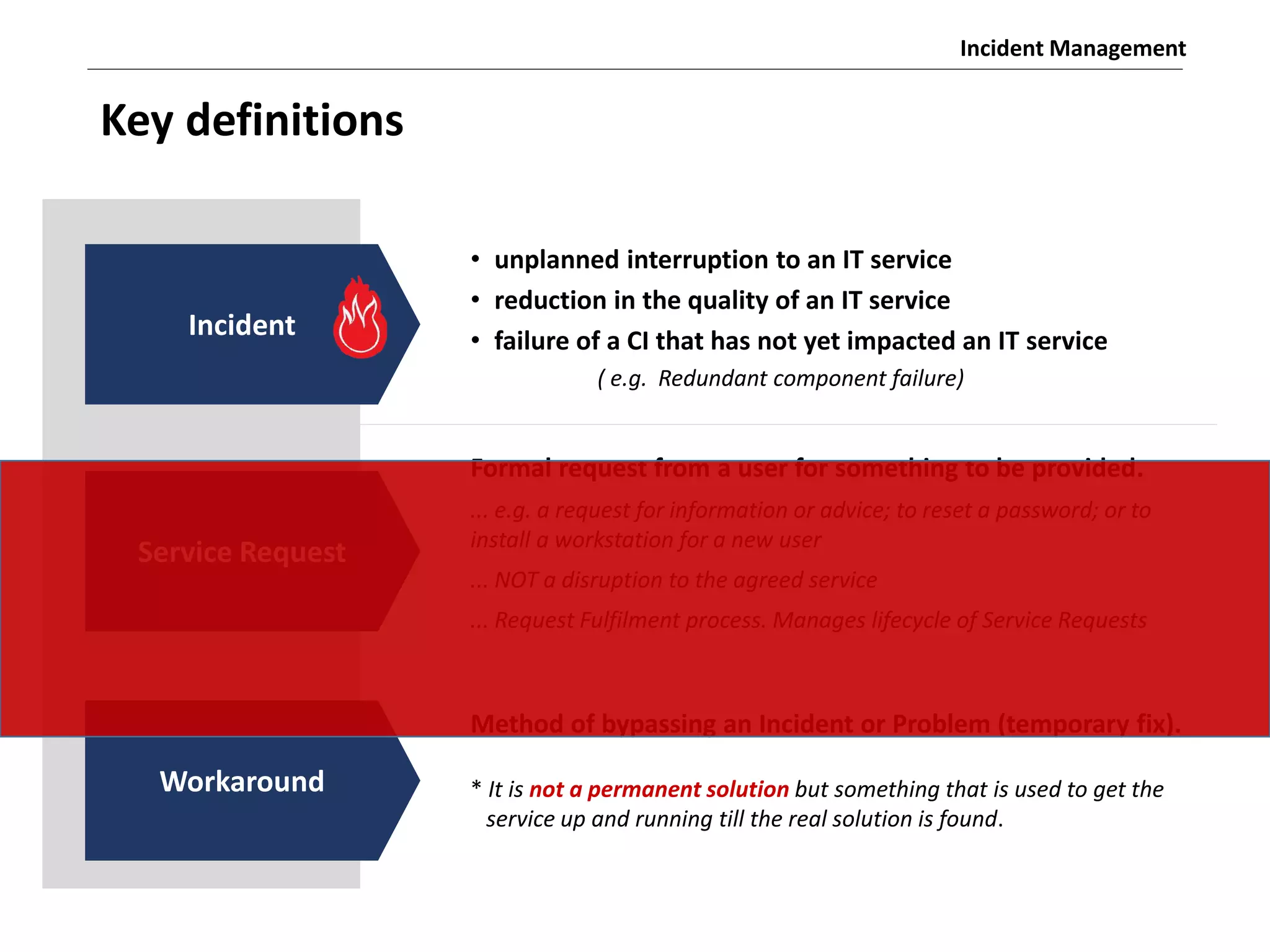
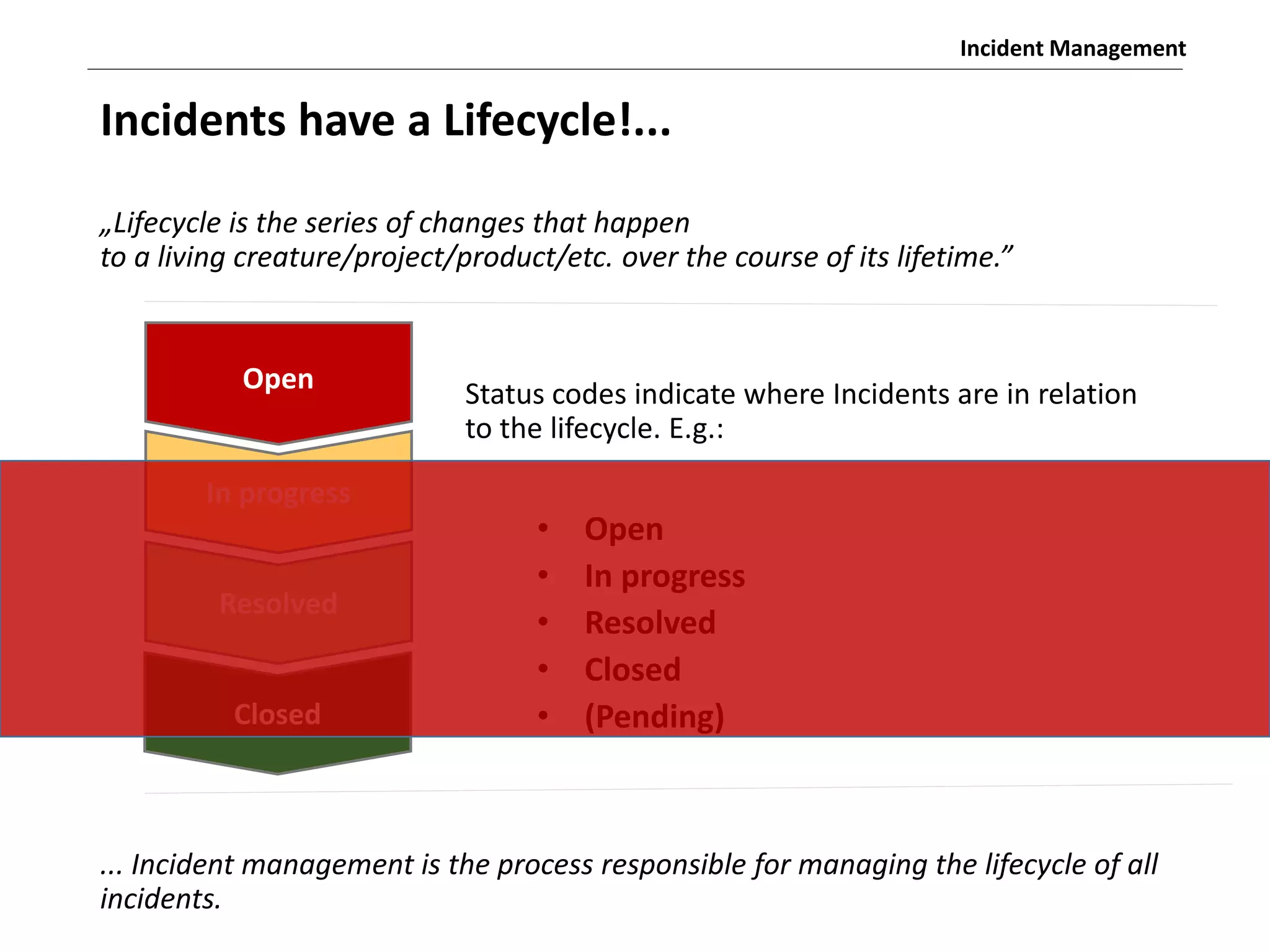
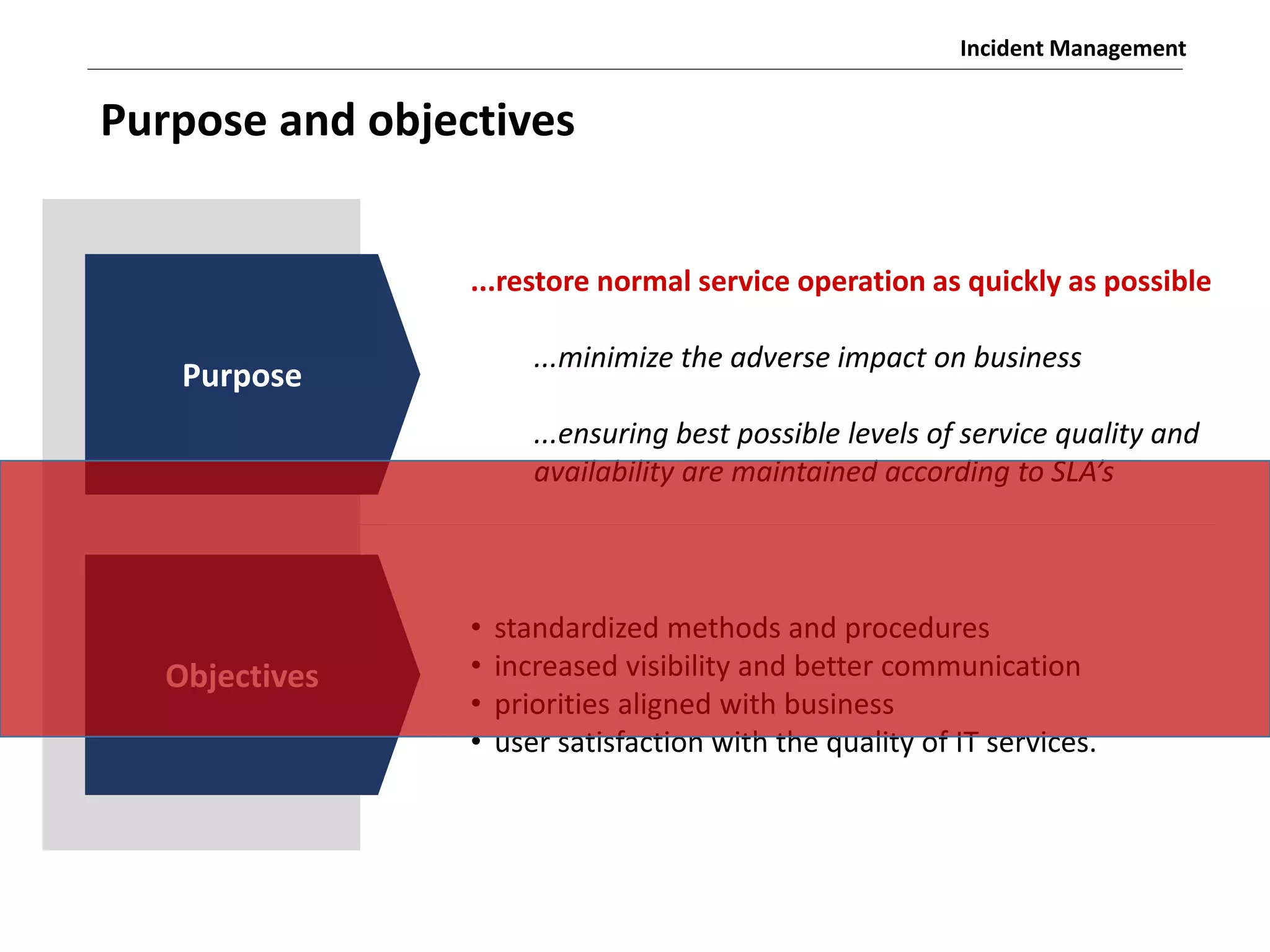
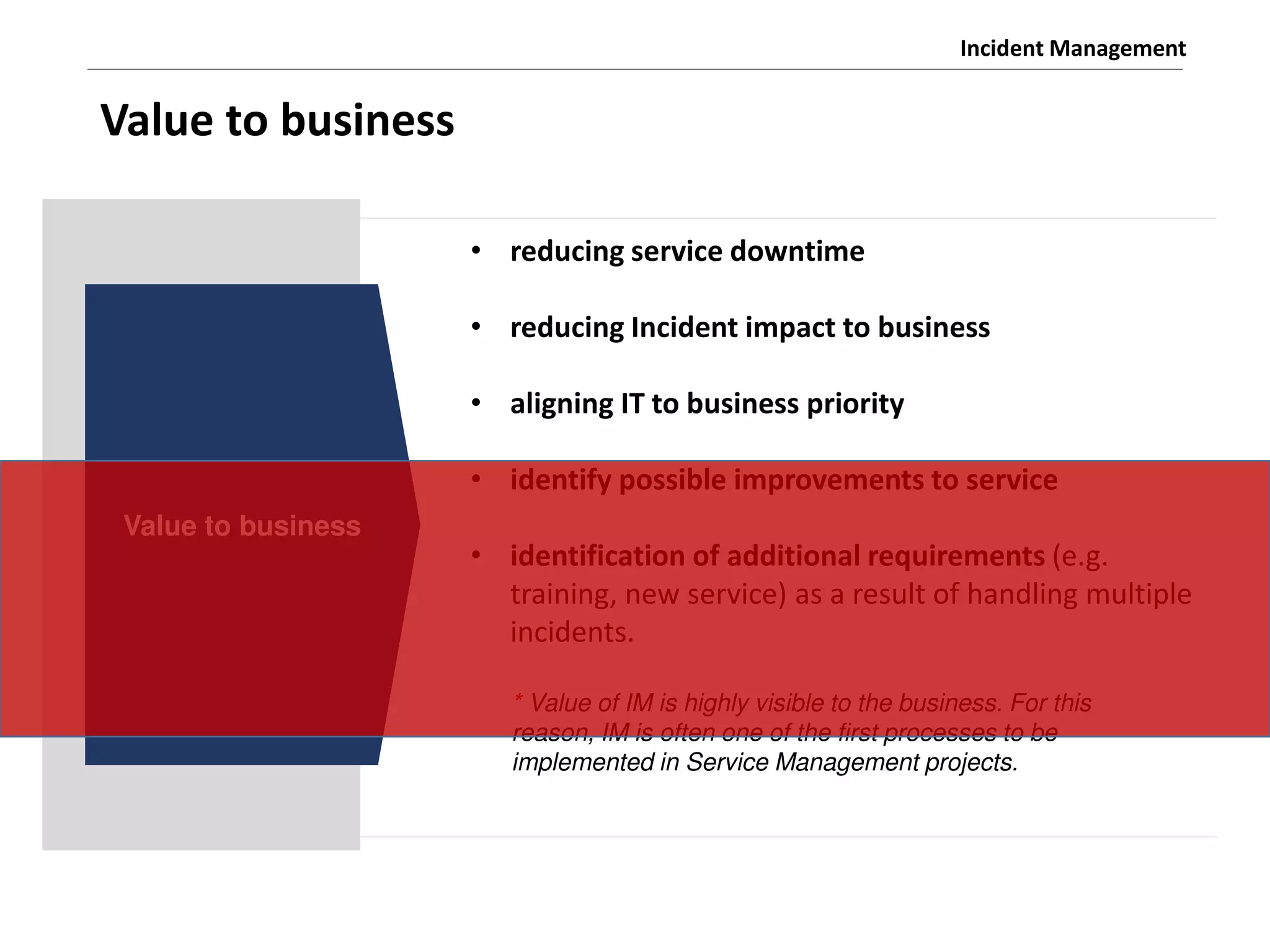
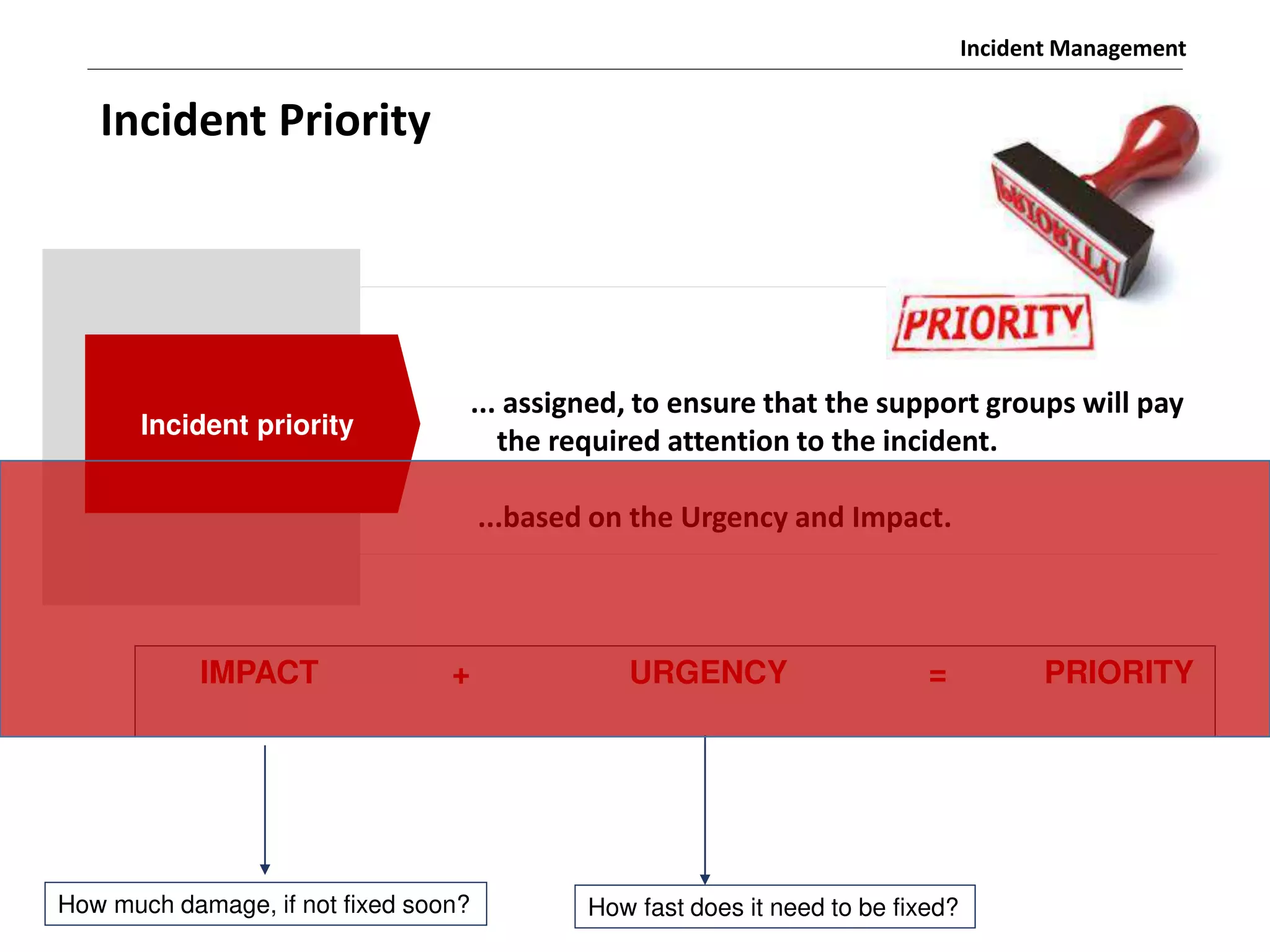
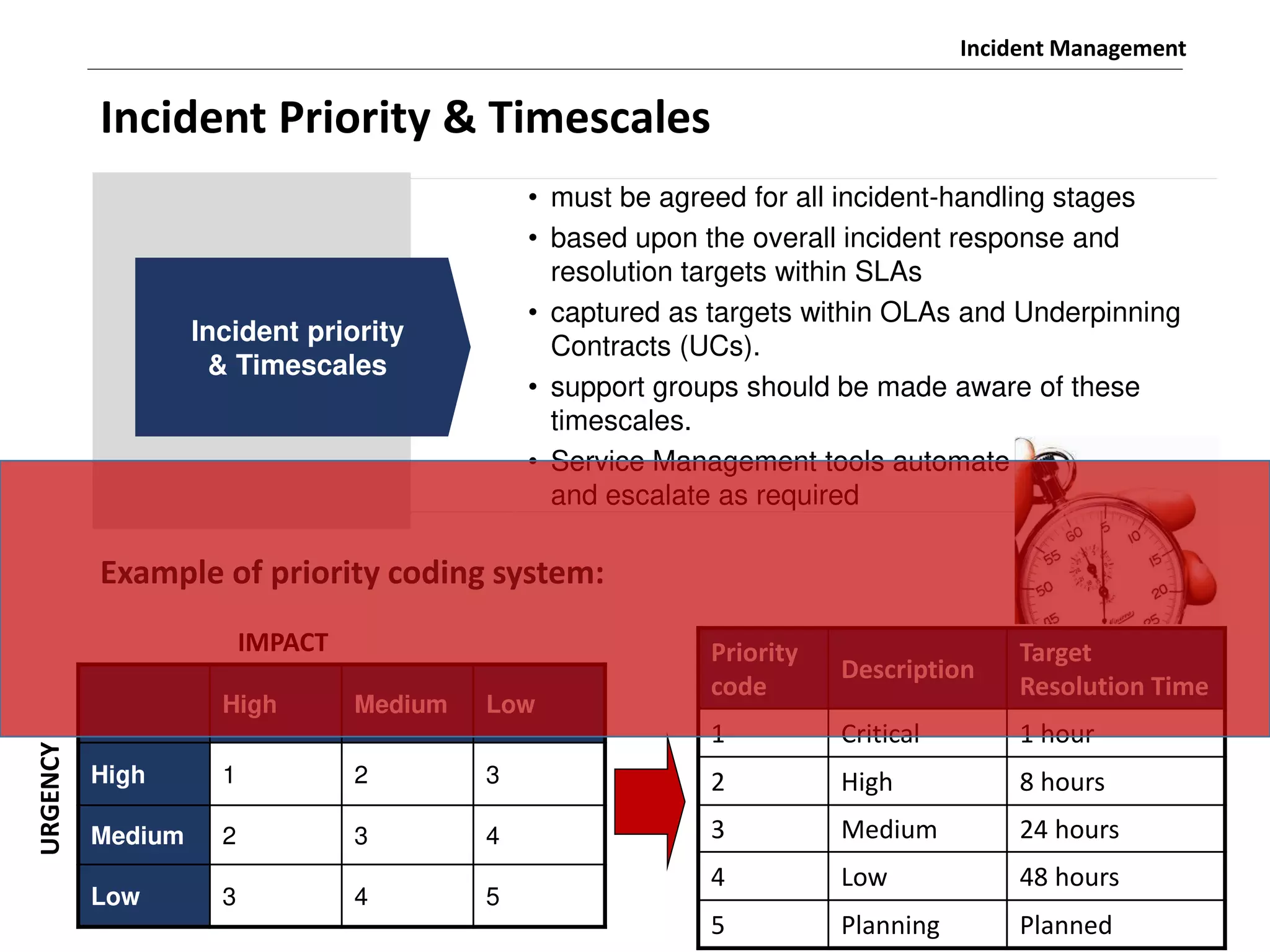
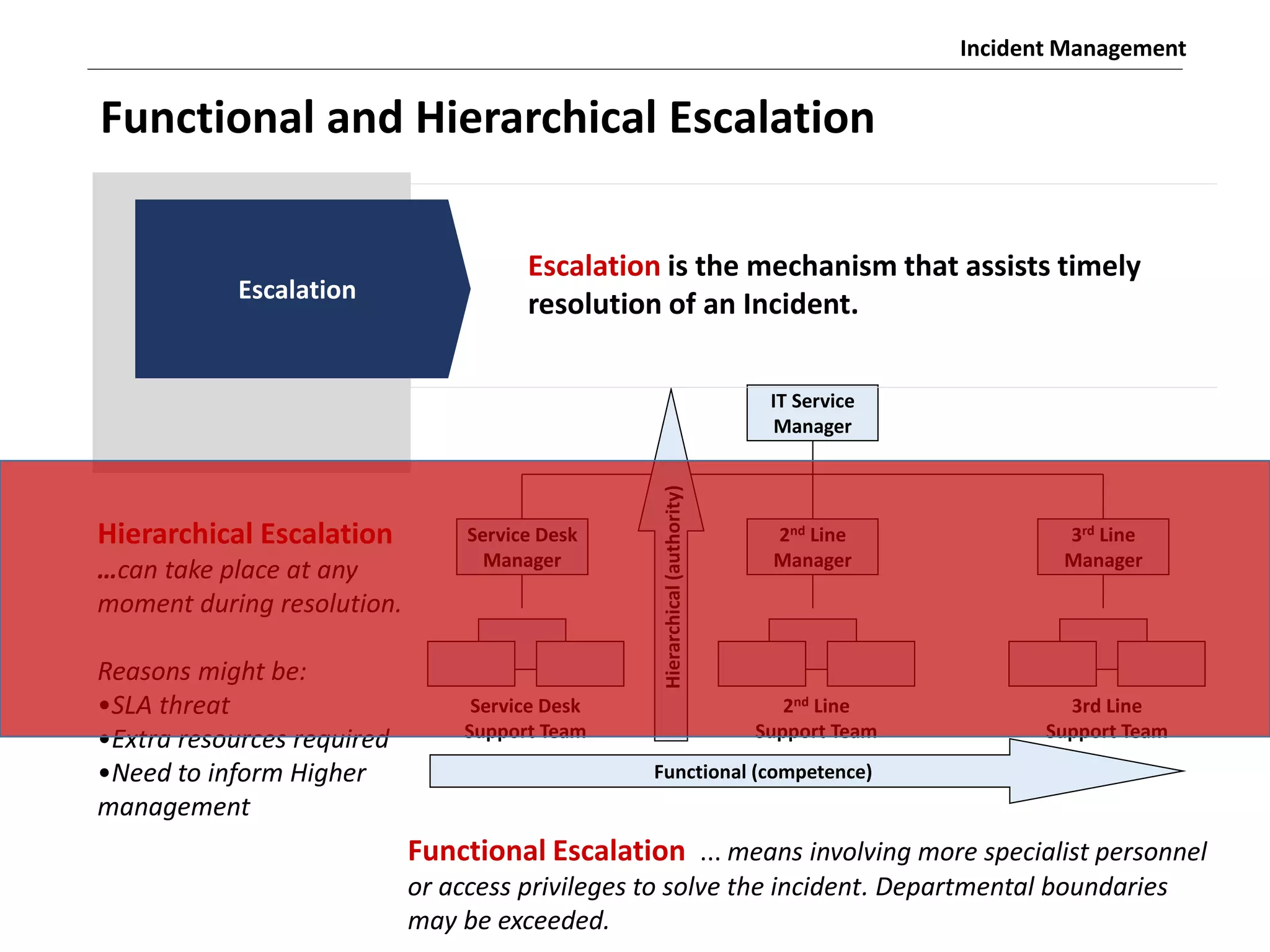
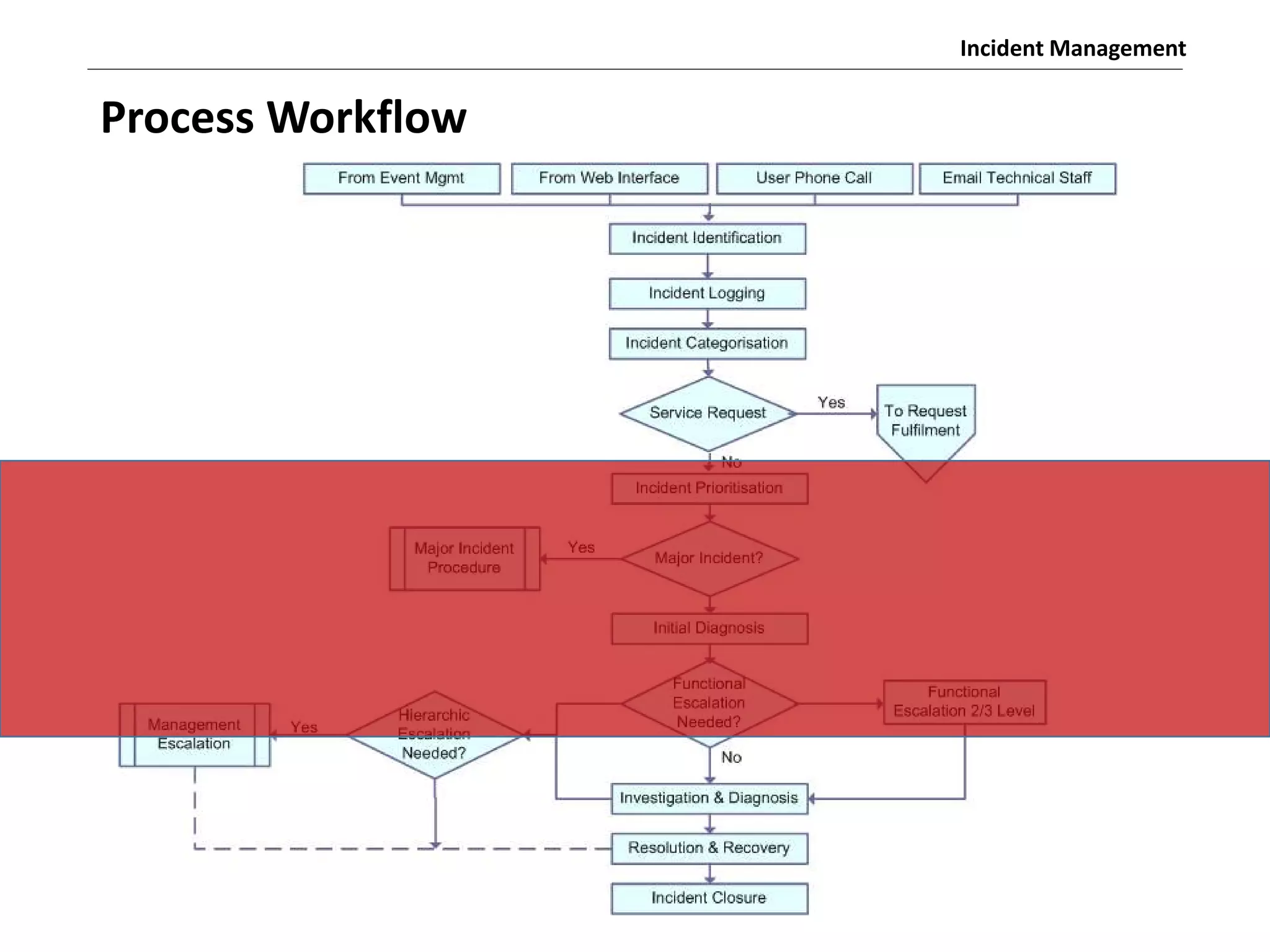
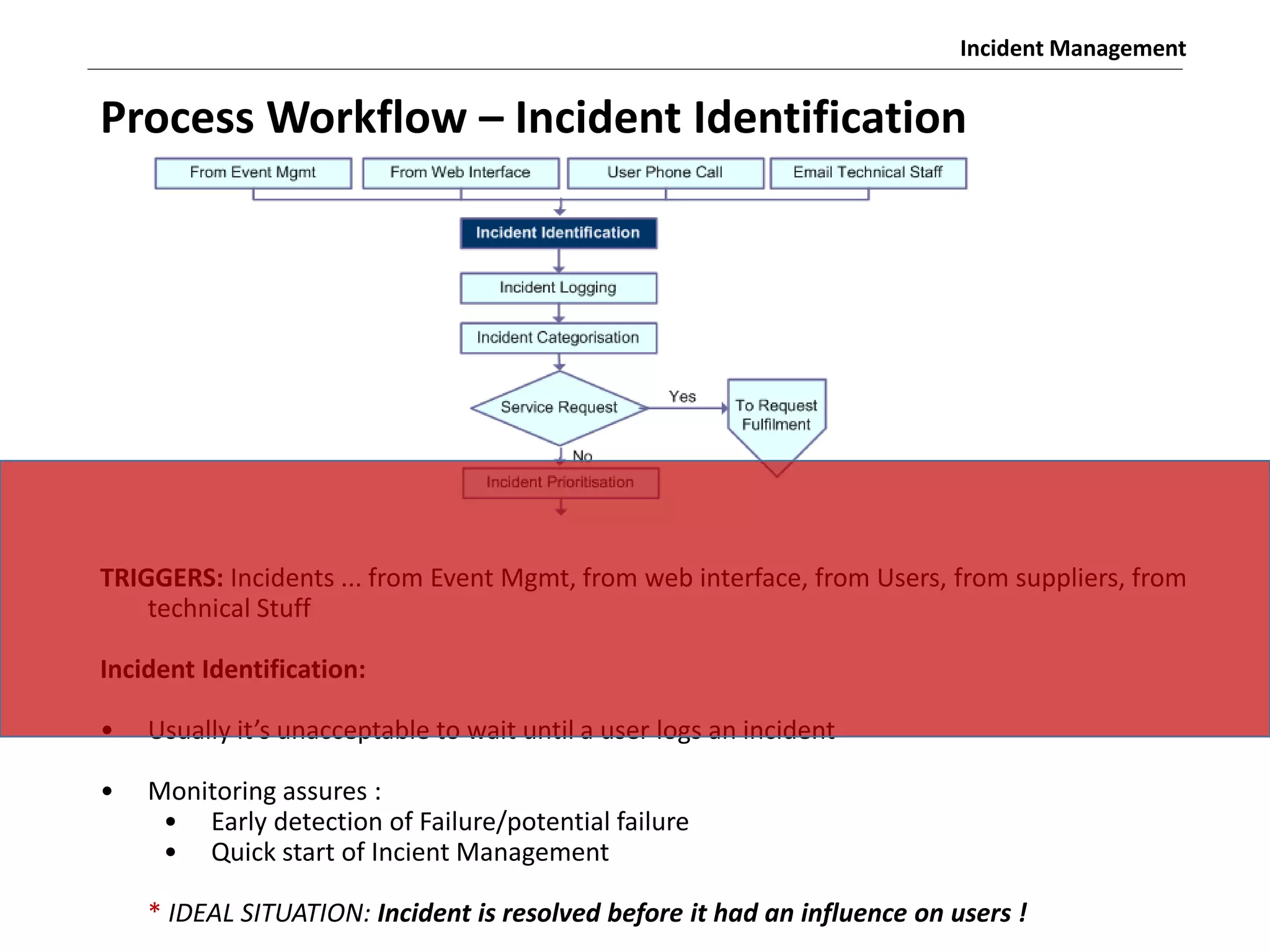
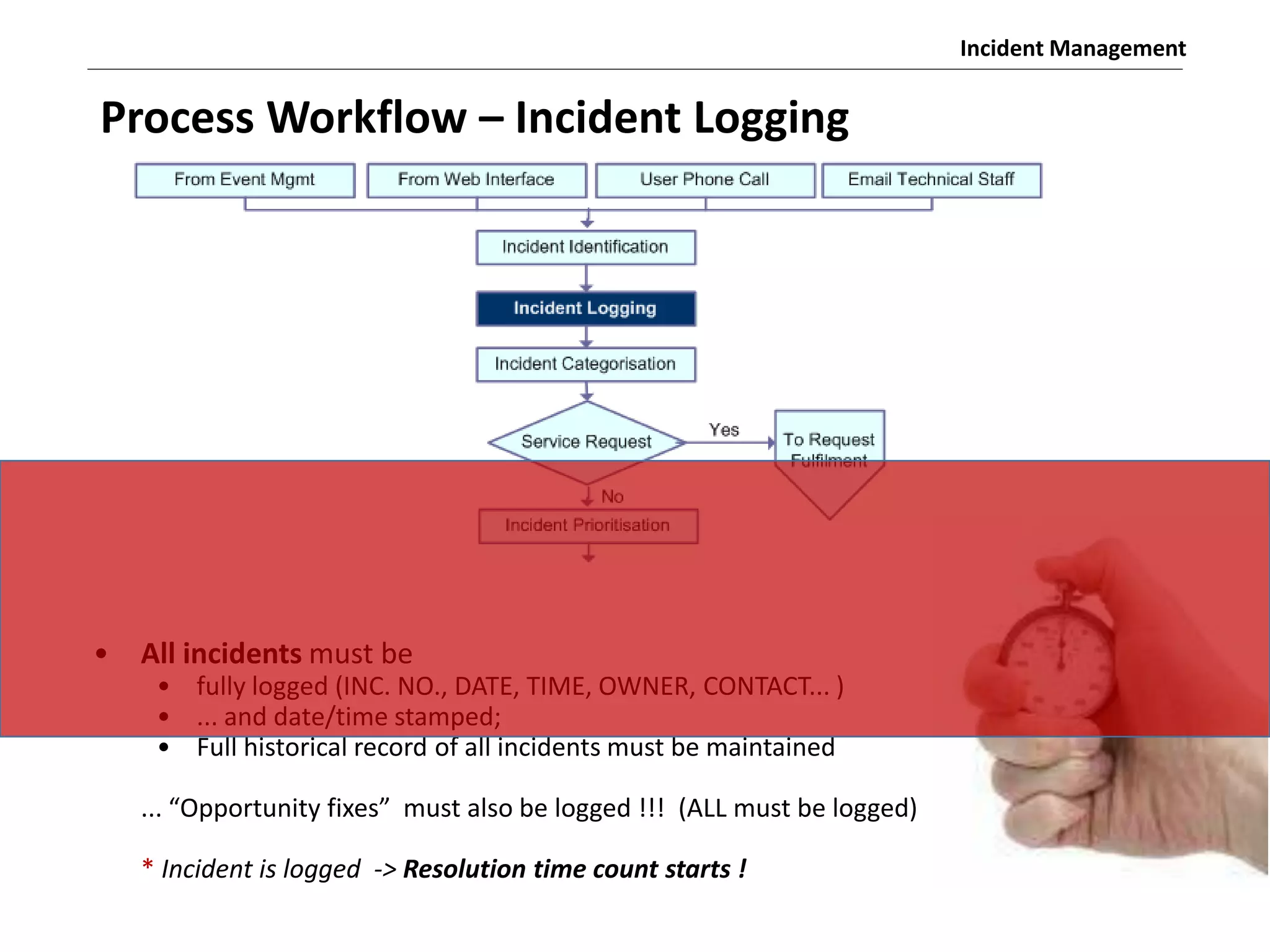
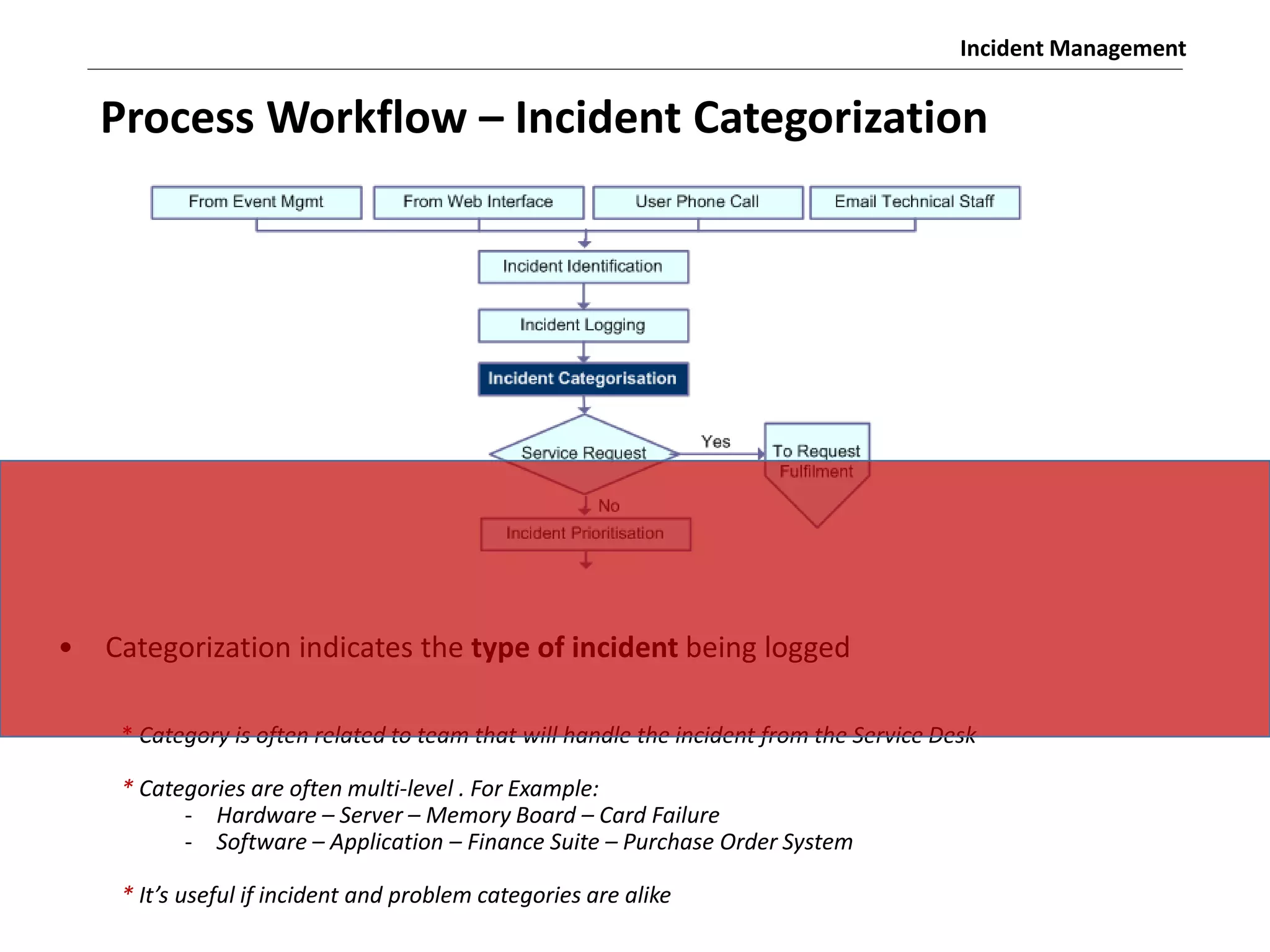
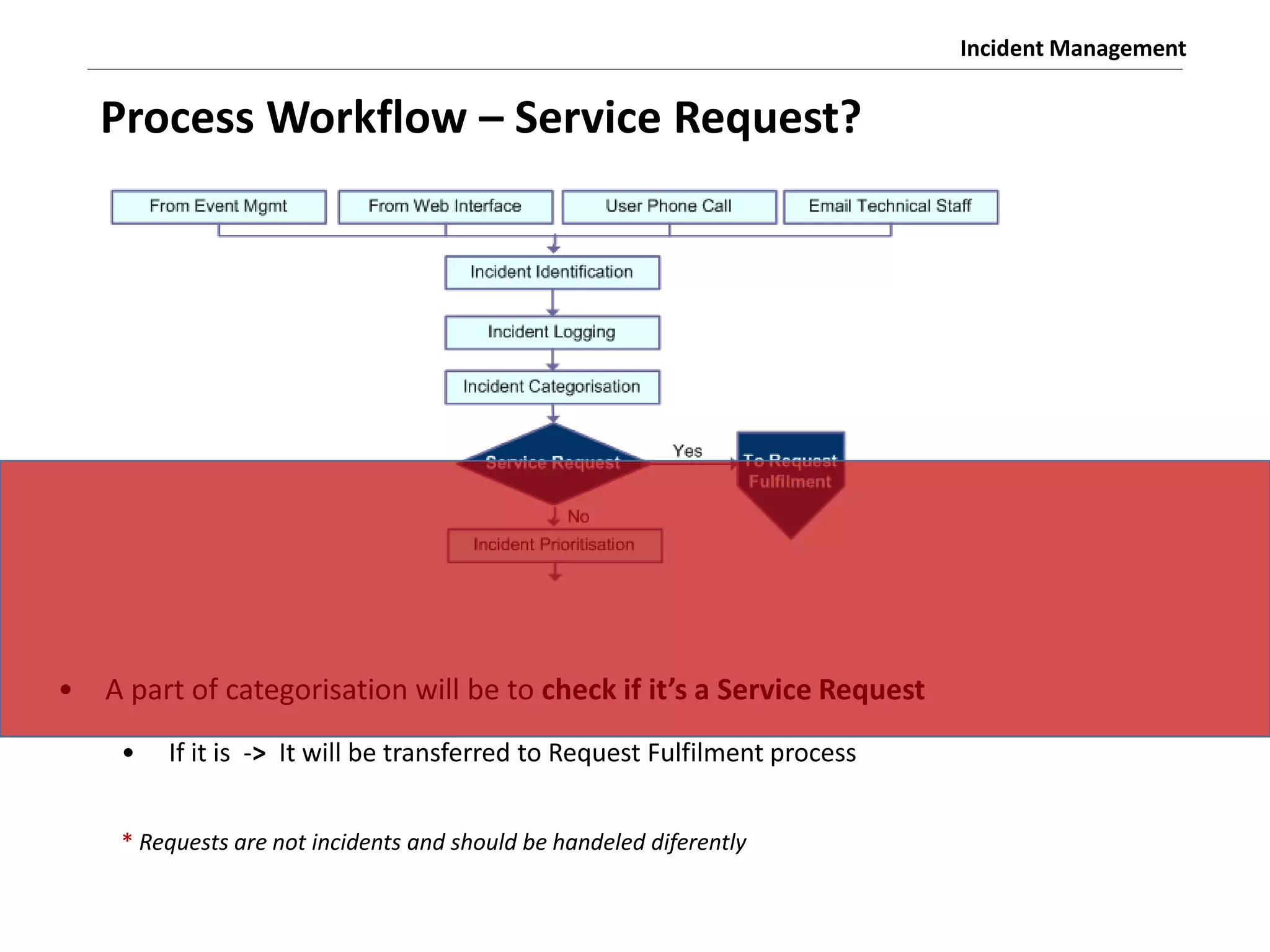
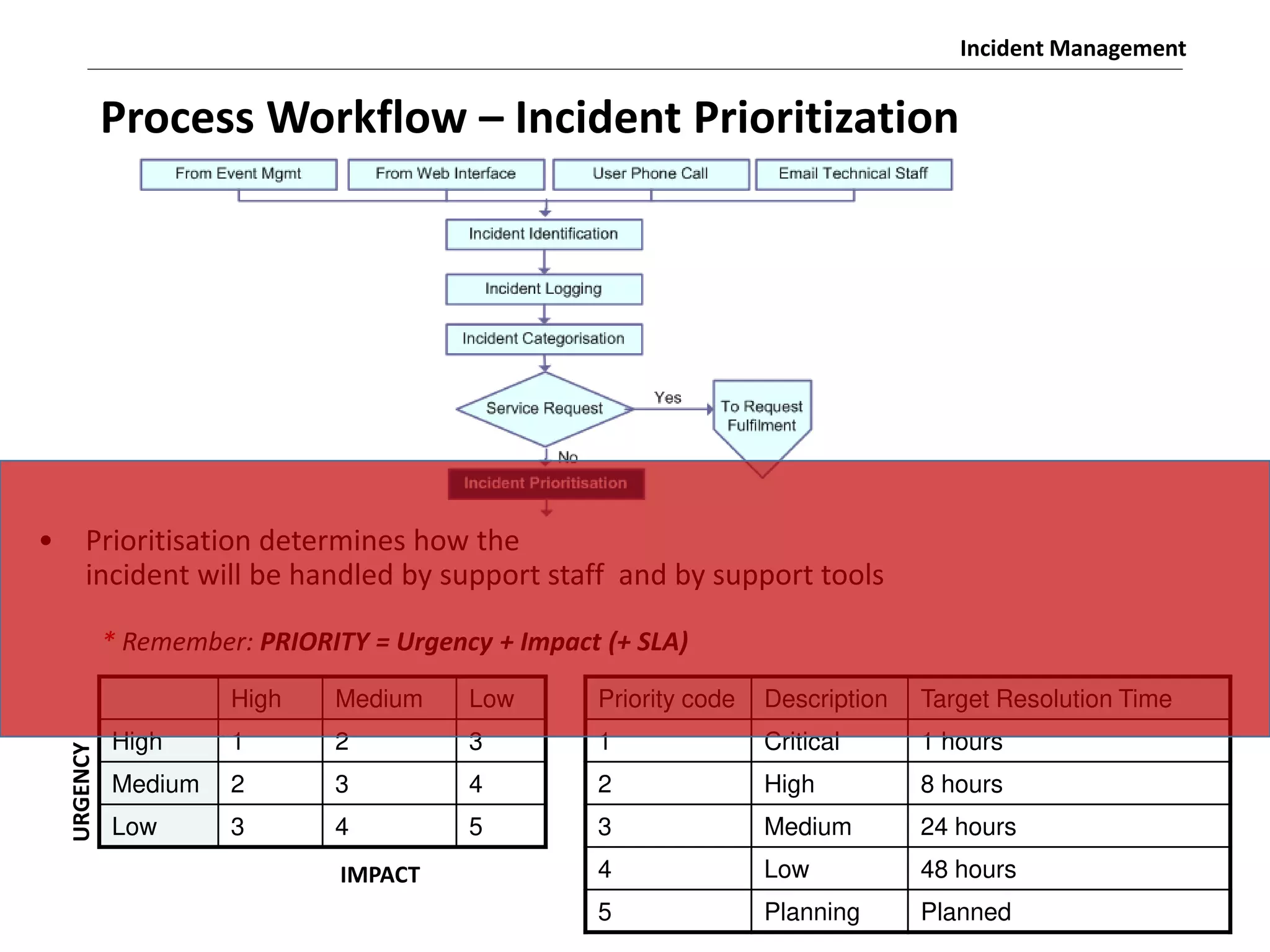
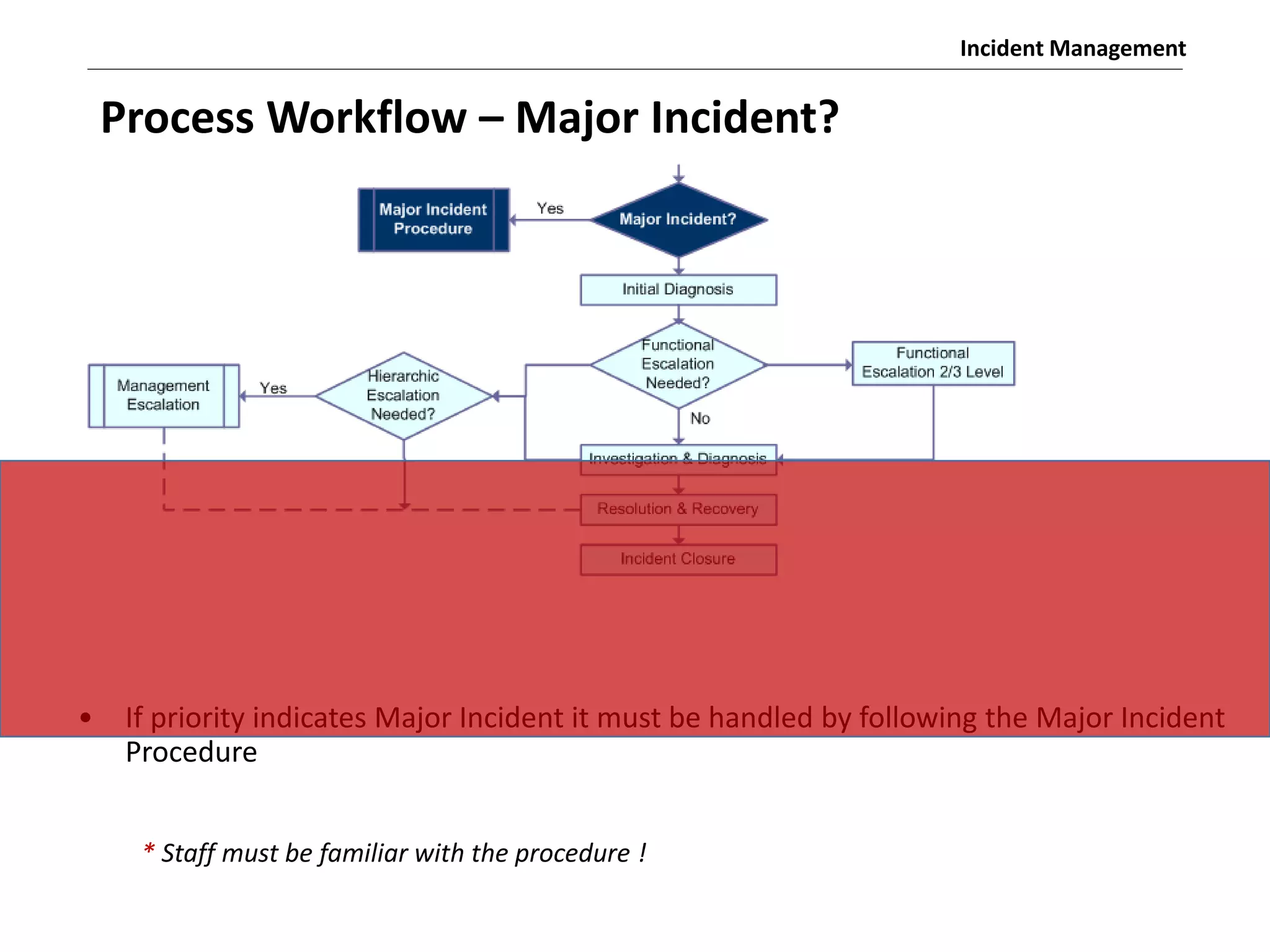
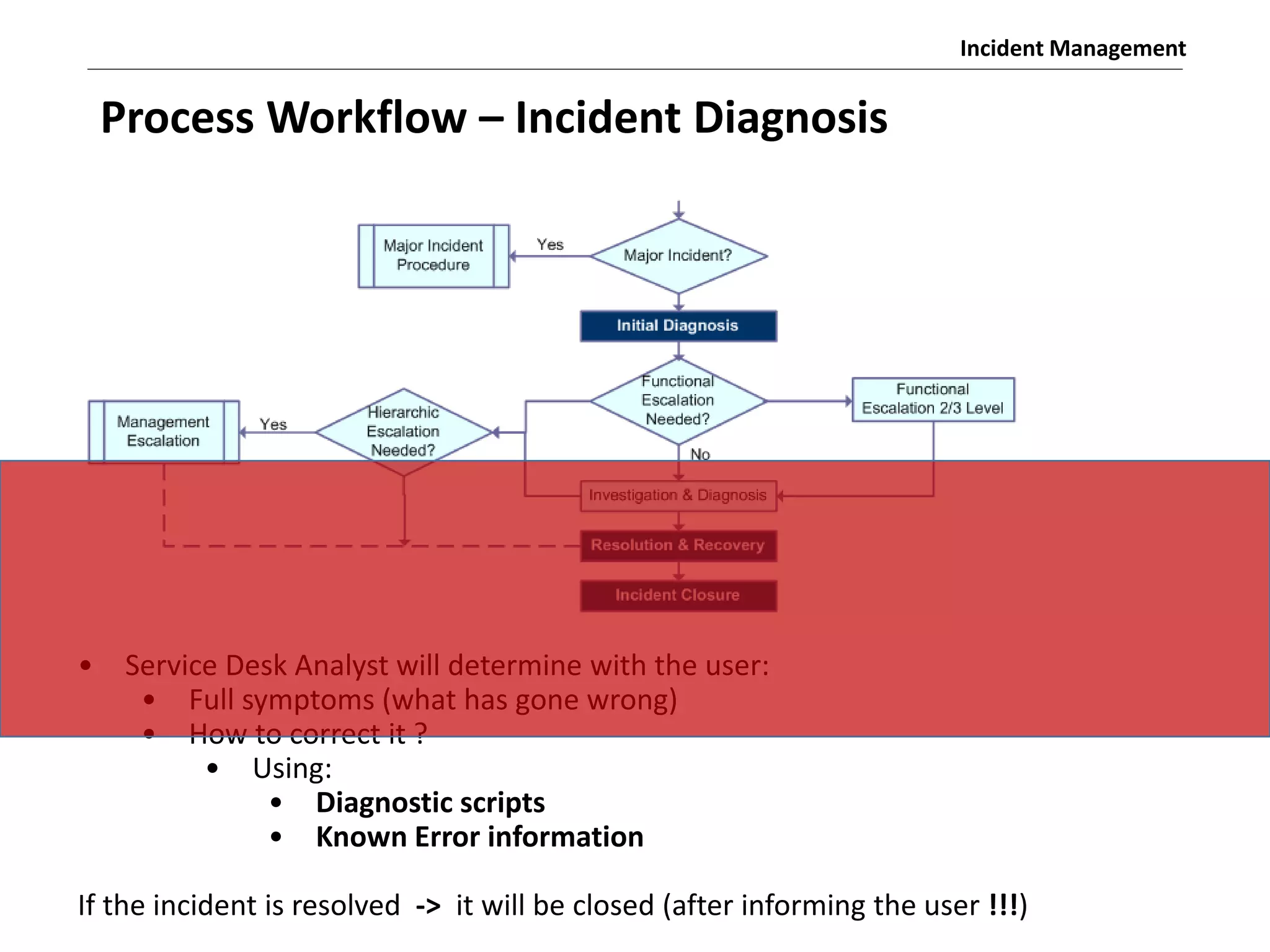
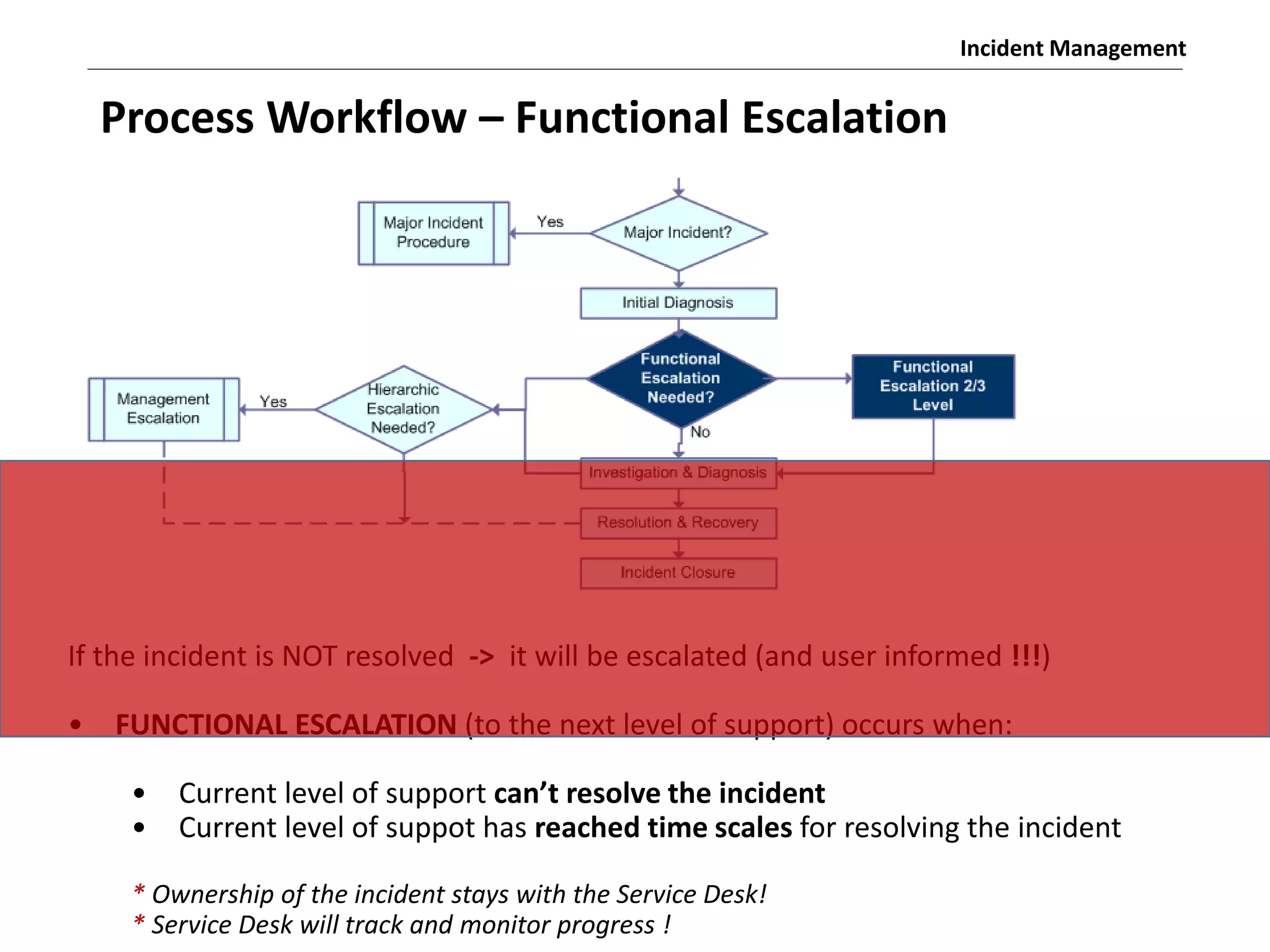
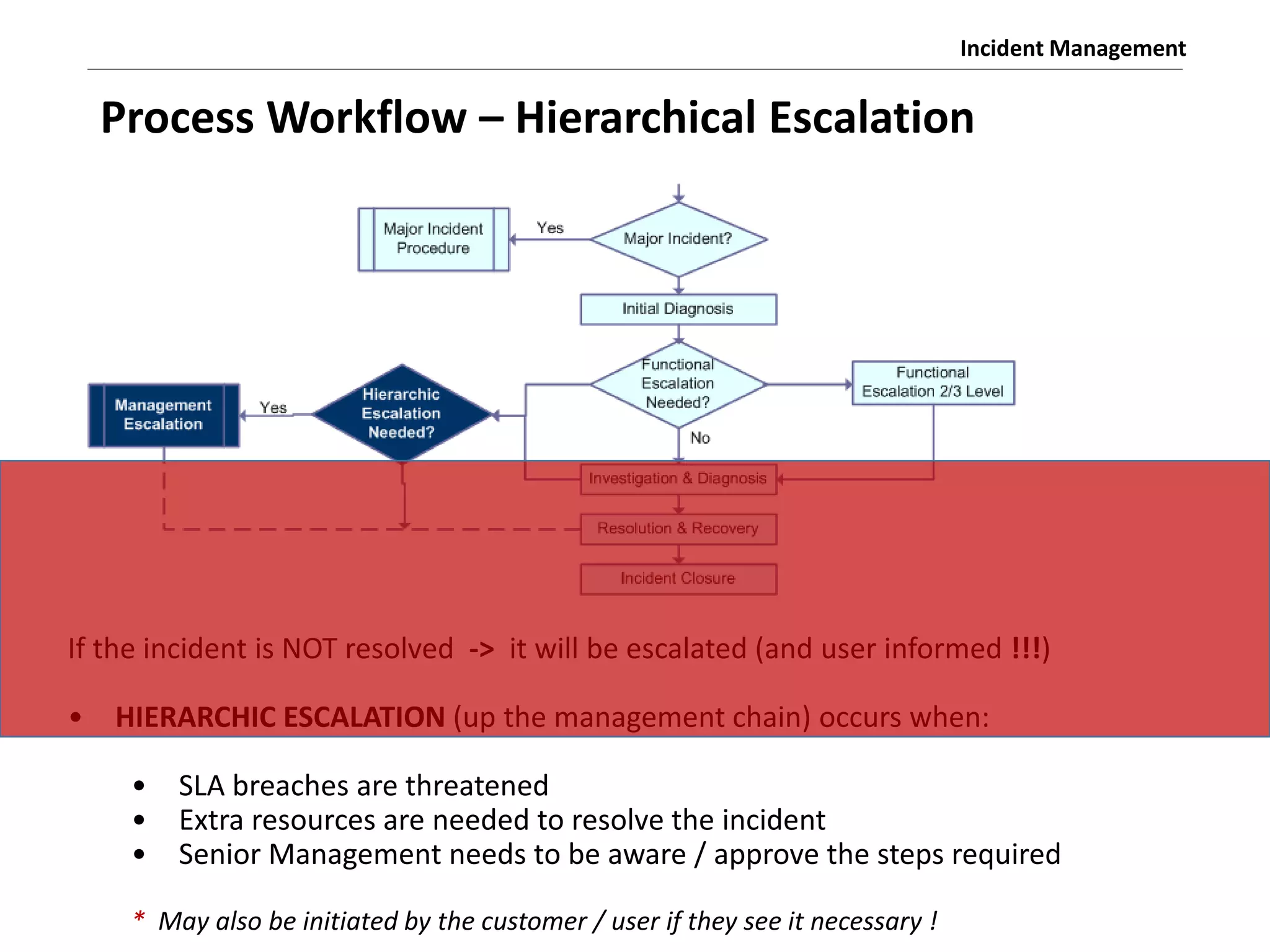
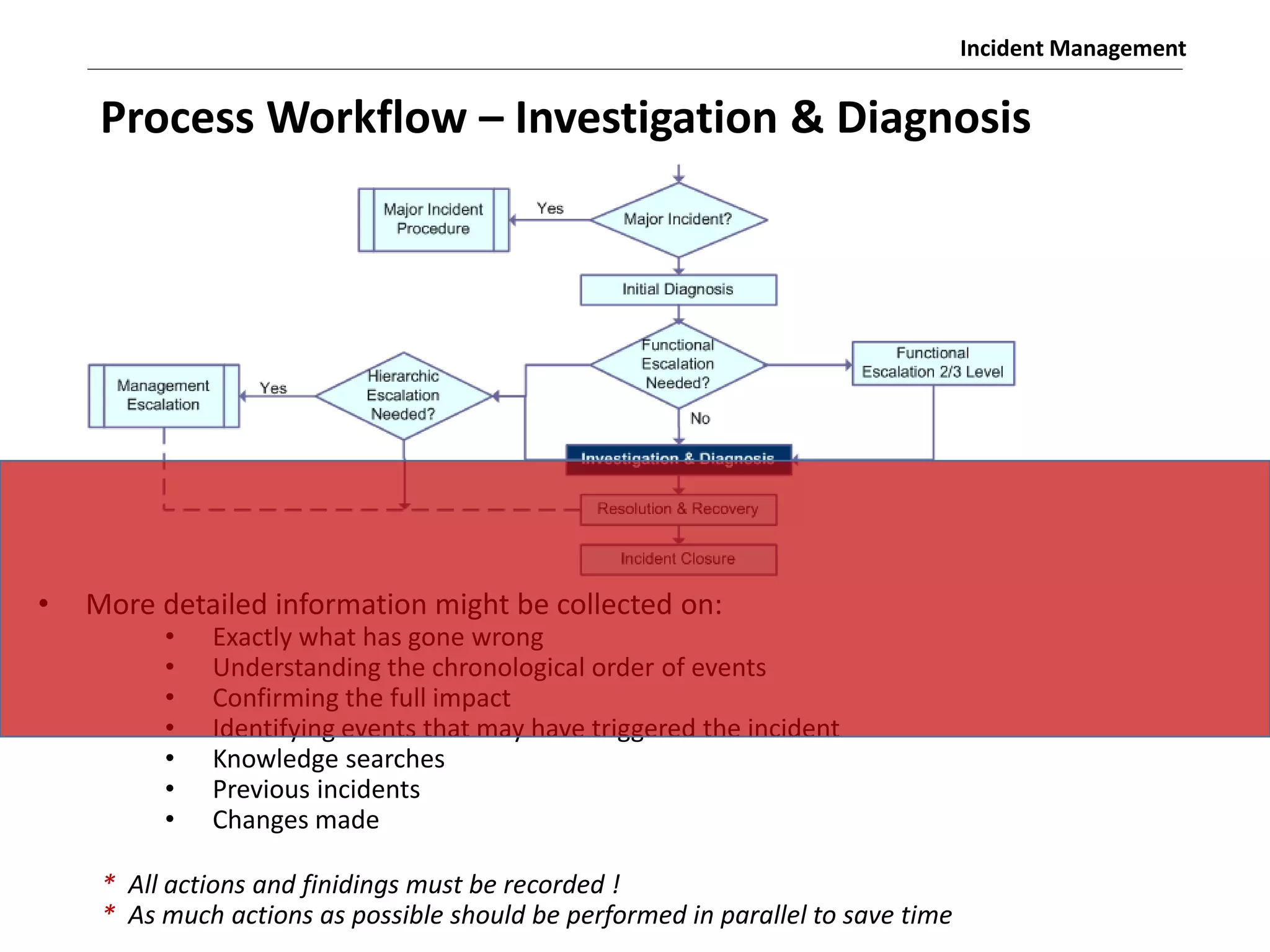
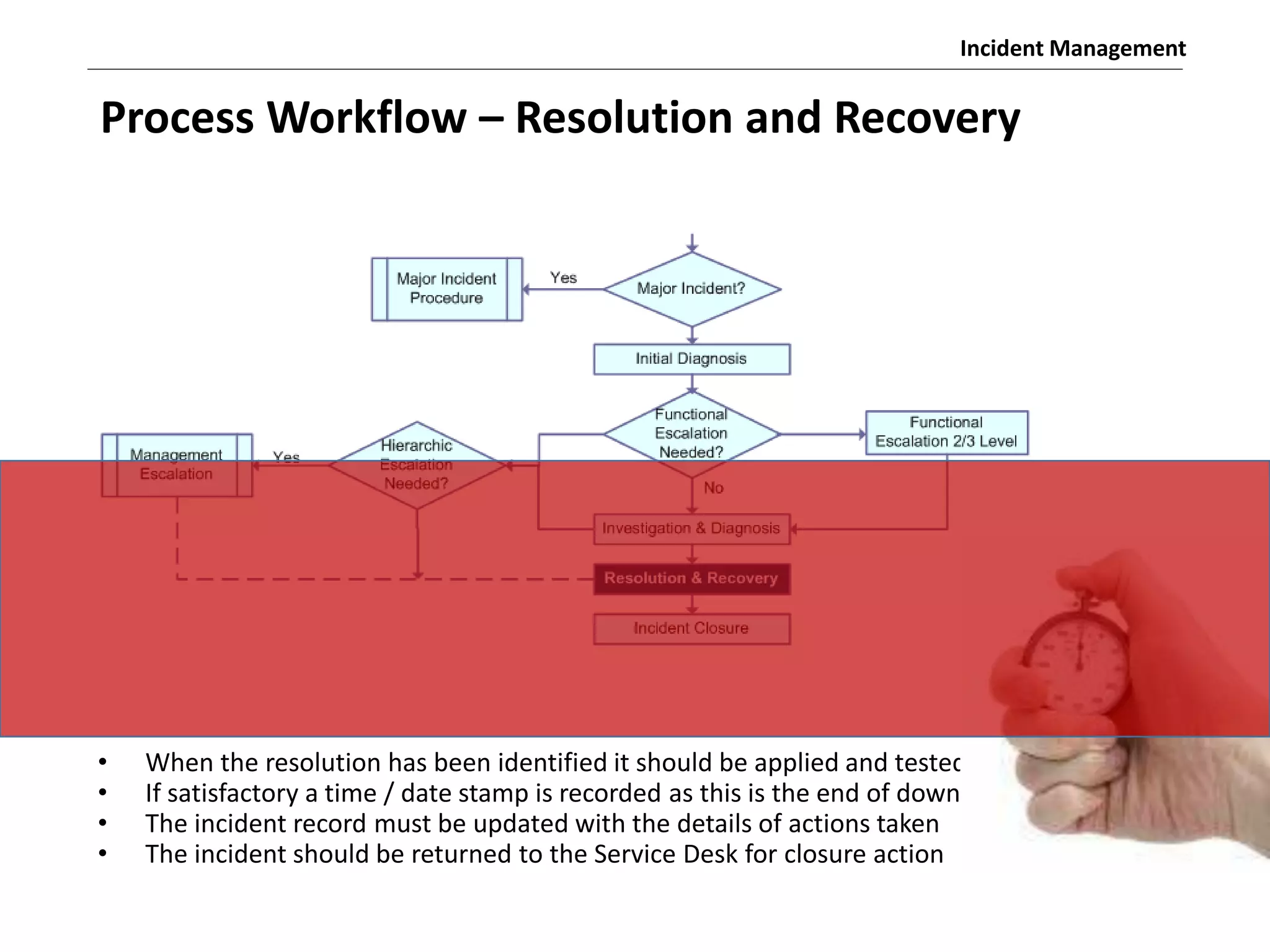
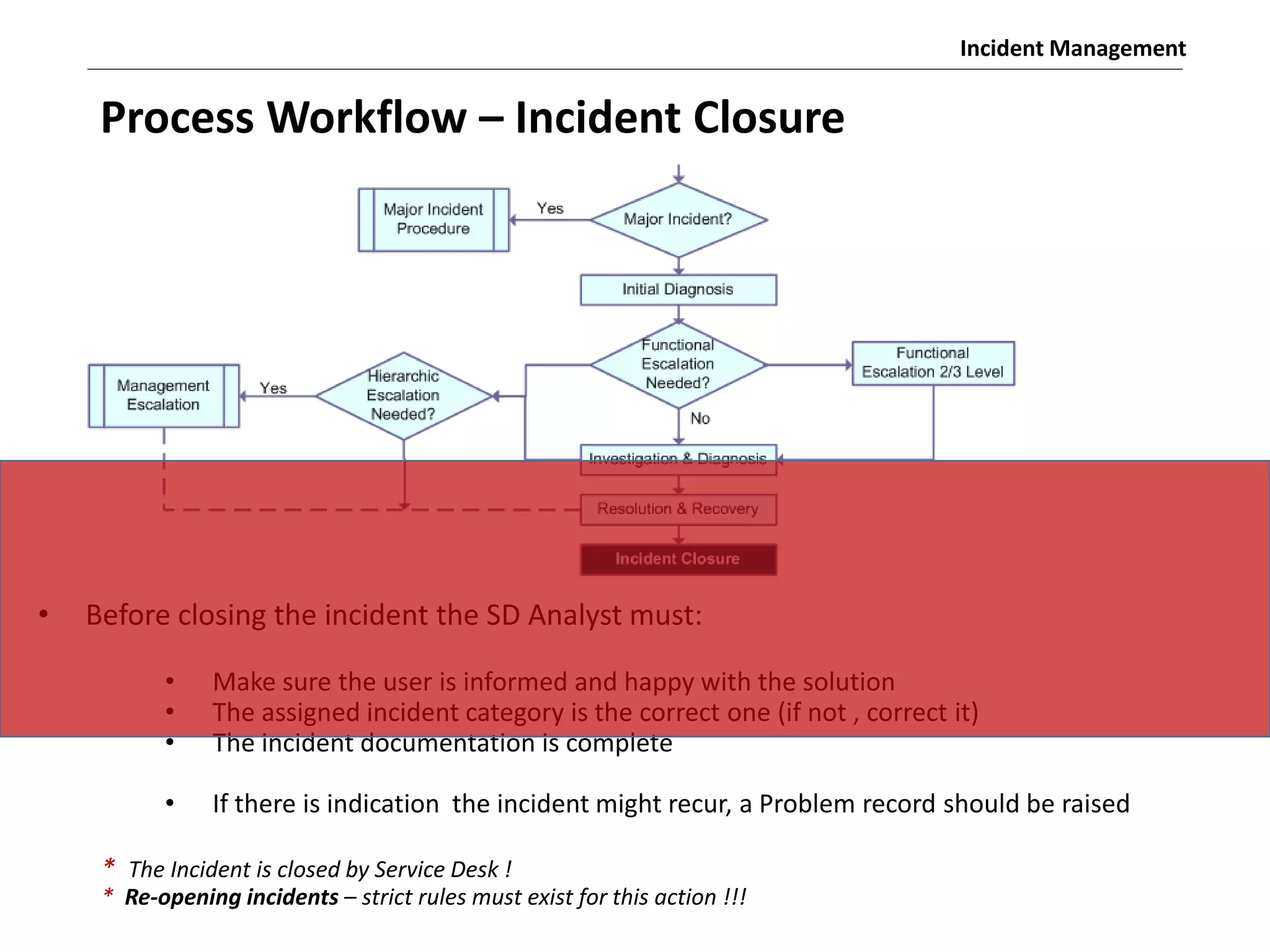
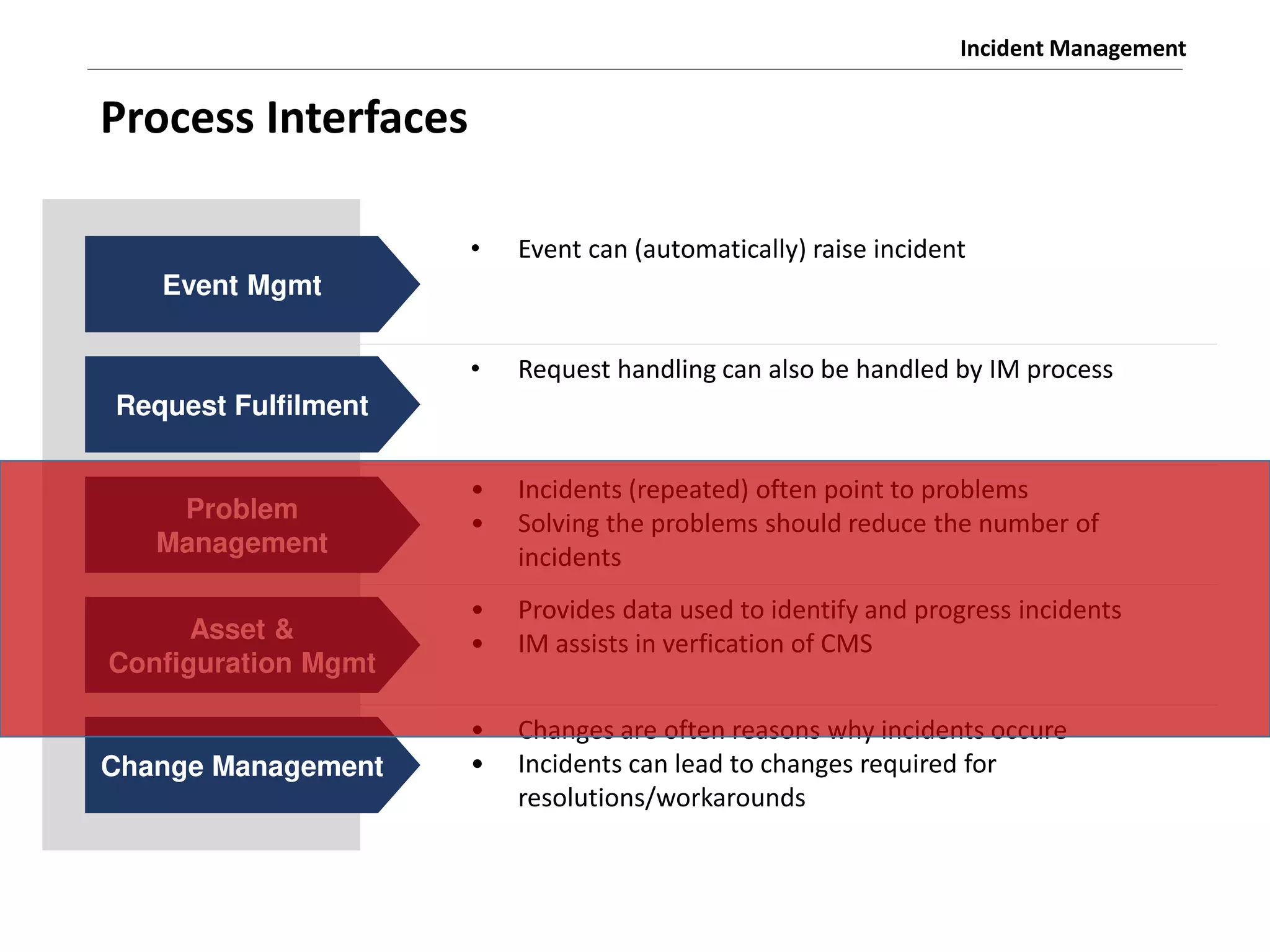
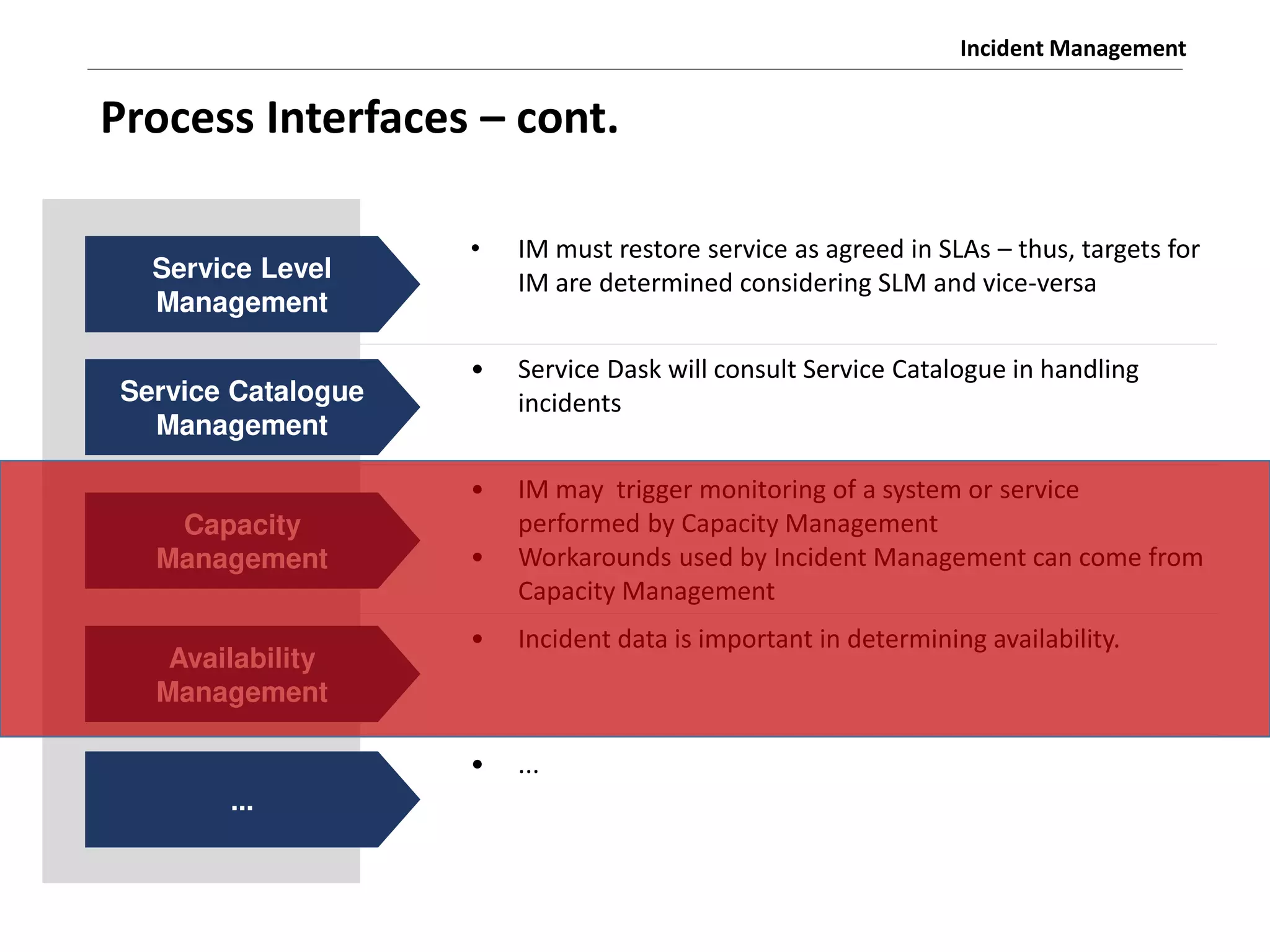
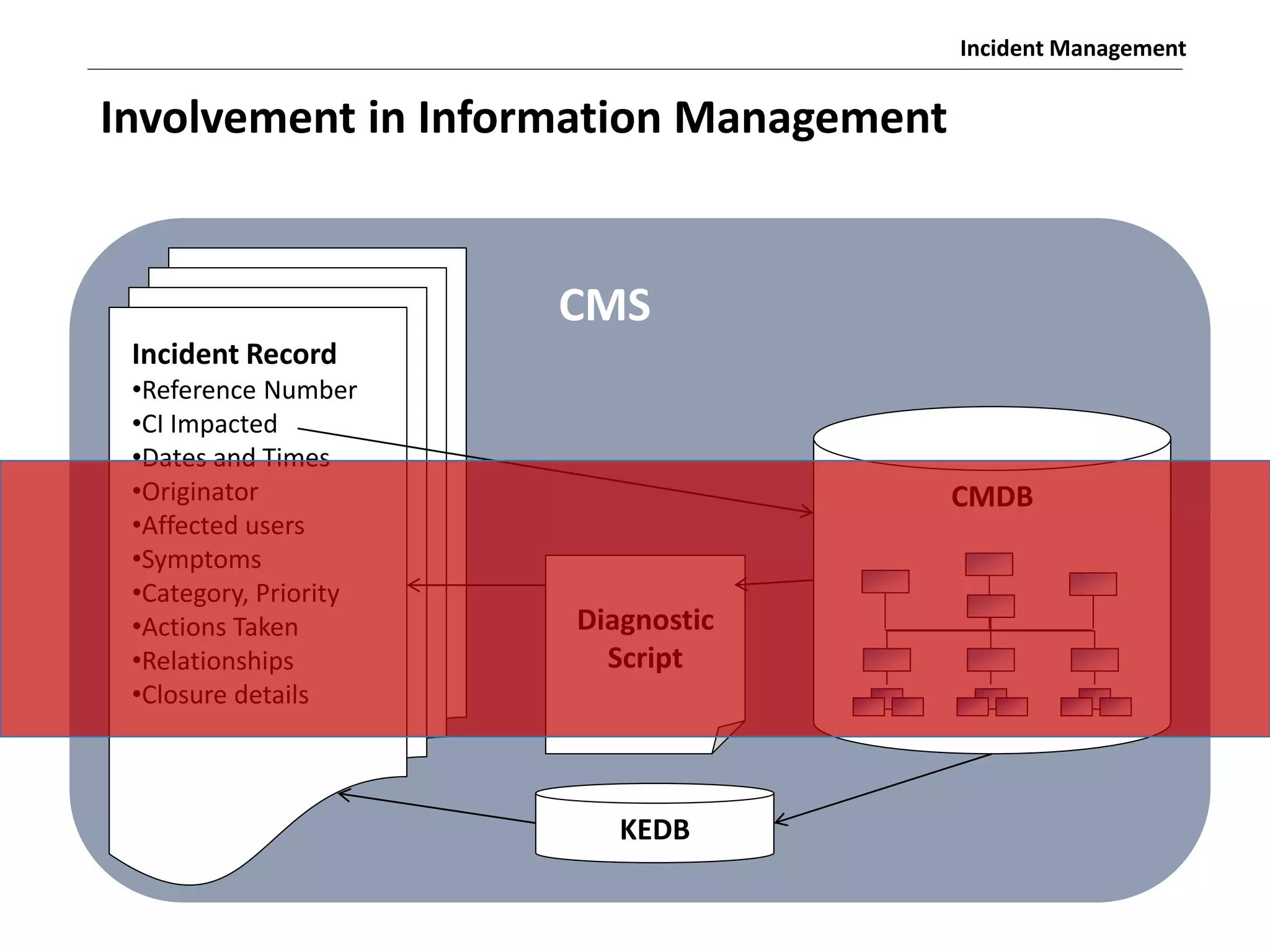
The document discusses the ITIL v3 Incident Management process. It defines key terms like incident, service request, and workaround. It describes the incident lifecycle of open, in progress, resolved, and closed. The purpose is to restore normal service operation as quickly as possible while minimizing impact. Value is provided through reducing downtime and improving user satisfaction. Incident priority is determined by urgency and impact. The workflow involves logging, categorizing, prioritizing, diagnosing, escalating, resolving, and closing incidents.