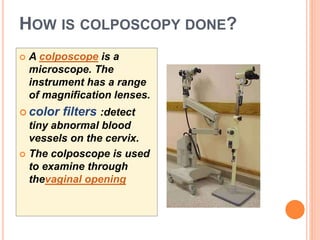
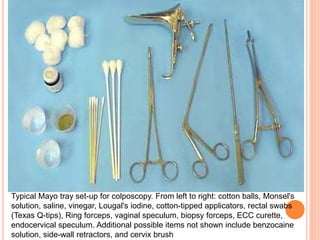
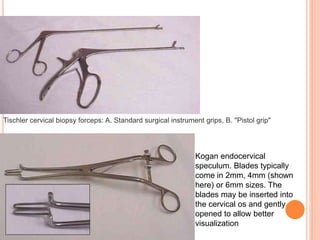
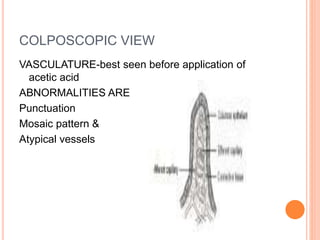
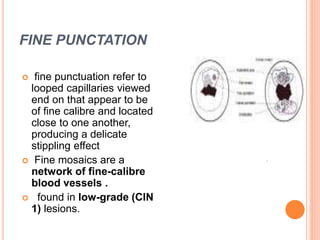
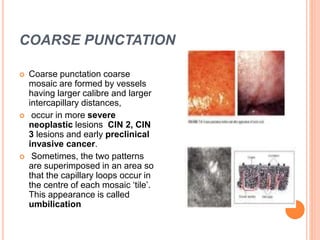
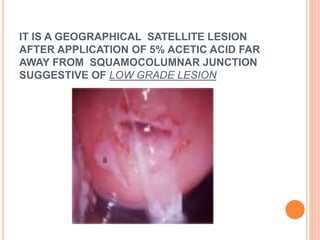
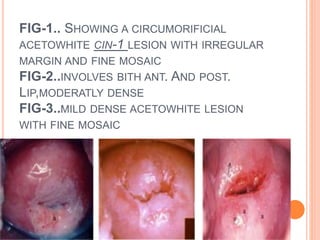
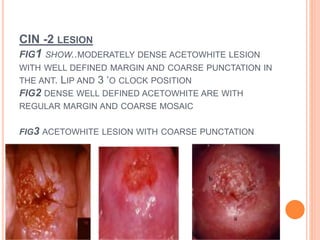
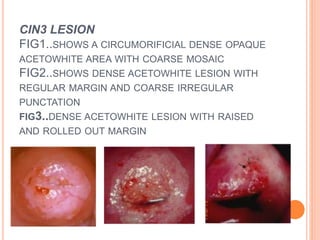
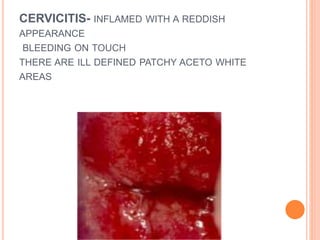
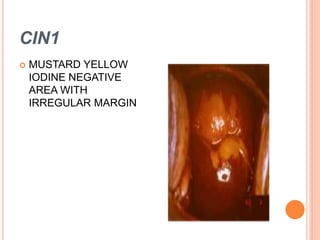
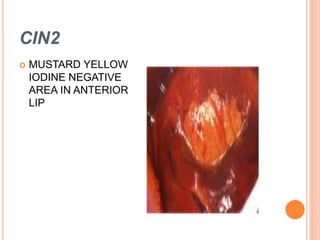
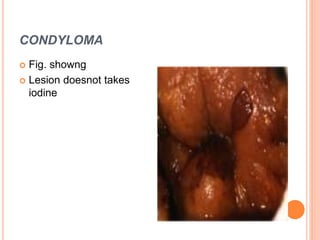
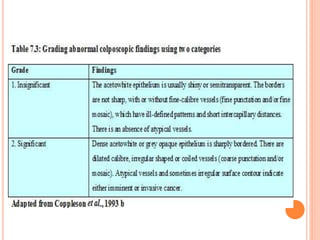
Colposcopy is a procedure that magnifies and illuminates the cervix, vagina, and vulva to examine them for abnormalities. It is usually performed when a Pap smear is abnormal or the cervix looks abnormal. During colposcopy, acetic acid is applied to help identify abnormal areas, which appear white. Biopsies may be taken of abnormal areas for further examination. Interpretation involves examining features like acetowhitening, vascular patterns, and iodine uptake to assess the severity of cervical lesions and guide treatment. Colposcopy allows close examination of the cervix to diagnose conditions like cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or condyloma.