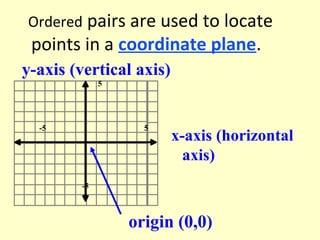
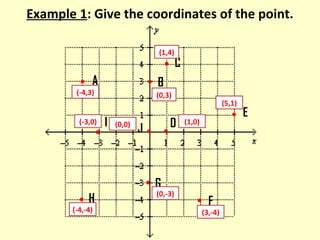
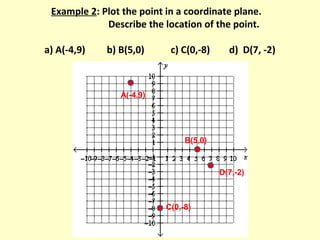
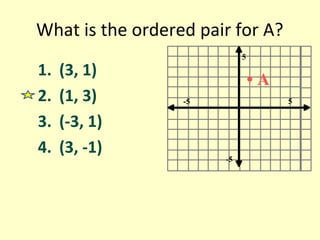
The document discusses ordered pairs and their use in graphing points on a coordinate plane. It explains that an ordered pair consists of an x-coordinate and y-coordinate, separated by a comma. The x-axis and y-axis intersect at the origin (0,0) and divide the plane into four quadrants, labeled I, II, III, and IV. Points in the plane are located based on their ordered pair coordinates and quadrant.