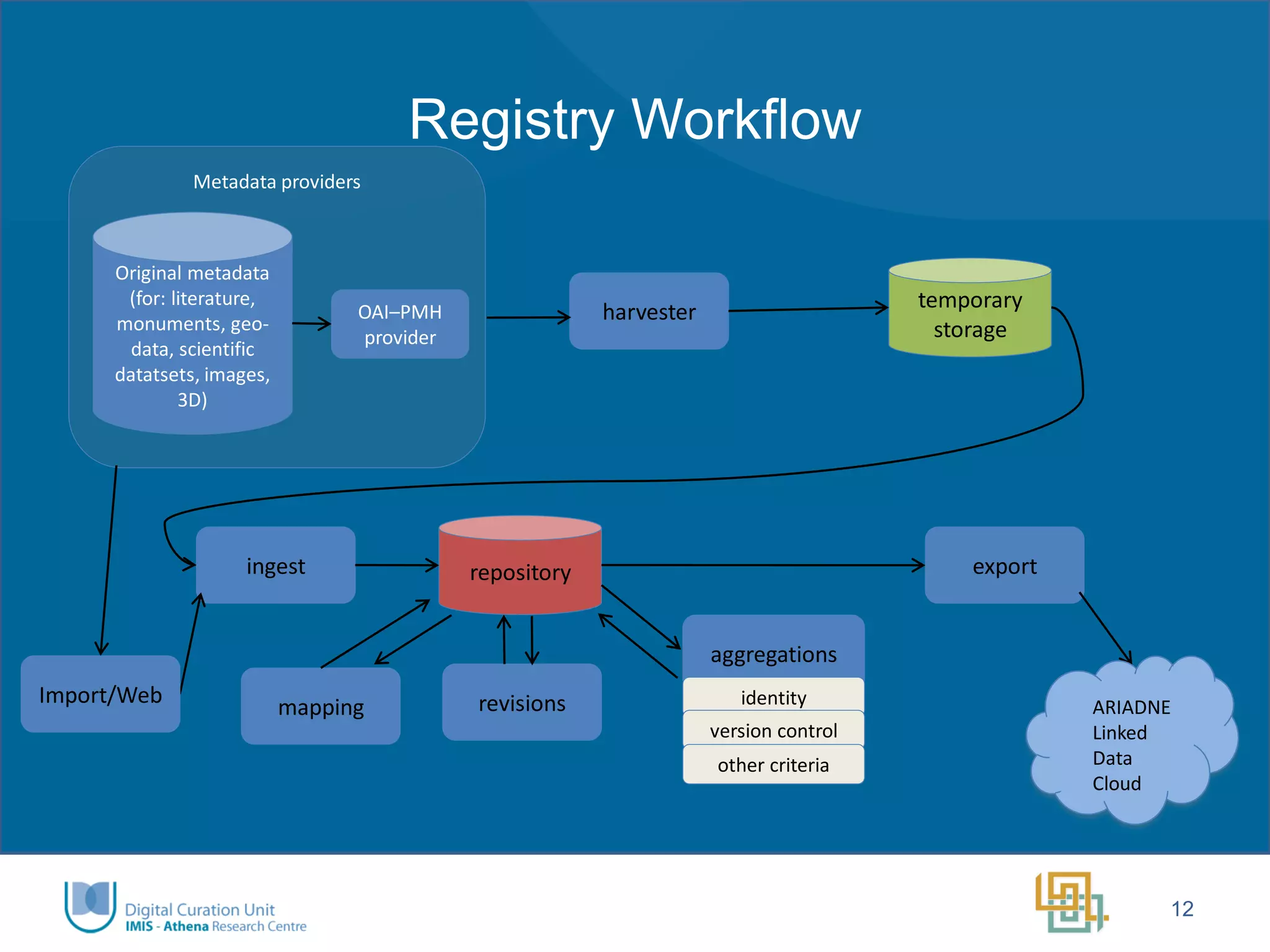
The Ariadne project aims to integrate and provide access to a vast array of archaeological datasets across Europe, enhancing interoperability and collaboration within the research community. Key objectives include addressing fragmentation, creating user-friendly interfaces, developing innovative tools for long-term data preservation, and fostering a new generation of researchers. Funded by the European Commission, the project emphasizes transnational access, training, and the use of advanced technologies, including semantic annotation and 3D visualization.