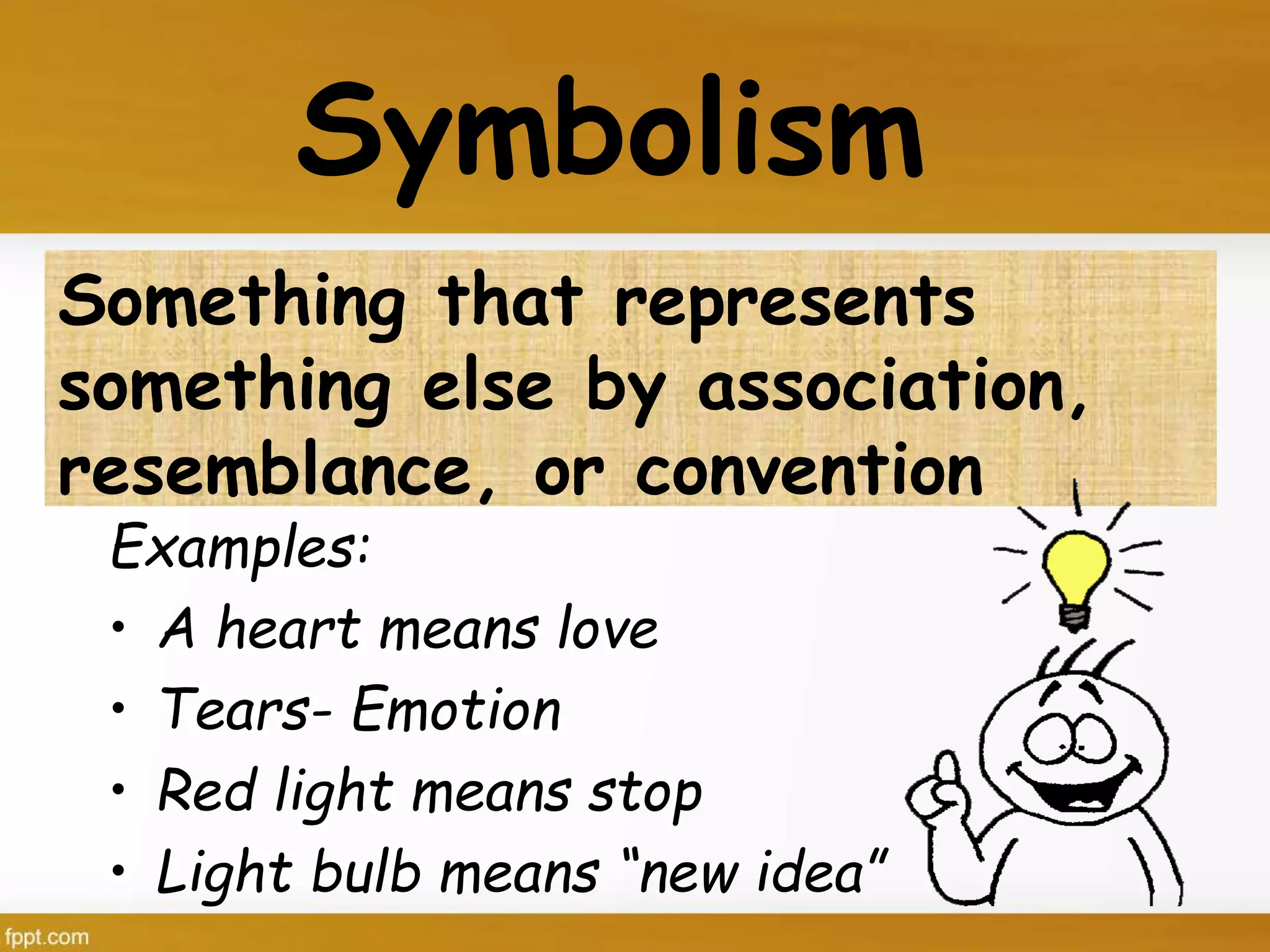
This document defines and provides examples of various types of figurative language. It discusses figurative devices such as simile, metaphor, personification, alliteration, onomatopoeia, hyperbole, idioms, irony, euphemism, metonymy, antithesis, apostrophe, assonance, paradox, litotes, oxymoron, and synecdoche. It also defines imagery and symbolism.