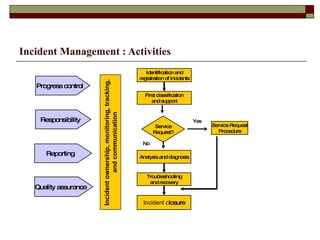
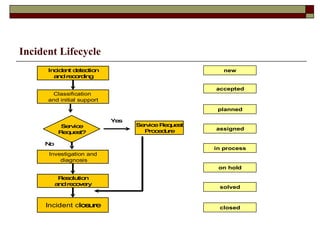
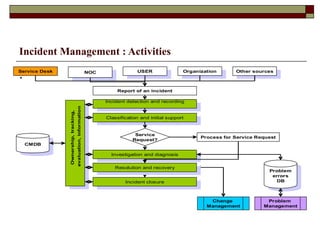
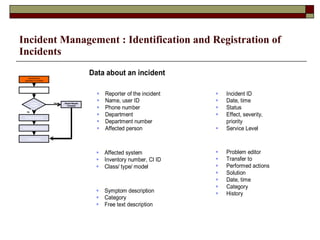
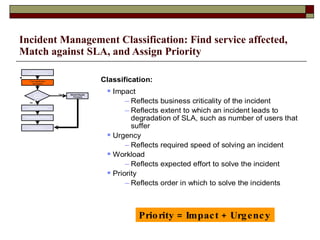
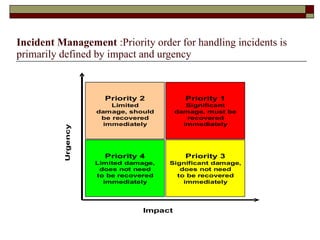
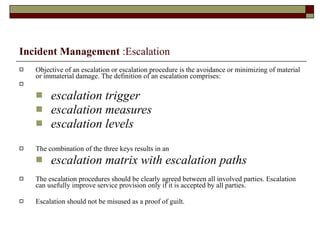
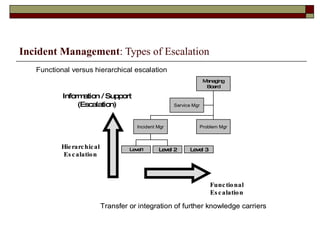
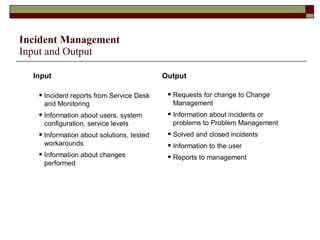
Incident management aims to restore normal service operation as swiftly as possible while minimizing business impact, following service level agreements. It involves activities such as incident detection, classification, escalation, and restoration, with roles outlined for incident managers and analysts. Success is measured through key performance indicators like response times and incident categorization, requiring proper resources and clear communication among involved parties.
![ITIL- Incident Management For Beginners Abhishek Agnihotry If any query mail me at [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/incidentmanagementabhishek-12704941383404-phpapp01/85/Incident-Management-1-320.jpg)